Liposome Corneal Permeability Assay
Inquiry
The cornea is located in the front of the eye and is a completely transparent, static barrier without blood vessels or lymph vessels. Based on the dual barrier function of the corneal epithelial cell layer and the stromal layer, only drug molecules with appropriate oil-water partition coefficient and dissociation constant (pKa) and lipid formulations with appropriate adhesion and permeability have good corneal permeability. Liposomes are promising delivery systems for drugs delivered to the anterior and posterior ocular segments via the ocular surface due to their good biocompatibility. CD Formulation has advanced liposome corneal permeability testing platforms. We are committed to providing customers with professional analysis and testing solutions.
Why Conduct Liposome Corneal Permeability Assay?
As the main drug delivery route, the ocular local drug delivery route can achieve non-invasive drug delivery to the ocular surface and is widely used in eye disease treatment in the anterior segment of the eye. Although ocular medication is widespread, local ocular drug delivery remains limited and challenging. This is due to a range of anatomical and physiological disorders of the eye, which can be roughly divided into static or osmotic disorders and dynamic or fluid flow disorders that limit the delivery of drugs. The cornea is the main static barrier of the eye after local administration. There are three key areas of the cornea: epithelium, stroma, and endothelium, and the permeability of the epithelium is the main reason for the low bioavailability of drugs in the anterior segment. Therefore, corneal permeability detection is significant for the quality control of ophthalmic liposomes.
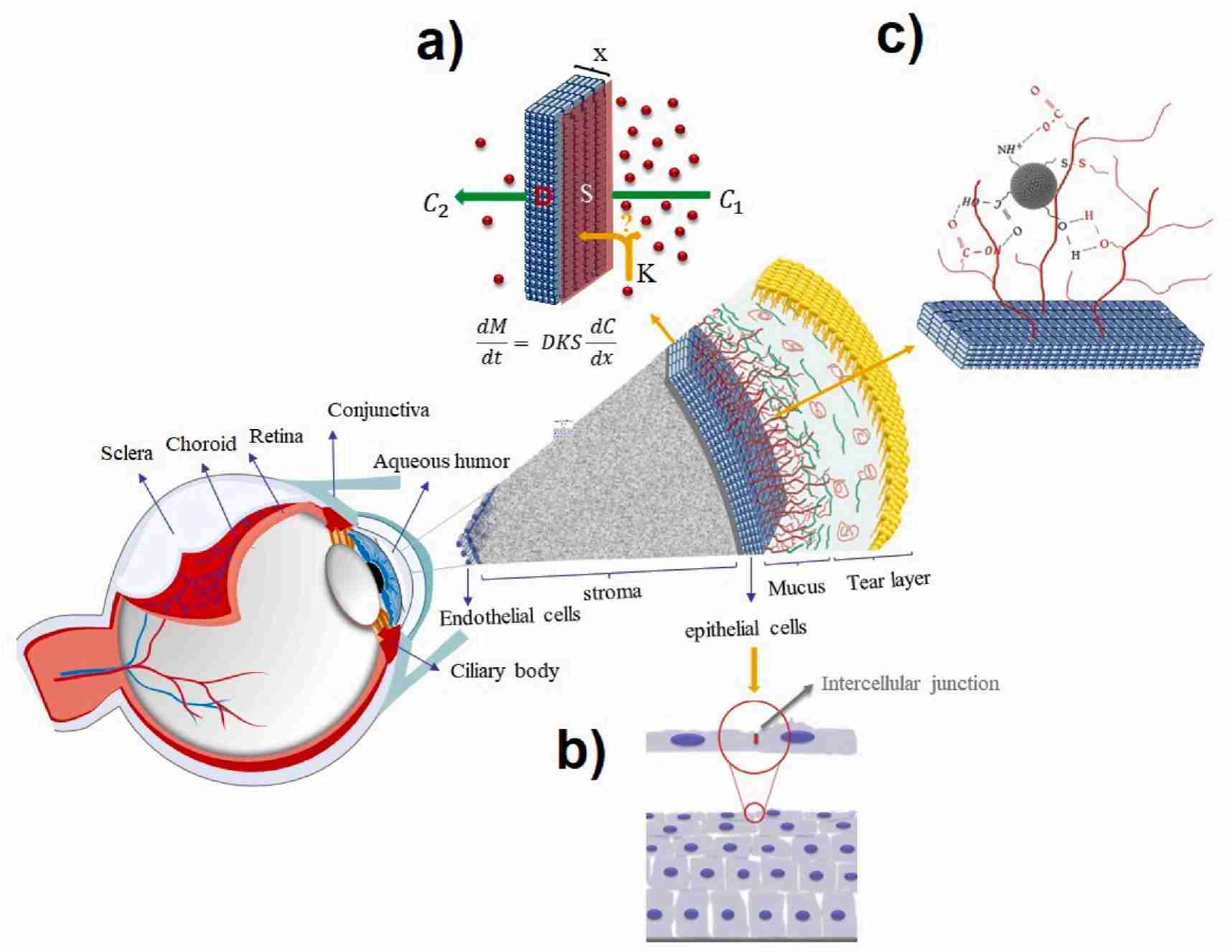 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the mechanism of drug molecules passing through the corneal barrier after local administration. (Nooshin Tasharrofi, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the mechanism of drug molecules passing through the corneal barrier after local administration. (Nooshin Tasharrofi, et al., 2022)
Our Services for Liposome Corneal Permeability Assay
In vitro ophthalmology studies can directly evaluate corneal permeability using corneal tissue, which eliminates the interference of other biological factors. This facilitates the design of preclinical in vivo experiments and the development of corneal permeability pathways for liposomal drugs.
