Co-encapsulation Nanomaterial Drug Delivery System for Nanoformulations
Inquiry
As co-encapsulation nanotechnology advances rapidly, it presents innovative avenues for oncological treatments. CD Formulation is dedicated to pioneering the development of co-encapsulated nanoformulations and the creation of sophisticated drug delivery systems based on co-encapsulated nanomaterials. We specialize in providing tailor-made co-encapsulation nanomaterial drug delivery systems to cater to the diverse requirements of our clientele.
What are Co-encapsulation Nanocarriers?
Co-encapsulated nanocarriers contain a variety of biological macromolecules (ranging from simple molecules to larger peptides) confined within a single nanocarrier, usually with a core-shell structure. They mainly include liposomes, polymeric micelles, polymer-drug conjugate, dendrimer, oil nanoemulsions, mesoporous silica nanoparticles and titanium oxide nanoparticles.
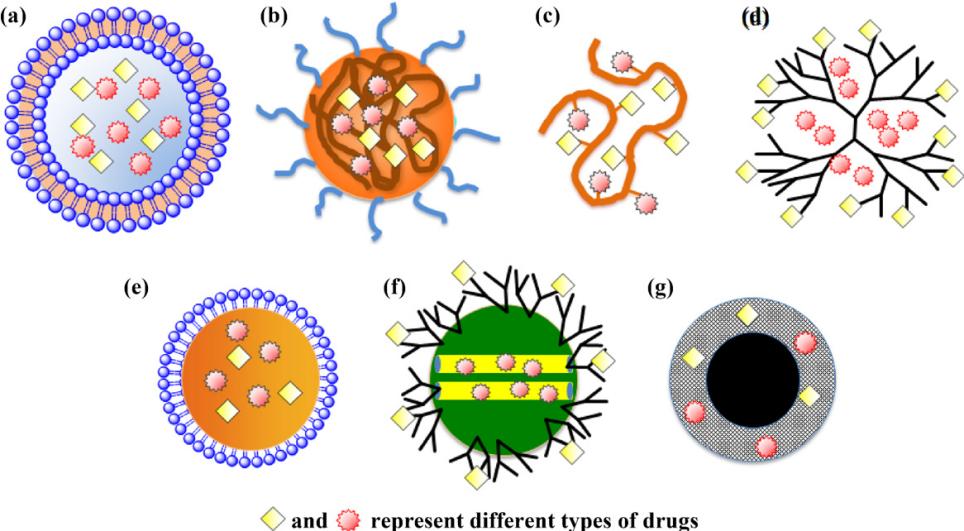 Fig.1 Schematic illustration of nanocarriers used for combinatorial drug delivery. (Che-Ming Jack Hu, et al. 2012)
Fig.1 Schematic illustration of nanocarriers used for combinatorial drug delivery. (Che-Ming Jack Hu, et al. 2012)
Advantages for Co-encapsulation Nanomaterials
Nanocarrier co-encapsulation can achieve synergistic effects of multiple drugs because of the following significant benefits of co-encapsulation nanomaterials.
- Co-encapsulation of drug molecules in nanocarriers can maintain the integrity of drug molecules.
- Nanocarriers isolate hydrophobic drug molecules from the ion-rich blood exterior to prevent aggregation, precipitation, or denaturation of the co-encapsulated drug delivery system.
- Co-encapsulated nanocarriers can achieve tunable and controllable drug delivery to targeted pathological tissues.
- Using a nanocarrier co-encapsulation system, synergistic effects may occur when multiple drugs are administered simultaneously.
Co-encapsulation Nanomaterial Drug Delivery Systems
CD Formulation is committed to investigating and constructing co-encapsulation nanomaterial drug delivery systems, covering liposome-based co-encapsulation, polymeric micelle-based co-encapsulation, dendrimer-based co-encapsulation, nanogel-based co-encapsulation, metal and inorganic nanoparticle-based co-encapsulation and biomimetic nanoparticle-based co-encapsulation.
Liposome-based Co-encapsulation for Nanoformulations
Liposomes have the advantages of a high encapsulation rate, good targeting and low toxicity, and are widely used as carriers for cancer therapy. Depending on our liposome delivery system platform, CD Formulation can provide clients with liposome-based co-encapsulation for nanoformulations, covering preparing and characterizing co-encapsulated nanoformulations...
Polymeric Micelle-based Co-encapsulation for Nanoformulations
Polymeric micelles have a hydrophobic core and a hydrophilic outer shell. They are simple to prepare, can be loaded with multiple drugs at the same time, and can be easily surface modified. CD Formulation has rich experience in the development and application of polymeric micelle-based co-encapsulated nanoformulations...
Dendrimer-based Co-encapsulation for Nanoformulations
Dendrimers such as polyethylenimine (PEI) and polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers have been widely studied and applied due to their clear chemical structure, monodispersity, easy multifunctionality and multivalent modification. CD Formulation is good at researching and developing dendrimer-based co-encapsulated nanoformulation...
