Nucleic Acid Formulation - CD Formulation
Call Us:
- Home
- Services
- Nucleic Acid Customization Services
- Custom Small Nucleic Acid Synthesis Services
- Custom Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) Synthesis
- Custom Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) Synthesis
- Custom Aptamer Synthesis
- Custom Small Activating RNA (saRNA) Synthesis
- Custom Single Guide RNA (sgRNA) Synthesis
- Custom MicroRNA (miRNA) Synthesis
- Custom Circular RNA (circRNA) Synthesis
- Custom Ribozyme Synthesis
- Custom DNAzyme Synthesis
- Custom Short Hairpin RNA (shRNA) Synthesis
- Custom Transfer RNA (tRNA) Synthesis
- Custom CpG Oligodeoxynucleotide Synthesis
- Custom Peptide Nucleic Acid Synthesis
- Custom Bridged Nucleic Acids (BNAs) Synthesis
- Custom Single-Stranded DNA (ssDNA) Synthesis
- Custom Double-Stranded RNA Synthesis
- Custom piRNA Synthesis Services
- Custom mRNA Synthesis
- Nucleic Acid Modification Services
- Custom Small Nucleic Acid Synthesis Services
- Nucleic Acid Therapeutic Formulation Development
- Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery Carriers Development
- Nucleic Acid-Conjugate Development
- GalNAc-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Lipid-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Antibody-siRNA Conjugate Development
- CpG-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Peptide-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Aptamer-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Cholesterol-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Folic Acid-siRNA Conjugate Development
- α-Tocopherol-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Protein-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Squalene-siRNA Conjugate Development
- GalNAc-ASO Conjugate Development
- Peptide-ASO Conjugate Development
- GalNAc-miRNA Conjugate Development
- Lipid-based Nanoparticle Development
- Inorganic Nanoparticle Development
- Polymer-based Nanoparticle Development
- Peptide-based Carriers Development
- Protein Carrier Development
- Exosome Carrier Development
- Bio-MOFs Development Services for Nucleic Acid Therapeutic Formulation
- Viral Vector Development
- Virus-like Particles Development for Nucleic Acid Therapeutic Formulation
- Natural Polysaccharide Development Services
- Nucleic Acid-Conjugate Development
- Design and Optimization Services for Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery System
- Dosage Form Development for Nucleic Acid Therapeutic Formulation
- Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery Carriers Development
