Transdermal Liposome Skin Irritation Testing
Inquiry
The strong market application potential of transdermal delivery is closely related to its advantages: it can avoid the first-pass effect of the liver and gastrointestinal tract irritation caused by oral administration, maintain a constant blood drug concentration, reduce the frequency of administration, and prolong the effective action time. It is a very convenient administration route as it can be discontinued at any time and the patient can administer it independently. Therefore, transdermal liposomes, a highly regarded formulation, are becoming increasingly important in measuring the quality of the product, especially its potential irritation. The complex requirements and influencing factors for skin irritation evaluation make it necessary to design a skin irritation test for transdermal liposomes with higher standards. CD Formulation has many years of experience in the development and quality assessment of transdermal formulations. We have a unique skin irritation testing platform for transdermal liposomes, fully capable of meeting the relevant testing needs.
Why Conduct Transdermal Liposome Skin Irritation Testing?
The skin barrier is the main contact route of transdermal liposomes. Due to the complex and diverse composition of transdermal liposomes, it is necessary to evaluate the primary irritants after the development and marketing of the product, especially to exclude factors that may cause skin inflammatory lesions. Severe skin severity may be characterized by a direct damaging reaction characterized by inflammation, severe irritation, skin blistering, and/or necrosis. Therefore, to evaluate whether transdermal liposome products have potential skin irritation, skin irritation testing is required.
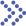
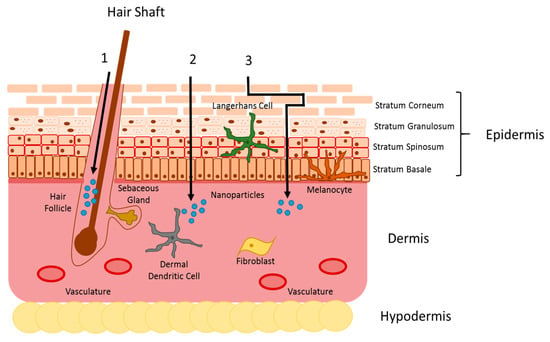 Fig.1 Illustration of nanoparticle skin penetration pathways. (Palmer, B.C., et al., 2016)
Fig.1 Illustration of nanoparticle skin penetration pathways. (Palmer, B.C., et al., 2016)
Our Services for Transdermal Liposome Skin Irritation Testing
In Vitro Skin Irritation Test
Many countries and regions in the world, led by the European Union, are calling for a ban on the use of animal experiments in cosmetic safety evaluation, which makes the development of in vitro cosmetics irritant evaluation methods to replace animal experiments become a future trend. At present, we provide the following types of skin stimulation in vitro tests: reconstructed human epidermis (RHE) model test, and transdermal electrical resistance (TER) test.
In Vivo Skin Irritation Test
The stimulation test follows a progressive approach, starting with in vitro tests, followed by animal testing, and concluding with human trials. The irritation assessment results are finally provided based on the reaction, and the human trial should only be conducted after previous trials have demonstrated no signs of irritation. We can provide animal and human skin irritation tests.
Our Workflow of Transdermal Liposome Skin Irritation Testing
Our service process is mainly divided into the following parts: experimental design, model screening and establishment, pre-experiment and formal experiment, data processing, and analysis.