Screening of Eye Tissue Samples
The reliability and accuracy of experimental data were improved by optimizing the screening method of experimental eye tissue samples. We offer the following screening methods:
- Sodium fluorescein staining (pre-assay): In vitro evaluation of corneal integrity. After staining with sodium fluorescein, the slit-lamp cobalt blue filter was used for detection.
- Determination of corneal Hydration Levels (after the experiment): The weight method was used to calculate the corneal hydration level HL (wet weight Wb and dry weight Wa after drying at 70℃ for 12h) using the experiment endpoint.
Experimental Animal Selection
Based on the properties of drugs and the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the eyeballs of different species, suitable animal species are the key to carrying out pre-clinical pharmacokinetic studies in ophthalmology. Due to the species differences between animals and humans, no animal model can fully simulate the metabolic process of drugs in the human body. Thus, we will provide customers with diverse animal model combinations for permeability testing.
Determination of Corneal Permeability Assay for Various Formulations
The addition of excipients can increase the retention time of liposome drugs on the ocular surface and affect the penetration rate of liposome drugs on the ocular surface. Therefore, different formulations of osmotic pressure testing can help balance the amount of excipients used with the duration of the drug in the eye and the rate of penetration in the development of liposome formulations for the eye.
Our Platforms for Liposome Corneal Permeability Assay
| Techniques & Platforms |
Detailed Information |
| Animal platforms |
- We offer a variety of animal model combinations for ophthalmic drug testing. Each animal species has different characteristics, and the eyeball structure is also different, so the advantages and disadvantages of each animal model should be considered in the selection of animal models.
- We provide monkey, pig, dog, rat, mouse, and other isolated eye tissue.
|
| Delivery route platform |
- Our team can currently perform procedures including eye drop administration, and subconjunctival injection to detect corneal osmotic pressure in the ophthalmic liposomal drug delivery system.
|
Our Key Advantages in Liposome Corneal Permeability Assay
- Low cost of preliminary screening test. The unique biological model can meet the recent demand for repeated sampling in ophthalmology, thus diminishing the reliance on laboratory animals.
- An abundance of biological sample repositories. The experiment is facilitated by the diverse tissue samples obtained from the eyes of rabbits, cows, sheep, and pigs.
- Less biological interference factors. To enhance efficiency and cost-effectiveness, while simplifying the challenges associated with sample analysis and data interpretation.
Published Data
Technology: Techniques in liposome corneal permeability assay
Journal: Drug Delivery and Translational Research
IF: 5.4
Published: 2024
Results: This study aimed to combine synthetic phosphatidylcholine liposomes containing LAT with hyaluronic acid (0.2% w/v) and the osmoprotective agents betaine (0.40% w/v) and leucine (0.90% w/v) (LAT-ha-LIP) to prolong the hypotensive effect of LAT. LAT-HA-LIP had a zeta potential of high drug loading (104.52 ± 4.10%), vesicle size (195.14 ± 14.34 nm) and -13.96 ± 0.78 mV. LAT-HA-LIP exhibits the best tolerance to human corneal and conjunctival epithelial cells in vitro. These findings suggest that LAT-HA-LIP has potential eye protection and antihypertensive effects in glaucoma treatment.
