Transdermal Liposome Characterization
Inquiry

The application of lipid-based formulations on the skin has the following advantages. Long-lasting sustained release: Lipid-like lipids (such as sphingomyelin) formulated into liposomes have a high degree of similarity to the lipids in the skin's stratum corneum, providing space for the storage of active ingredients in the skin and increasing accumulation in the local area; Effectiveness: The active ingredient is encapsulated by the liposome, avoiding degradation or photo-decomposition; Targeted delivery: Liposomes can be surface-modified to have targeted drug delivery properties; Nutrition and health care for the skin: Liposomes in cosmetics can play a role in moisturizing, antioxidant, softening the skin, and nutrient supplementation. CD Formulation utilizes proprietary liposome platform to provide comprehensive analytical services for transdermal liposome characterization.
Why You Need Transdermal Liposome Characterization?
Liposomes have demonstrated efficacy in delivering small molecule drugs, peptides, and proteins for local, transdermal, and follicular applications. However, their main mechanism of action involves drug storage within the stratum corneum rather than direct penetration into the body. Liposomes can interact extensively with the skin surface to enhance transdermal drug absorption. Nevertheless, different nanoparticle formulations engage with the skin through distinct mechanisms. For instance, liposomes composed of lipid molecules that resemble the structure of the stratum corneum attach to and hydrate the skin surface gradually leading to loosening and polarity changes in intercellular lipid domains until lipid exchange occurs and allows drug entry into the body. Consequently, characterizing transdermal liposomes is increasingly crucial.
Explore Our Services for Transdermal Liposome Characterization
The transdermal absorption refers to the process in which after applying main active substances on the skin, their functional components are released, penetrate into the skin, and reach a specific depth of skin tissue, thereby playing a role. Our services include but not limit to:
We can simulate the diffusion of liposomes across semipermeable membranes or barriers such as skin, intestinal walls, etc. using Franz diffusion chambers. The membranes used in Franz diffusion chambers can be dialysis bags, artificially simulated membranes, cells, or human and animal skin or epithelial tissues.
The investigation of the skin retention and penetration behavior of drug-loaded liposomes and gel formulations is essential for elucidating the transdermal absorption characteristics of the formulations. This service are conducted using a Franz diffusion chamber. Samples are taken at different time points and the drug concentrations are determined. The cumulative drug flux is calculated at each time point, and a flux-time plot is obtained.
We conducted the Buehler test to investigate the sensitization caused by applying bovine colostrum patches to guinea pig skin, and observed the skin irritation caused by single or multiple applications of bovine colostrum patches to intact and damaged rabbit skin. We also examined the effects of local application of different concentrations of transdermal permeation enhancers on the viability of dermal cells and the structure of skin tissue using the MTT assay and skin pathology examination.
Our Workflow of Transdermal Liposome Characterization
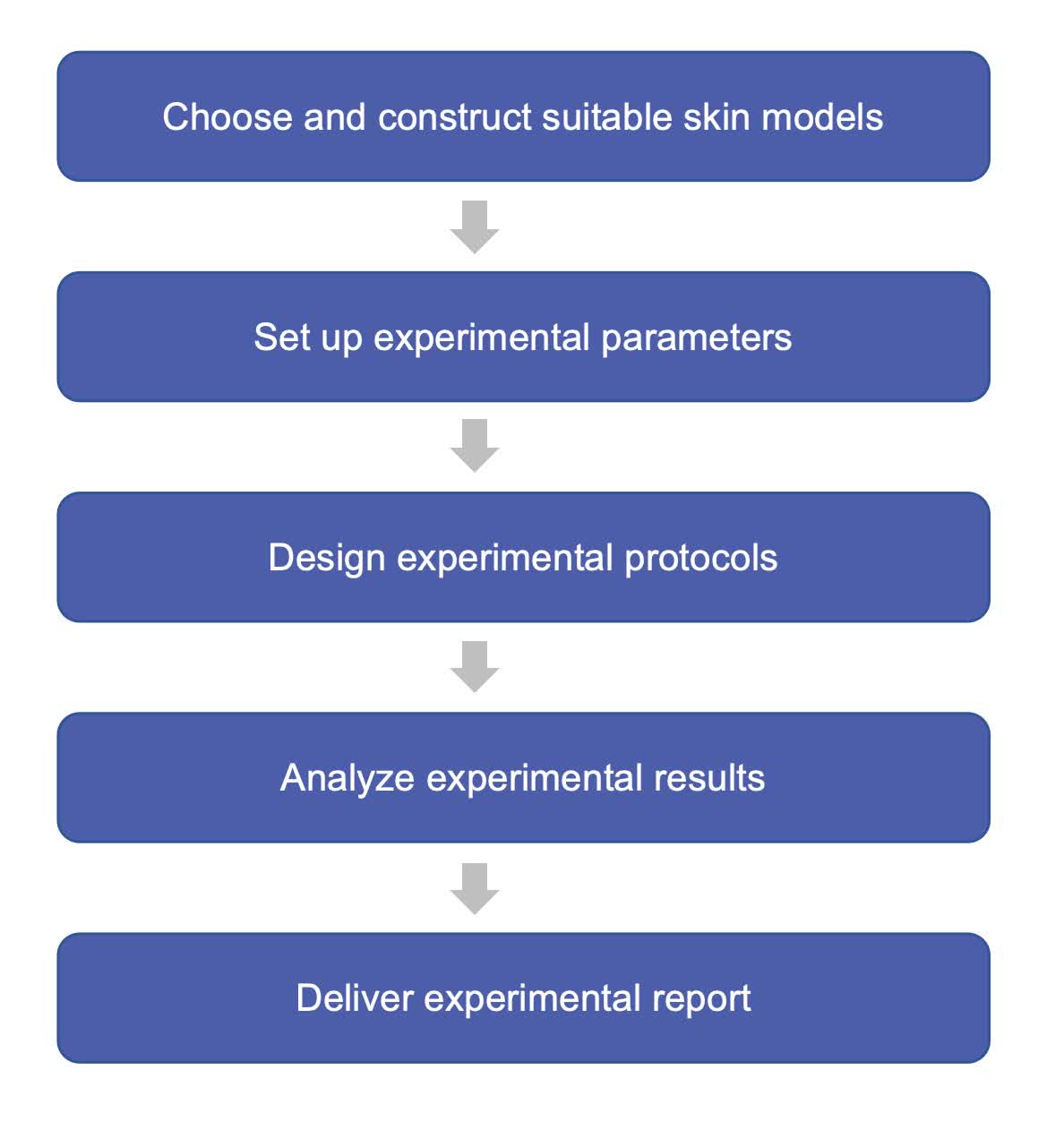 Fig.1 Our workflow for transdermal liposome characterization. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Our workflow for transdermal liposome characterization. (CD Formulation)