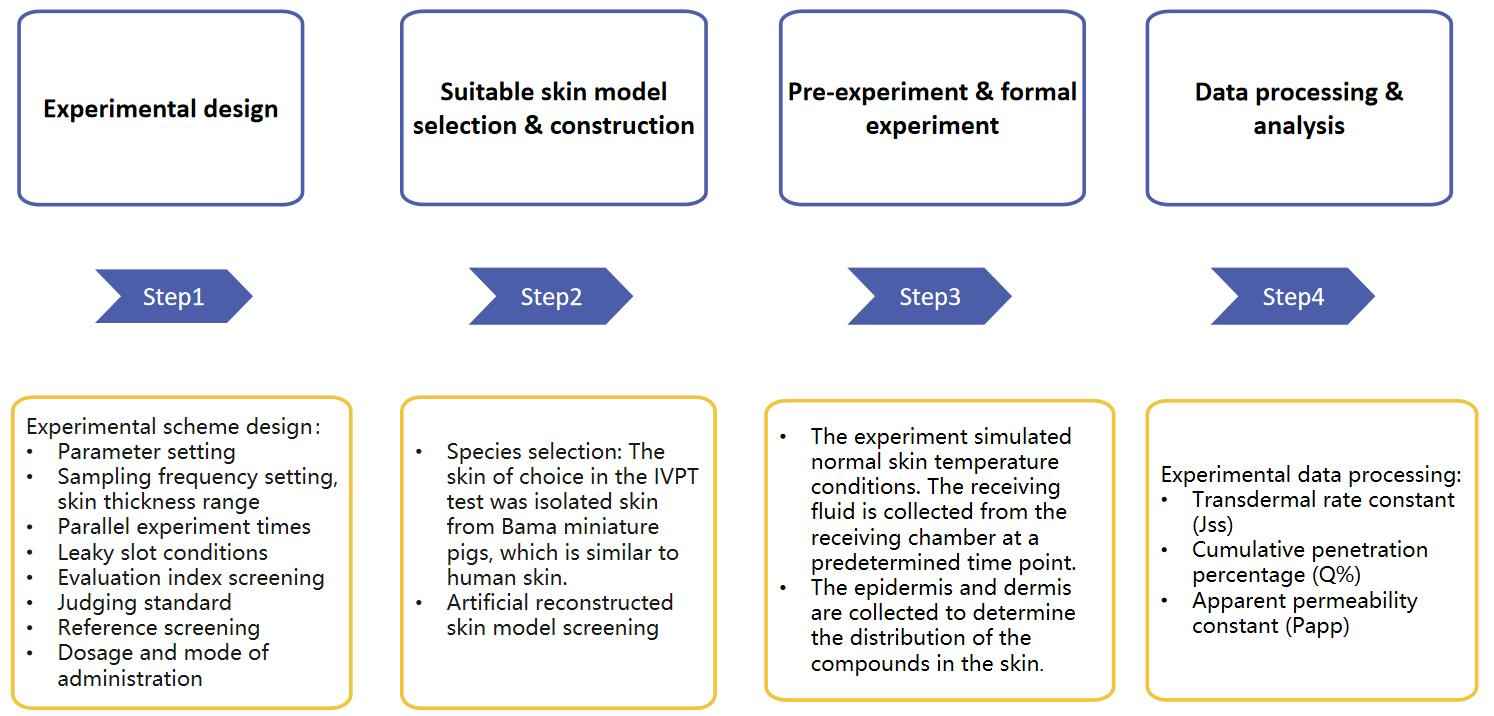 Fig. 2 Our workflow of transdermal liposome skin Irritation testing. (CD Formulation)
Fig. 2 Our workflow of transdermal liposome skin Irritation testing. (CD Formulation)
Our Platforms for Transdermal Liposome Skin Irritation Testing
| Items |
Detailed Information |
| Reconstructed human epidermis (RHE) model |
The model simulates the barrier function of the human stratum corneum, as well as a complete living epidermis. Ideal for evaluating the effects of preclinical and developed topical compounds on human skin. Applications include:
- Effects of UVA / UVB radiation
- Permeability assays
- Gene expression
- Differentiation
- Corrosion and irritation
|
| Transdermal electrical resistance (TER) test |
- Isolated animal skin models
- Compared with the human skin model test, the TER test has the advantages of simplicity, economy, and less demanding test conditions.
|
Our Key Advantages in Transdermal Liposome Skin Irritation Testing
- Professional Teams. We have in vitro and in vivo analysis teams for experimental analysis of skin irritation in transdermal liposomes. Our experimental platform supports the screening of multiple skin models and the establishment of different methods.
- Efficiency and Cost-effective. Test results are delivered to customers quickly and efficiently throughout the process. Cost-effective and customized service solutions according to customer requirements.
- Unique. Independent project management system for transdermal liposome skin irritation testing services.