Co-encapsulation Based on Metal and Inorganic Nanoparticles for Nanoformulations
Metal and inorganic nanoparticles usually have photothermal therapy and photodynamic therapy effects, high drug-loading capacity, easy functional modification, and no immunogenicity. They are both good drug carriers and tumor therapeutic agents. CD Formulation can provide co-encapsulation based on metal and inorganic nanoparticles to help researchers develop metal or inorganic nanoparticle-based co-encapsulated nanoformulations...
Nanogel-based Co-encapsulation for Nanoformulations
Nanogels are nanoscale hydrogel scaffolds with good biocompatibility, high water content, and good compatibility with various therapeutic agents (such as small molecule drugs and biological macromolecule drugs). They are widely used in cancer therapy. CD Formulation can design and develop nanogel-based co-encapsulated nanoformulations according to customers' different requirements...
Co-encapsulation Based on Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Nanoformulations
Bionic nanocarriers have natural-like structures or morphologies, surface properties, and sizes, have stronger targeting and good biocompatibility, and can deliver drugs to target cells or tissues. Bionic nanocarriers include albumin, high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, transferrin family proteins and their derivative proteins, etc. CD Formulation is committed to researching and developing biomimetic nanoparticle-based co-encapsulated nanoformulations...
Explore Our Co-encapsulation Technologies for Nanoformulations
The main techniques for co-encapsulation include spray drying, freeze drying, extrusion, coagulation, electrospraying and emulsification. We have explored and practiced the following co-encapsulation technologies for nanoformulation development.
Emulsification
The technology is divided into two dispersed phases, a polymer suspension containing cells and an organic solution as a continuous phase. We homogenize the mixture with a surfactant to prepare an emulsion, and form particles in the organic phase by making the water-soluble polymer insoluble by applying a cross-linking agent or cooling process.
Spray Drying
In the spray drying method, we prevent oxidative degradation of the active ingredient by converting the liquid form into a powder.
Freeze Drying
Freeze drying or lyophilization can improve the storage of active ingredients. This method is mainly achieved through three processes, such as freeze drying, primary drying and secondary drying.
Extrusion
In this approach, we mix a polymer solution (such as hydrocolloid solution) with microbial cells and project the suspension through a syringe needle into a solution of a high-pressure cross-linker causing gelation.
Coacervation Process
The technology is based on the coagulation of biopolymeric phase separation under specific composition, temperature or pH solution, and then forms microspheres by precipitating coagulation around the core component.
Electrospraying
The method requires an external electric field to be applied between two electrodes and then to a polymer solution without the need for temperature. This approach can produce encapsulated particles with a large surface-to-volume ratio.
Advanced Custom Co-Encapsulated Nanoformulation Development
- With the support of our advanced co-encapsulation nanomaterial drug delivery system, we are able to customize high-quality co-encapsulated nanoformulations to meet customers' needs.
- We can offer co-encapsulated nanoformulation development services based on liposome, polymeric micelle, dendrimer, metal and inorganic nanoparticle, nanogel and biomimetic nanoparticle technology platforms.
- We also have rich experience in exploring and constructing a verity of co-encapsulation technologies including emulsification, spray drying, freeze drying, extrusion, coagulation and electrospraying.
Custom Nanoformulation Development Services
CD Formulation pays great attention to the development and research of nanoformulations. With our advanced co-encapsulated nanomaterial delivery system, we can provide customers with nanoformulation development and customization services. Our professional technical team has conducted in-depth research on nanomaterial co-encapsulation technology, and can develop nanoformulations for different purposes, which has promoted the clinical transformation and commercial application of nanoformulations.
Nanoparticle Development for Nanomedicine
Leveraging our nanoparticle technology and co-encapsulation techniques, we customize a variety of nanoparticles such as liposomes, metal, inorganic, and biomimetic types. Our thorough research on co-encapsulation preparation processes enables us to offer professional solutions to enhance nanoparticle bioavailability.
Polymeric Micelle Development for Nanomedicine
Leveraging our polymeric micelle and co-encapsulation technology, we can quickly customize high-quality polymeric micelles to meet customers' specific needs. With an in-depth understanding of polymer micelle properties and preparation methods, we offer professional solutions to enhance bioavailability and clinical safety.
Nanogel Development for Nanomedicine
Using our advanced nanogel and co-encapsulation technology, we can swiftly customize nanogels to meet customer needs, providing one-stop solutions to enhance the synergistic efficacy of multiple drugs.
Liposome Development for Nanomedicine
Using our advanced liposome nanotechnology, we customize liposomes with co-encapsulation to meet customer needs. We conduct deep research to offer high-quality solutions that enhance liposome bioavailability and clinical efficacy.
Published Data
Technology: pH-responsive co-encapsulation drug delivery system
Journal: Chemical Science
IF: 7.6
Published: 2020
Results:
The authors developed a supramolecular strategy to achieve drug delivery by forming aggregates composed of self-assembled amphiphiles between carboxyl pillararene (CP6A) and oxaliplatin (OX)-type Pt (IV) prodrugs (PtC10). The chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin (DOX) was encapsulated in the vesicles (PtC10⊂CP6A) to obtain the supramolecular combinatorial chemotherapeutic system DOX@PtC10⊂CP6A. Drug release studies confirmed the release of PtC10 and DOX in an acidic environment. In vivo studies showed that DOX@PtC10⊂CP6A could not only effectively delay tumor growth but also reduce drug-related toxicity in BALB/c nude mice bearing HepG-2 subcutaneous tumor xenografts. The study showed that the composite not only benefited from the enhanced permeability and retention effect in vivo, but also allowed the pH-based release of PtC10 and DOX at the tumor site.