- Analytical and Characterization Services for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Identification of Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Structural Characterization for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Physicochemical Characterization for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Molecular Weight Analysis for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Particle Size Analysis for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Zeta Potential Analysis for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Morphological Analysis for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Optical Rotation Testing for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- pH Testing for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Nucleic Acid Drug pKa Determination
- Moisture Content Determination for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Molar Extinction Coefficient Determination for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Melting Temperature (Tm) Testing for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Impurity Analysis for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Stability Analysis for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Safety Analysis for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Nucleic Acid Drug Evaluation and Bioanalytical Services
- In Vivo Nucleic Acid Drug Distribution Measurement
- In Vitro ADME Assays for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Metabolite Identification for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Pharmacokinetics (PK) Assays for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Pharmacodynamic (PD) Assays for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Nucleic Acid Drug Biomarker Testing
- Nucleic Acid Drug Toxicology Analysis
- Nucleic Acid Drugs Immunogenicity Testing
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Assessment for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Pharmacodynamic Evaluation for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Nucleic Acid Drug Process Development
- Nucleic Acid Customization Services
- Technologies & Platforms
- Nucleic Acid Drug Design Platform
- Nucleic Acid Drug Preparation Technology
- Nucleic Acid Formulation Preparation Technology
- Solid Dispersion Preparation Technology for Nucleic Acid Formulations
- Hot Melt Extrusion Technology for Nucleic Acid Formulations
- Medicinal Nanocrystals Technology for Nucleic Acid Formulations
