Oral Thin Film for Cardiovascular Therapeutic Research
Inquiry
According to statistics, cardiovascular diseases cause the highest amount of deaths globally. The drug dosage forms used to treat the disease are usually capsules or tablets. However, some of these drugs may suffer from extensive first-pass metabolism after oral administration, thus leading to low bioavailability. Therefore, incorporating drugs to treat cardiovascular disease into the oral thin films and utilizing oral thin films in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases would considerably improve patient compliance. CD Formulation specializes in developing oral thin film drug delivery systems for cardiovascular therapeutic research. Our experienced oral thin film experts provide services ranging from API screening, formulation design, development, characterization, in vivo and in vitro studies to drug metabolism research.
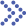
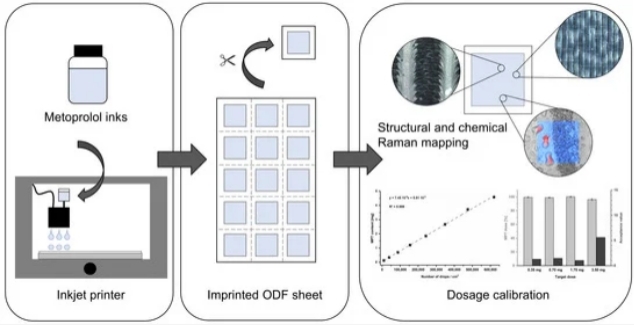 Fig.1 Investigations into Metoprolol Tartrate Deposition on Orodispersible Films. (Olga Kieferr, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Investigations into Metoprolol Tartrate Deposition on Orodispersible Films. (Olga Kieferr, et al., 2021)
Highlights of Oral Thin Film for Cardiovascular Therapy
 Fig.2 The Advantages of Oral Thin Film for Cardiovascular Therapy. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 The Advantages of Oral Thin Film for Cardiovascular Therapy. (CD Formulation)
Rapid Onset: The oral thin film can dissolve quickly in the mouth, allowing for fast absorption and onset of action, which can be particularly beneficial in acute cardiovascular events such as chest pain or heart attack.
Improved Patient Compliance: The oral thin film is convenient and easy to use. Utilizing oral thin films in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases would considerably enhance patient compliance, especially for hypertensive patients after a stroke.
Dosing Accuracy: Oral thin film formulations can be easily tailored to provide precise dosing, allowing for more accurate and personalized treatment of cardiovascular conditions.
Reduced Gastrointestinal Irritation: Oral thin films can bypass the digestive system, reducing the risk of gastrointestinal irritation or side effects.
Improve Bioavailability: Oral thin films can improve bioavailability by decreasing broad metabolism in the liver and increasing API solubility and permeability through the buccal mucosa.
Cases of Oral Thin Film for Cardiovascular Therapy
Amlodipine besylate, a dihydropyridine-derivative drug to cure cardiovascular diseases, was formulated with poly (ethylene oxide) into the nanofiber orodispersible films by applying electrospinning technology.
An oral film containing enalapril maleate was prepared using inkjet printing technology to treat cardiovascular diseases.
The therapeutic single dose for children 0.5 mg enalapril has been successfully printed onto the film.
Metoprolol succinate rapidly dissolving oral strips, an anti-hypertensive agent, was prepared by solvent casting using hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-5 cps and polyvinyl alcohol as film-forming polymers.
Custom Oral Thin Film Development
CD Formulation offers specialized oral thin film drug development services customized for cardiovascular therapeutic research. Our services include custom formulation development, targeted drug delivery, biocompatible and controlled release, and commercial manufacturing.
Custom Formulation Development
We work closely with pharmaceutical clients to develop custom formulations for oral thin film drug products specifically designed to deliver medications for cardiovascular conditions, and we optimize formulations to achieve the desired drug release profiles, bioavailability, and therapeutic outcomes.
Targeted Drug Delivery
Our formulations are designed to efficiently and rapidly deliver medications used for cardiovascular diseases cardiovascular diseases, such as antihypertensive drugs, antiplatelet agents, lipid-lowering medications, and other cardiovascular therapies.