Published Data
Technology: biocompatible transdermal drug delivery technique
Journal: Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology
IF: 9.7
Published: 2020
Results: In this study, the authors developed an HHA-liposome transdermal system (HHL) by using reverse evaporation, high-speed homogenization, and microinjection techniques to embed HHA into the liposome structure. The effective penetration and long-term stay of HHA in skin tissue were verified in multiple dimensions, and the dynamics of HHA in the skin were deeply studied. In addition, studies have shown that HHL can significantly enhance the activity of human keratinocytes and effectively inhibit photoinduced cell aging. In addition, a mouse model of laser ablation-induced acute skin injury was established, and the transdermal system showed obvious anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects, promoted skin hyperplasia and scar repair, and showed great potential in accelerating skin wound healing. At the same time, HHL can significantly improve the skin barrier dysfunction induced by simulated sunlight exposure, inhibit skin erythema, inflammatory response and oxidative stress, and promote collagen expression in chronic photodamaged skin models. Therefore, this biocompatible transdermal drug delivery system represents a promising new strategy for the non-invasive use of HHA in skin photodamage, showing great clinical translational potential and broad application prospects.
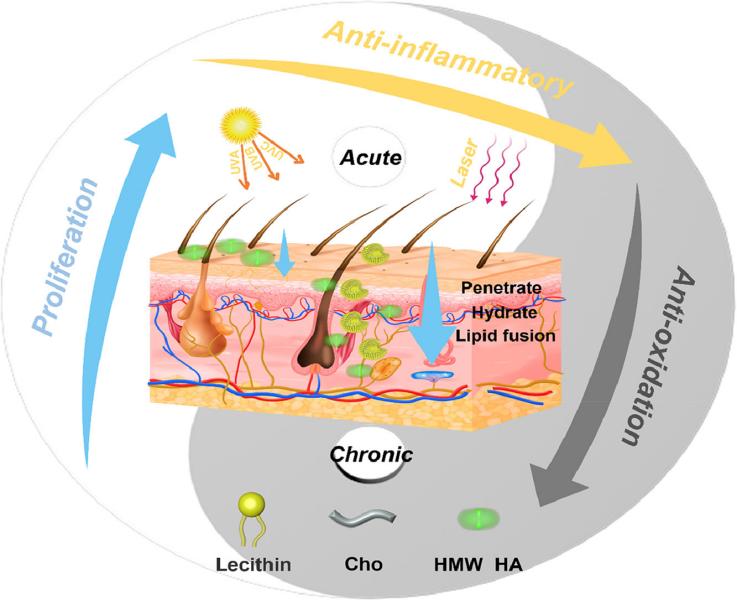 Fig.3 The hyaluronic acid-liposome delivery system used for effective transdermal treatment of acute and chronic skin photodamage. (Hui Xing, et al., 2022)
Fig.3 The hyaluronic acid-liposome delivery system used for effective transdermal treatment of acute and chronic skin photodamage. (Hui Xing, et al., 2022)
CD formulation offers a comprehensive solution for quantitatively analyzing skin biological samples. This enables efficient completion of experiments and provides accurate and reliable data to support the development of transdermal liposomes for skin drugs. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you require any assistance.
References
- Palmer, B.C.; DeLouise, L.A. Nanoparticle-Enabled Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems for Enhanced Dose Control and Tissue Targeting. Molecules. 2016, 21, 1719.
- Hui Xing, Xiangjun Pan, et al. High molecular weight hyaluronic acid-liposome delivery system for efficient transdermal treatment of acute and chronic skin photodamage, Acta Biomaterialia,b 2024, ISSN 1742-7061.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Illustration of nanoparticle skin penetration pathways. (Palmer, B.C., et al., 2016)
Fig.1 Illustration of nanoparticle skin penetration pathways. (Palmer, B.C., et al., 2016) Fig. 2 Our workflow of transdermal liposome skin Irritation testing. (CD Formulation)
Fig. 2 Our workflow of transdermal liposome skin Irritation testing. (CD Formulation) Fig.3 The hyaluronic acid-liposome delivery system used for effective transdermal treatment of acute and chronic skin photodamage. (Hui Xing, et al., 2022)
Fig.3 The hyaluronic acid-liposome delivery system used for effective transdermal treatment of acute and chronic skin photodamage. (Hui Xing, et al., 2022)