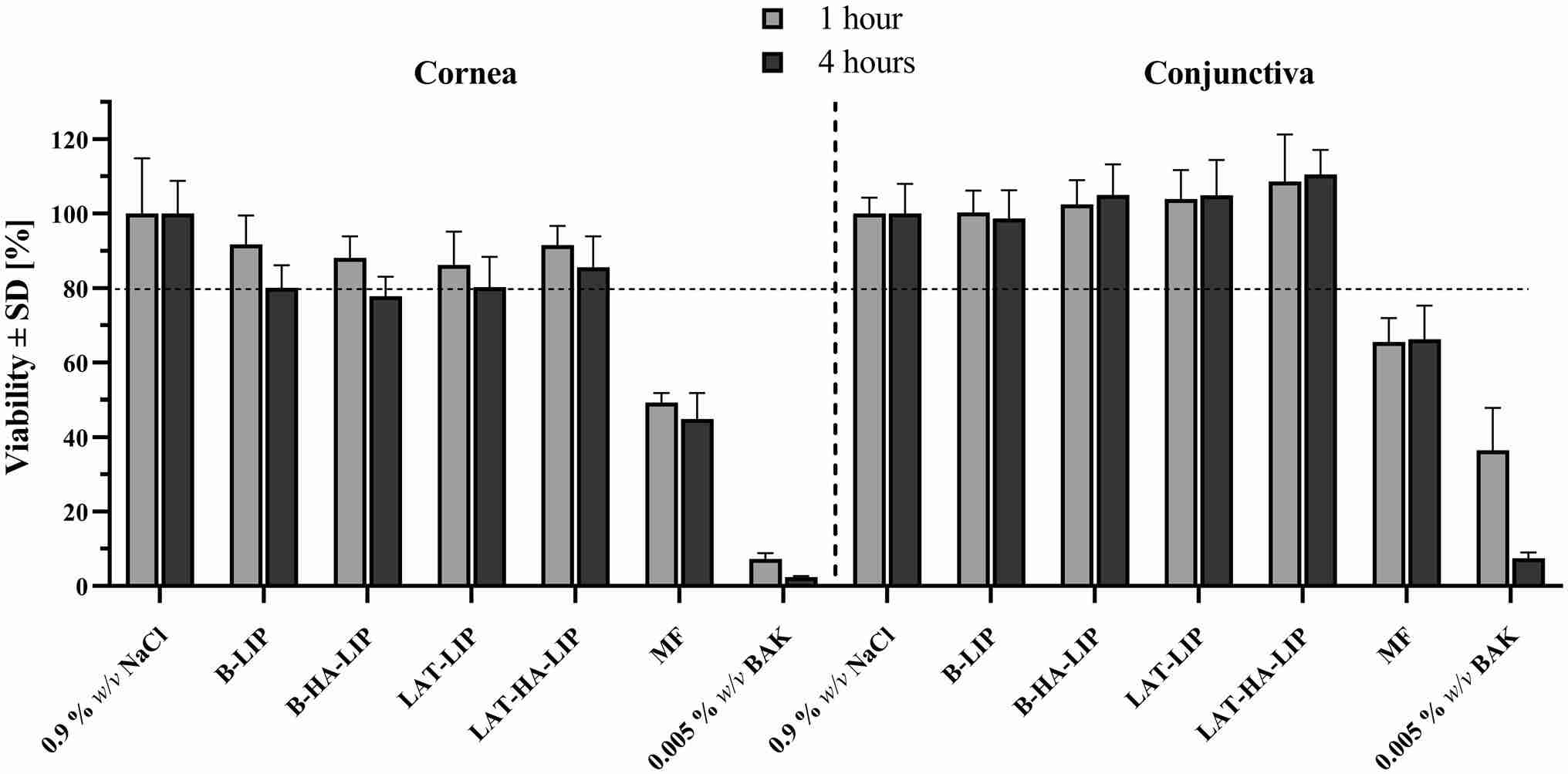 Fig.2 In vitro tolerance of the liposomal formulations developed in corneal (hTERT-HCECs) and conjunctival (IM-HConEpiC) cells. (Brugnera, M., et al., 2024)
Fig.2 In vitro tolerance of the liposomal formulations developed in corneal (hTERT-HCECs) and conjunctival (IM-HConEpiC) cells. (Brugnera, M., et al., 2024)
CD Formulation has developed the in vitro ophthalmic permeability research platform and completed the corneal permeability research of a variety of liposome drugs. If you need any help, please contact us immediately.
References
- Brugnera, M., Vicario-de-la-Torre, M., et al. Enhancing the hypotensive effect of latanoprost by combining synthetic phosphatidylcholine liposomes with hyaluronic acid and osmoprotective agents. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. 2024.
- Nooshin Tasharrofi, Mohammad Nourozi, et al. How liposomes pave the way for ocular drug delivery after topical administration. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2022, 67.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the mechanism of drug molecules passing through the corneal barrier after local administration. (Nooshin Tasharrofi, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the mechanism of drug molecules passing through the corneal barrier after local administration. (Nooshin Tasharrofi, et al., 2022) Fig.2 In vitro tolerance of the liposomal formulations developed in corneal (hTERT-HCECs) and conjunctival (IM-HConEpiC) cells. (Brugnera, M., et al., 2024)
Fig.2 In vitro tolerance of the liposomal formulations developed in corneal (hTERT-HCECs) and conjunctival (IM-HConEpiC) cells. (Brugnera, M., et al., 2024)