Our Platforms for Transdermal Liposome Characterization
| Platforms |
Specifics |
| Transdermal Liposome Release In Vitro Platform |
- The in vitro release platform helps customers analyze in vitro release speed, skin penetration, and drug accumulation
|
| Model Building Platform |
- We can build skin models of different parts according to customer needs.
- According to the purpose of the experiment, a reasonable skin model was selected.
|
Highlights for Transdermal Liposome Characterization
- Expertise. Our team of experts utilizes advanced liposome platforms to provide extensive expertise in transdermal liposome analysis, ensuring to offer our customers the most precise and dependable results.
- Flexible. Customizable, affordable and designed to meet the specific needs of individual customers.
- Advanced. We have developed and created a variety of skin models to characterize the efficacy of transdermal liposomes in vitro and provide valuable reference data for in vivo use.
Published Data
Technology: Cationic liposomes mediated transdermal delivery technology
Journal: International Journal of Pharmaceutics
IF: 10.5
Published: 2021
Results: In this study, the author prepared novel liposomes modified with pyrolidinium surfactants containing hydroxyethyl fragments (CnPB, n = 12, 14, 16) for transdermal delivery of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). To obtain the optimal composition, the molar ratio of surfactant to lipid was (0.02/1; 0.029/1; 0.04/1), with varying hydrophobic tail lengths. Rhodamine B was included in all formulations, while meloxicam and ketoprofen were included in some formulations. The studied liposomes had hydrodynamic diameters of 80 to 130 nm and zeta potentials of +35 to +50 mV, with entrapment efficiencies of 75 to 99%. Liposome modification resulted in prolonged ex vivo release of Rhodamine B (up to 10-12 h) and faster release of the NSAIDs (up to 7-8 hours). The Franz cell was used to study the ability of meloxicam and ketoprofen liposomes to penetrate the skin barrier. In vitro transdermal permeation studies showed that the total amount of ketoprofen liposomes that penetrated the skin in 51 hours was 140 to 162 μg/cm². C16PB-modified liposomes were the most effective anti-inflammatory agents in a rat paw carrageenan edema model.
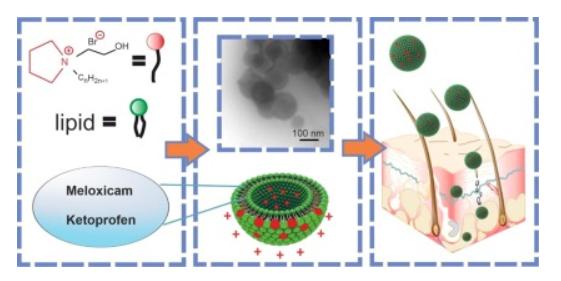 Fig.2 Cationic liposomes mediated transdermal delivery. (Kuznetsova DA, et al., 2021)
Fig.2 Cationic liposomes mediated transdermal delivery. (Kuznetsova DA, et al., 2021)
CD Formulation team has accumulated extensive expertise and experience in the characterization of transdermal liposomes. Over the years, the core of our dedication lies in delivering a tailored and all-encompassing solution to meet the unique needs of our esteemed customers. If you require any assistance, please do not hesitate to contact us immediately.
References
- Kuznetsova DA, Vasileva LA, et al. Cationic liposomes mediated transdermal delivery of meloxicam and ketoprofen: Optimization of the composition, in vitro and in vivo assessment of efficiency. Int J Pharm. 2021;605:120803
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services



 Fig.1 Our workflow for transdermal liposome characterization. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Our workflow for transdermal liposome characterization. (CD Formulation) Fig.2 Cationic liposomes mediated transdermal delivery. (Kuznetsova DA, et al., 2021)
Fig.2 Cationic liposomes mediated transdermal delivery. (Kuznetsova DA, et al., 2021)