Ocular Liposome Characterization
Inquiry
The development of eye drops capable of delivering hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs to the internal structures of the eye, as well as restoring the tear film, has emerged as a cutting-edge topic in recent years. The formulation of eye drops into liposomes offers several advantages, including enhanced corneal permeability, sustained drug release, and reduced toxic reactions. CD Formulation is committed to providing comprehensive and professional analytical profiling services for liposomal eye drop products, thereby driving the advancement of this field.
Why You Need Ocular Liposome Characterization?
A tiny vesicle formed by the phospholipid bilayer encapsulates hydrophilic/lipotropic drugs. It is widely used in the treatment of retinal diseases. It is easy to penetrate into the cornea and has a certain adsorption effect, increasing the retention time of drugs in the cornea. Liposome cholesterol-containing phospholipid vesicles are a favorable delivery system for retinal diseases, carrying hydrophobic and hydrophilic molecules, prolongating intraocular retention after intraocular (intravitreal or subretinal) injection, protecting drugs and delaying deterioration, and have a history of clinical approval. Therefore, the characterization of ophthalmic liposomes is very important and related to clinical efficacy.
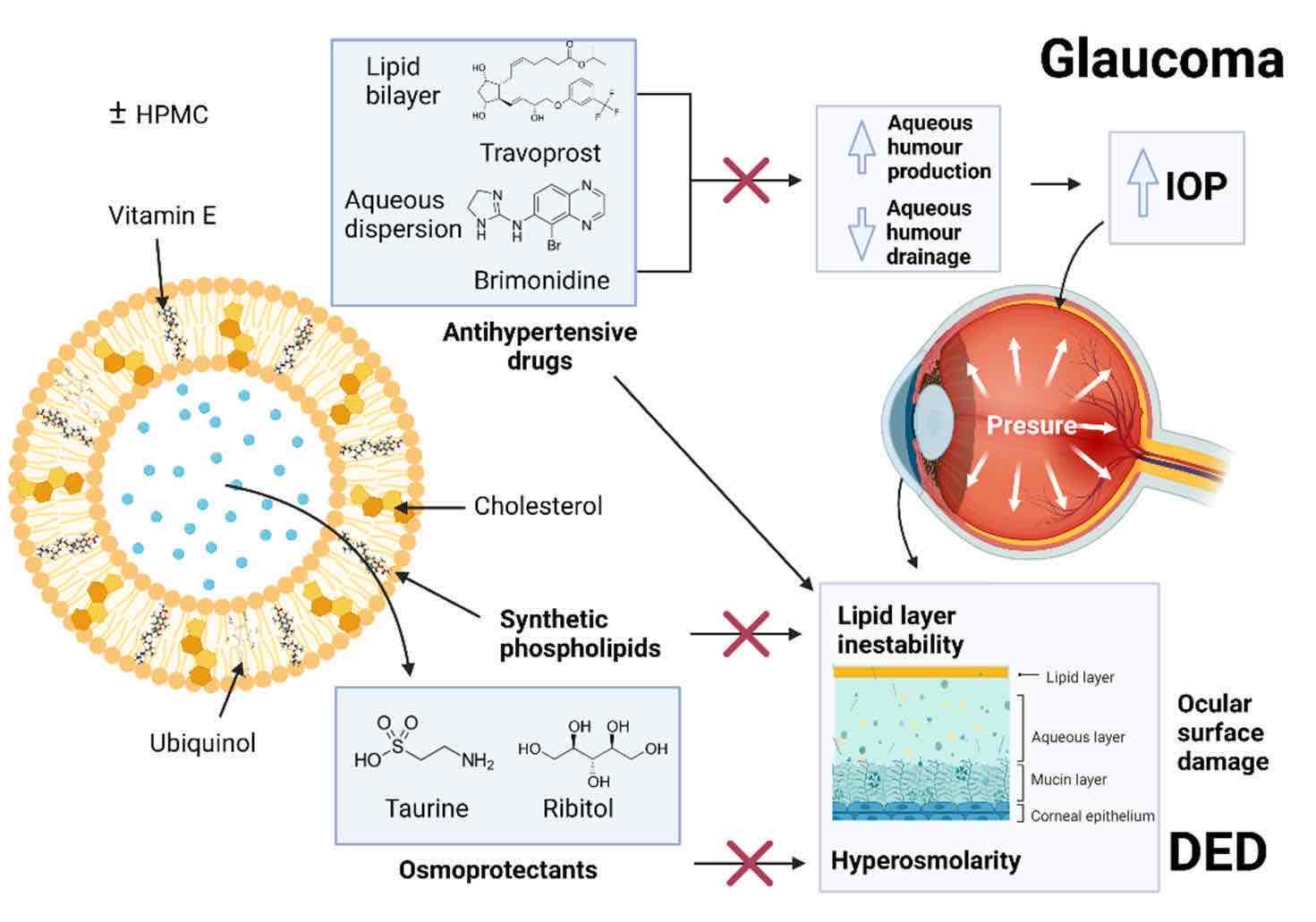 Fig.1 Liposome structure and mechanism for the treatment of glaucoma and prevention of dry eye. (González-Cela-Casamayor. Miriam, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Liposome structure and mechanism for the treatment of glaucoma and prevention of dry eye. (González-Cela-Casamayor. Miriam, et al., 2022)
Explore Our Services for Ocular Liposome Characterization
We offer many kinds of methods to test the liposome surface tension such as, capillary elevation method/drop plate method and deloop method, maximum bubble pressure method, drop volume method, drop profile method, and so on.