Biocompatible and Controlled Release
In the formulation development, we screen biocompatible materials and controlled release strategies, ensuring cardiovascular medications' stability and controlled release within the oral thin film delivery system.
Commercial Manufacturing
We provide commercial manufacturing services, scaling up the production of oral thin film cardiovascular drug manufacturing.
Why Choose CD Formulation?
- With the support of our advanced oral thin film drug delivery system, we can customize high-quality oral thin film for cardiovascular therapy to meet customers' needs.
- Rigorous quality control measures guarantee that each strip meets the highest standards of safety and effectiveness.
- We offer customizable formulations to meet the specific needs of different clients, ensuring optimal delivery and efficacy for each therapeutic compound.
Published Data
Technology: A sublingual film for treatment of cardiovascular disease
Journal: Biochem. Cell. Arch.
IF: 3.8
Published: 2024
Results: In this study, a stable sublingual film of Nifedipine for the treatment of cardiovascular disease (Angina pectoris, Hypertension) was prepared by using pullulan, which released the drug over the 300 sec to prevent first-pass metabolism to the most significant possible extent.
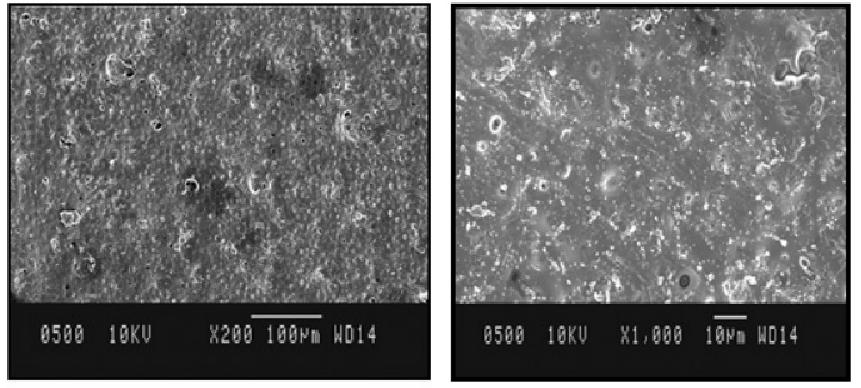 Fig.3 SEM photograph of sublingual film for treatment of cardiovascular disease. (Rajveer Bhaskar, et al., 2024)
Fig.3 SEM photograph of sublingual film for treatment of cardiovascular disease. (Rajveer Bhaskar, et al., 2024)
CD Formulation provides a customized oral thin film for cardiovascular therapeutic research. Researchers can select from types of oral thin film, active pharmaceutical ingredients, polymers and more. We can also help customers solve problems such as solubility of active ingredients, unacceptable taste, etc. So that you can develop an oral thin film that meets the market's needs. In addition, we can help you optimize the process for large-scale manufacturing. If you require our oral thin film services for cardiovascular therapeutic research, please contact us by phone or email, and our colleagues will get back to you within three working days.
References
- Rajveer Bhaskar, Ravi M. Parjane, et al. DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT AND BIOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF NIFEDIPINE- LOADED ORAL FILM IN THE MANAGEMENT OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES. Pharmaceutics. 2024, Vol (24):653-661.
- Yu Tian, Jiangtao Lin, et al. Recent progress in orodispersible films-mediated therapeutic applications: A review. MedComm–Biomaterials and Applications. 2022.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services


 Fig.1 Investigations into Metoprolol Tartrate Deposition on Orodispersible Films. (Olga Kieferr, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Investigations into Metoprolol Tartrate Deposition on Orodispersible Films. (Olga Kieferr, et al., 2021) Fig.2 The Advantages of Oral Thin Film for Cardiovascular Therapy. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 The Advantages of Oral Thin Film for Cardiovascular Therapy. (CD Formulation) Fig.3 SEM photograph of sublingual film for treatment of cardiovascular disease. (Rajveer Bhaskar, et al., 2024)
Fig.3 SEM photograph of sublingual film for treatment of cardiovascular disease. (Rajveer Bhaskar, et al., 2024)