- Coating Technology for Nucleic Acid Formulations
- 3D Printing Technology for Nucleic Acid Formulations
- Microfluidics Technology for Nucleic Acid Formulations
- Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery Platforms
- GalNAc-Conjugated Delivery System Platforms
- Lipid Nanocarrier Drug Delivery System Platforms
- Polymer-Based Nanoparticle Delivery System Platforms
- Exosome Delivery System Platforms
- Inorganic Nanoparticle Delivery System Platforms
- Peptide Nanoparticles Delivery Platforms
- Protein Nanoparticles Delivery System Platforms
- Viral Vector Platforms for Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery
- Natural Polysaccharide Drug Delivery System Platforms
- Virus-like Particle Drug Delivery Platforms
- Bio-MOFs Drug Delivery Platforms
- Analytical Technology Platforms
- HPLC Platforms for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Gas Chromatography (GC) Platforms for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Infrared Spectroscopy Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- NMR Technology Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Mass Spectrometry (MS) Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Circular Dichroism (CD) Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Zeta Potential Analysis Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Technology Platforms for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Technology Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Technology Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- ELISA Technology Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- MSD Technology Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Gel Electrophoresis Technology Platform
- Sequencing Technology Platform
- ICP (Inductively Coupled Plasma) Technology Platforms
- Solutions
- Resources
- Online Order
- Company

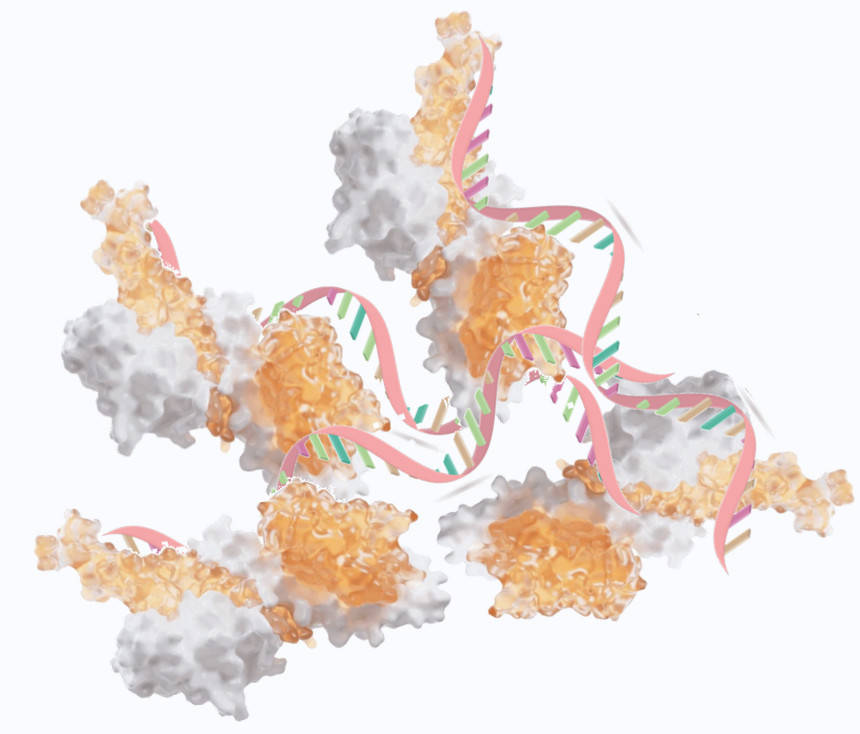 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of proteins as nucleic acid carriers. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of proteins as nucleic acid carriers. (CD Formulation)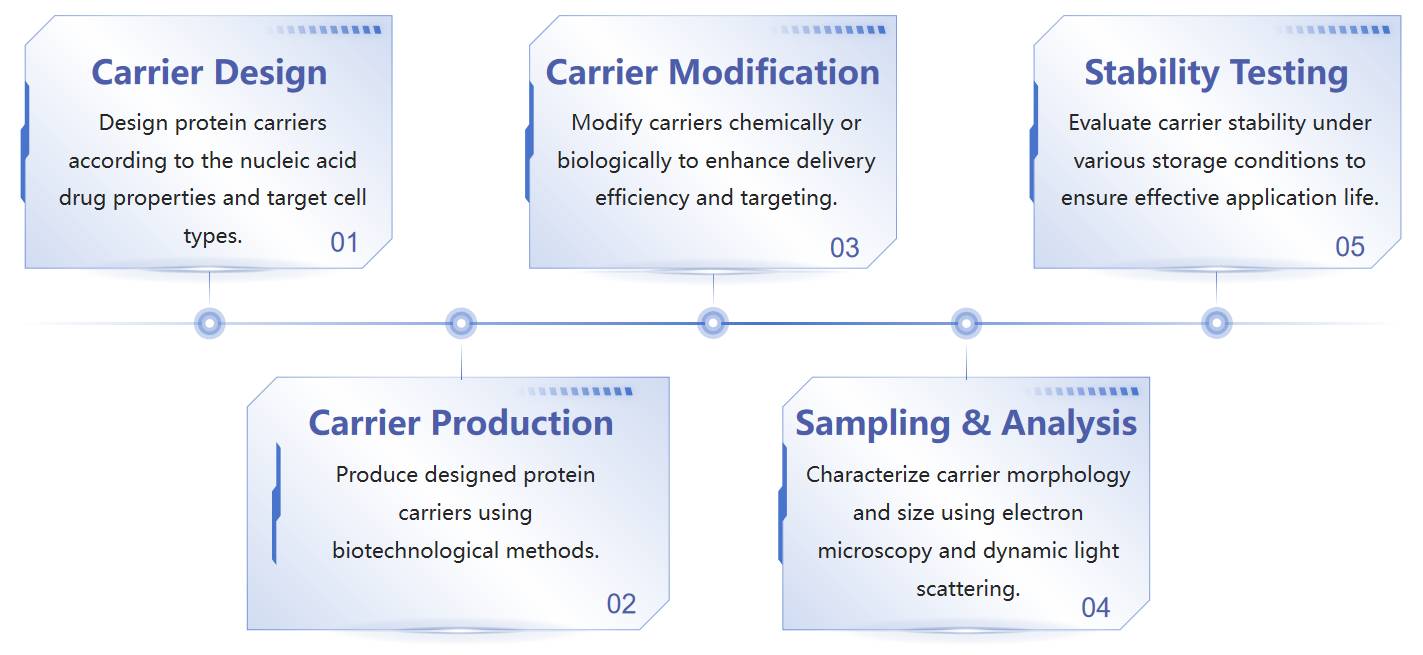 Fig.2 Flow chart of protein carrier development. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 Flow chart of protein carrier development. (CD Formulation)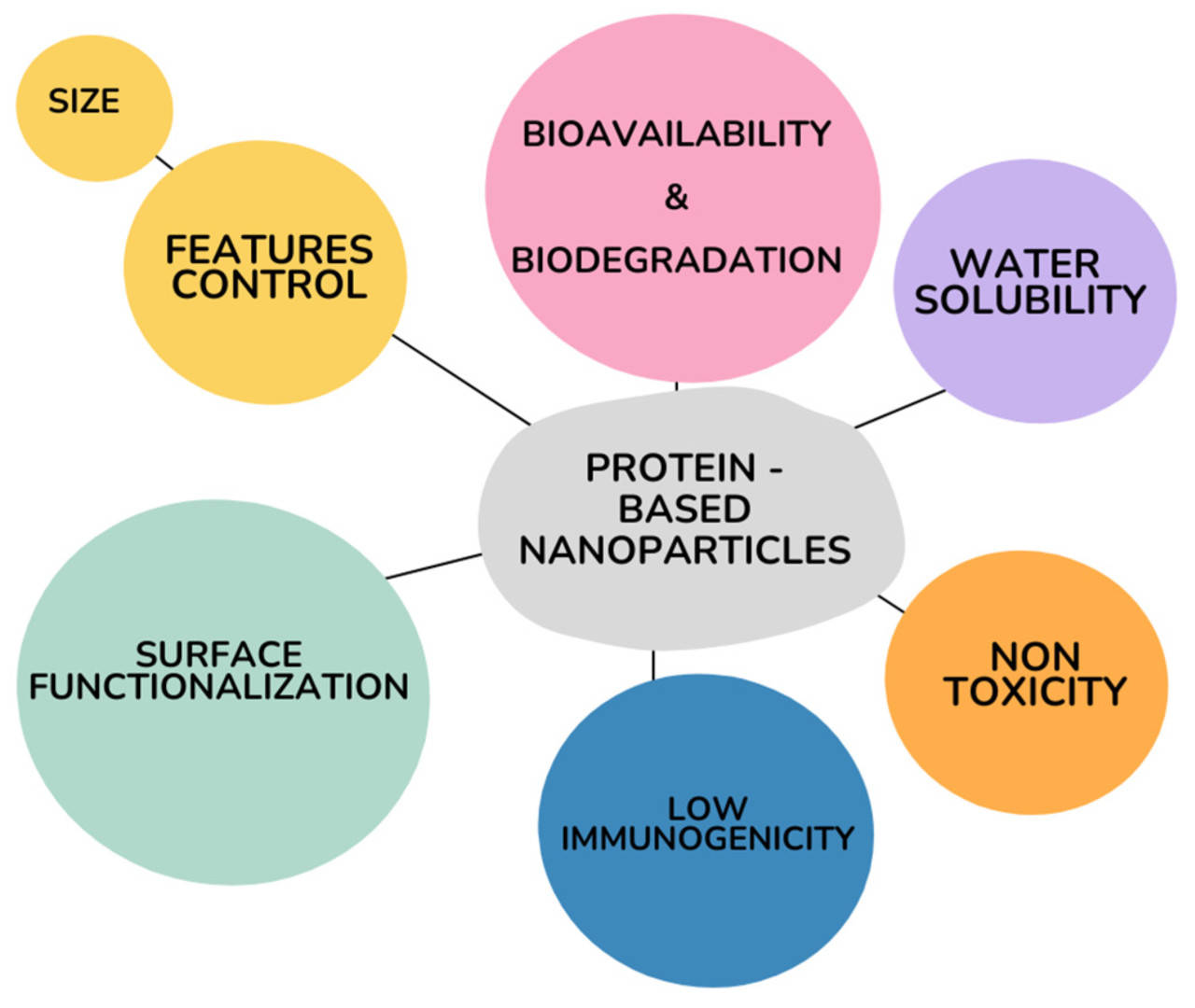 Fig.3 Advantages in the adoption of protein-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. (Ferraro C, et al., 2024)
Fig.3 Advantages in the adoption of protein-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. (Ferraro C, et al., 2024)