The cornea is the main static barrier for drug absorption into aqueous humor after local administration. Understanding the factors that affect corneal permeability is expected to lead to the development of eye drops with higher bioavailability. To evaluate the corneal permeability of liposomal drugs, we introduced corneal models in rabbits, pigs, and cattle.
Eye irritation test is a test to evaluate whether the tested sample has an irritating/corrosive effect on the eyes of animals after direct or indirect contact with them. We introduced choriallantoic membrane vascular assay(CAMVA) method and bovine corneal opacity and permeability assay(BCOP), isolated chicken eye (ICE) test method, reconstructed Human keratoid Epithelial Eye Stimulation Test (RhCE EIT), fluorescein leakage (FL) test method.
Our Platforms for Ocular Liposome Characterization
| Platforms |
Specifics |
| Ocular Irritation Assessment Platforms |
- Choriallantoic membrane vascular assay(CAMVA) method
- Bovine corneal opacity and permeability assay(BCOP),
- Isolated chicken eye (ICE) test method, reconstructed Human keratoid Epithelial Eye Stimulation Test (RhCE EIT),
- fluorescein leakage (FL) test method.
|
| Corneal Permeability Assay Platform |
- Many corneal models such as in rabbits, pigs, and cattle, etc.
|
| Liposome Surface Tension Study Platform |
- Capillary elevation method/drop plate method and deloop method
- Maximum bubble pressure method
- Drop volume method
- Drop profile method, and so on.
|
Highlights for Ocular Liposome Characterization
- Advanced. Platforms are equipped with a wide range of analytical instruments and for ocular liposome characterization, such as liposome surface tension study, liposome ocular irritation assessment, corneal permeability assay, etc.
- Rapid. Test results are delivered to customers quickly and efficiently throughout the process.
- Comprehensive. We have many professional analysts who can meet the services of ophthalmic liposome characterization, from physicochemical characterization, stability characterization, to in vitro release characterization and more.
Published Data
Technology: Ocular Delivery of Thymoquinone technique
Journal: Pharmaceutics
IF: 10.5
Published: 2021
Results: Thymoquinone (TQ) is the main component of black seed oil. In vitro studies have shown that it has a protective effect against H2O-induced oxidative stress in human retinal pigment epithelial cells, and in vivo experiments have shown that it has a role in reducing corneal neovascularization and alleviating inflammation in experimental dry eye models in mice. Its therapeutic use is limited by poor bioavailability, low solubility and poor permeability. In this study, the authors developed two liposome formulations, both composed of phosphatidylcholine and the liquid lipid Plurol Oleique, one of which was coated with 0.1% w/v hyaluronic acid (HA) to increase TQ solubility and its ocular therapeutic potential. Each formulation, with a size of less than 200 nm and an EE% of about 70%, was determined by scattering techniques and HPLC-DAD analysis methods, respectively, and they increased the TQ solubility by a factor of 2. HA coated liposomes were stable at +4 °C for more than 2 months, and both coated and uncoated liposomes showed gradual and prolonged release of TQ. Two cell lines, human corneal epithelial cells (HCEC-2) and human conjunctival epithelial cells (HConEC), were used to study the safety of liposome formulations. Absorption studies were also carried out using fluorescent liposomes. Both liposomes, especially HA-coated liposomes, reduced the high-dose TQ toxicity observed in HCEC-2 and HConEC cells, and both agents increased cell-level absorption, especially at the nuclear level, with HA-coated liposomes having a more pronounced effect.