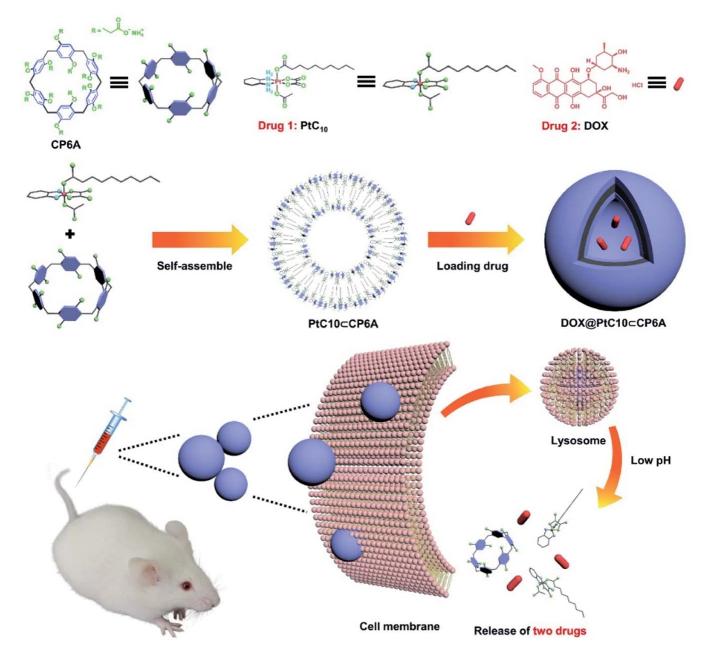 Fig.2 Schematic illustration of the preparation of DOX@PtC10⊂CP6A. (Junyi Chen, et al. 2020)
Fig.2 Schematic illustration of the preparation of DOX@PtC10⊂CP6A. (Junyi Chen, et al. 2020)
Nanoformulations prepared using co-encapsulation technology can improve the stability of nanoformulations, control their drug release, and improve bioavailability. CD Formulation as a world-class nanoformulation development and manufacturing servicing company, can offer co-encapsulated nanoformulation based on liposomes, polymeric micelles, dendrimers, metal and inorganic nanoparticles, nanogels and biomimetic nanoparticles. If you are interested in our co-encapsulation technologies for nanoformulations, please contact us.
References
- Che-Ming Jack Hu, Liangfang Zhang. Nanoparticle-based combination therapy toward overcoming drug resistance in cancer. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2012,83(5):1104-1111.
- Junyi Chen, Yadan Zhang, Zhao Meng, et al. Supramolecular combination chemotherapy: a pH-responsive co-encapsulation drug delivery system. Chemical Science. 2020,11,6275-6282.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services


 Fig.1 Schematic illustration of nanocarriers used for combinatorial drug delivery. (Che-Ming Jack Hu, et al. 2012)
Fig.1 Schematic illustration of nanocarriers used for combinatorial drug delivery. (Che-Ming Jack Hu, et al. 2012)
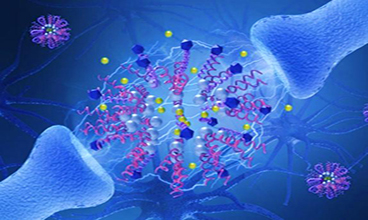
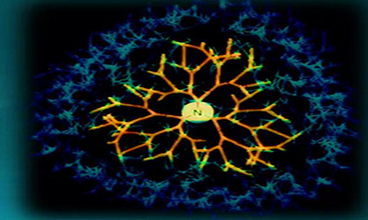
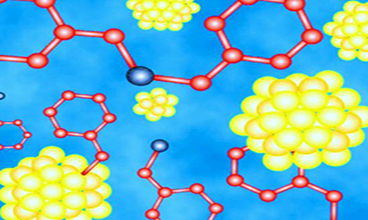
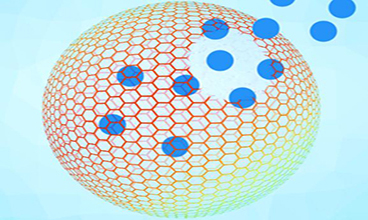
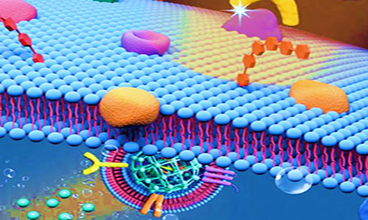
 Fig.2 Schematic illustration of the preparation of DOX@PtC10⊂CP6A. (Junyi Chen, et al. 2020)
Fig.2 Schematic illustration of the preparation of DOX@PtC10⊂CP6A. (Junyi Chen, et al. 2020)