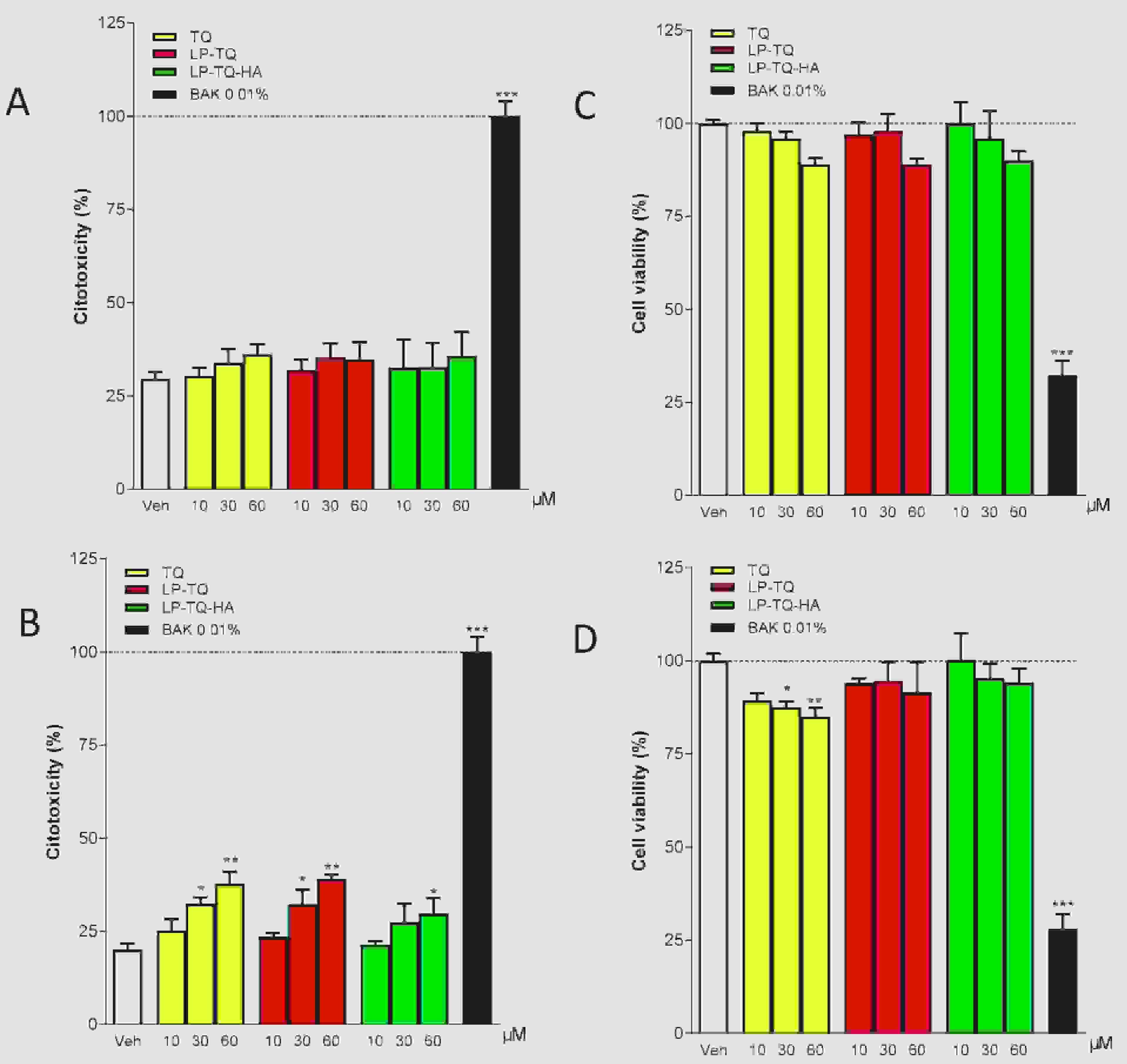 Fig.2 Evaluation of LDH and MTT assay in the human corneal epithelial cells. (Landucci, E., et al., 2021)
Fig.2 Evaluation of LDH and MTT assay in the human corneal epithelial cells. (Landucci, E., et al., 2021)
CD Formulation's ophthalmic liposome characterization services are designed to provide comprehensive analytical services to our clients. If you need any kind of assistance, please contact us immediately.
References
- González-Cela-Casamayor, Miriam; Lopez-Cano, Jose; et al. Novel Osmoprotective DOPC-DMPC Liposomes Loaded with Antihypertensive Drugs as Potential Strategy for Glaucoma
-
Landucci, E.; Bonomolo, F.; et al. Preparation of Liposomal Formulations for Ocular Delivery of Thymoquinone: In Vitro Evaluation in HCEC-2 e HConEC Cells. Pharmaceutics. 2021, 13, 2093.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Liposome structure and mechanism for the treatment of glaucoma and prevention of dry eye. (González-Cela-Casamayor. Miriam, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Liposome structure and mechanism for the treatment of glaucoma and prevention of dry eye. (González-Cela-Casamayor. Miriam, et al., 2022) Fig.2 Evaluation of LDH and MTT assay in the human corneal epithelial cells. (Landucci, E., et al., 2021)
Fig.2 Evaluation of LDH and MTT assay in the human corneal epithelial cells. (Landucci, E., et al., 2021)