Nucleic Acid Formulation - CD Formulation
Call Us:
- Home
- Services
- Nucleic Acid Customization Services
- Custom Small Nucleic Acid Synthesis Services
- Custom Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) Synthesis
- Custom Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) Synthesis
- Custom Aptamer Synthesis
- Custom Small Activating RNA (saRNA) Synthesis
- Custom Single Guide RNA (sgRNA) Synthesis
- Custom MicroRNA (miRNA) Synthesis
- Custom Circular RNA (circRNA) Synthesis
- Custom Ribozyme Synthesis
- Custom DNAzyme Synthesis
- Custom Short Hairpin RNA (shRNA) Synthesis
- Custom Transfer RNA (tRNA) Synthesis
- Custom CpG Oligodeoxynucleotide Synthesis
- Custom Peptide Nucleic Acid Synthesis
- Custom Bridged Nucleic Acids (BNAs) Synthesis
- Custom Single-Stranded DNA (ssDNA) Synthesis
- Custom Double-Stranded RNA Synthesis
- Custom piRNA Synthesis Services
- Custom mRNA Synthesis
- Nucleic Acid Modification Services
- Custom Small Nucleic Acid Synthesis Services
- Nucleic Acid Therapeutic Formulation Development
- Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery Carriers Development
- Nucleic Acid-Conjugate Development
- GalNAc-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Lipid-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Antibody-siRNA Conjugate Development
- CpG-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Peptide-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Aptamer-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Cholesterol-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Folic Acid-siRNA Conjugate Development
- α-Tocopherol-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Protein-siRNA Conjugate Development
- Squalene-siRNA Conjugate Development
- GalNAc-ASO Conjugate Development
- Peptide-ASO Conjugate Development
- GalNAc-miRNA Conjugate Development
- Lipid-based Nanoparticle Development
- Inorganic Nanoparticle Development
- Polymer-based Nanoparticle Development
- Peptide-based Carriers Development
- Protein Carrier Development
- Exosome Carrier Development
- Bio-MOFs Development Services for Nucleic Acid Therapeutic Formulation
- Viral Vector Development
- Virus-like Particles Development for Nucleic Acid Therapeutic Formulation
- Natural Polysaccharide Development Services
- Nucleic Acid-Conjugate Development
- Design and Optimization Services for Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery System
- Dosage Form Development for Nucleic Acid Therapeutic Formulation
- Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery Carriers Development
- Analytical and Characterization Services for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Identification of Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Structural Characterization for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Physicochemical Characterization for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Molecular Weight Analysis for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Particle Size Analysis for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Zeta Potential Analysis for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Morphological Analysis for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Optical Rotation Testing for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- pH Testing for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Nucleic Acid Drug pKa Determination
- Moisture Content Determination for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Molar Extinction Coefficient Determination for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Melting Temperature (Tm) Testing for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Impurity Analysis for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Stability Analysis for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Safety Analysis for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Nucleic Acid Drug Evaluation and Bioanalytical Services
- In Vivo Nucleic Acid Drug Distribution Measurement
- In Vitro ADME Assays for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Metabolite Identification for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Pharmacokinetics (PK) Assays for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Pharmacodynamic (PD) Assays for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Nucleic Acid Drug Biomarker Testing
- Nucleic Acid Drug Toxicology Analysis
- Nucleic Acid Drugs Immunogenicity Testing
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Assessment for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Pharmacodynamic Evaluation for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Nucleic Acid Drug Process Development
- Nucleic Acid Customization Services
- Technologies & Platforms
- Nucleic Acid Drug Design Platform
- Nucleic Acid Drug Preparation Technology
- Nucleic Acid Formulation Preparation Technology
- Solid Dispersion Preparation Technology for Nucleic Acid Formulations
- Hot Melt Extrusion Technology for Nucleic Acid Formulations
- Medicinal Nanocrystals Technology for Nucleic Acid Formulations
- Coating Technology for Nucleic Acid Formulations
- 3D Printing Technology for Nucleic Acid Formulations
- Microfluidics Technology for Nucleic Acid Formulations
- Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery Platforms
- GalNAc-Conjugated Delivery System Platforms
- Lipid Nanocarrier Drug Delivery System Platforms
- Polymer-Based Nanoparticle Delivery System Platforms
- Exosome Delivery System Platforms
- Inorganic Nanoparticle Delivery System Platforms
- Peptide Nanoparticles Delivery Platforms
- Protein Nanoparticles Delivery System Platforms
- Viral Vector Platforms for Nucleic Acid Drug Delivery
- Natural Polysaccharide Drug Delivery System Platforms
- Virus-like Particle Drug Delivery Platforms
- Bio-MOFs Drug Delivery Platforms
- Analytical Technology Platforms
- HPLC Platforms for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Gas Chromatography (GC) Platforms for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Infrared Spectroscopy Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- NMR Technology Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Mass Spectrometry (MS) Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Circular Dichroism (CD) Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Zeta Potential Analysis Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Technology Platforms for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Technology Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Technology Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- ELISA Technology Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- MSD Technology Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Platform for Nucleic Acid Drugs
- Gel Electrophoresis Technology Platform
- Sequencing Technology Platform
- ICP (Inductively Coupled Plasma) Technology Platforms
- Solutions
- Resources
- Online Order
- Company

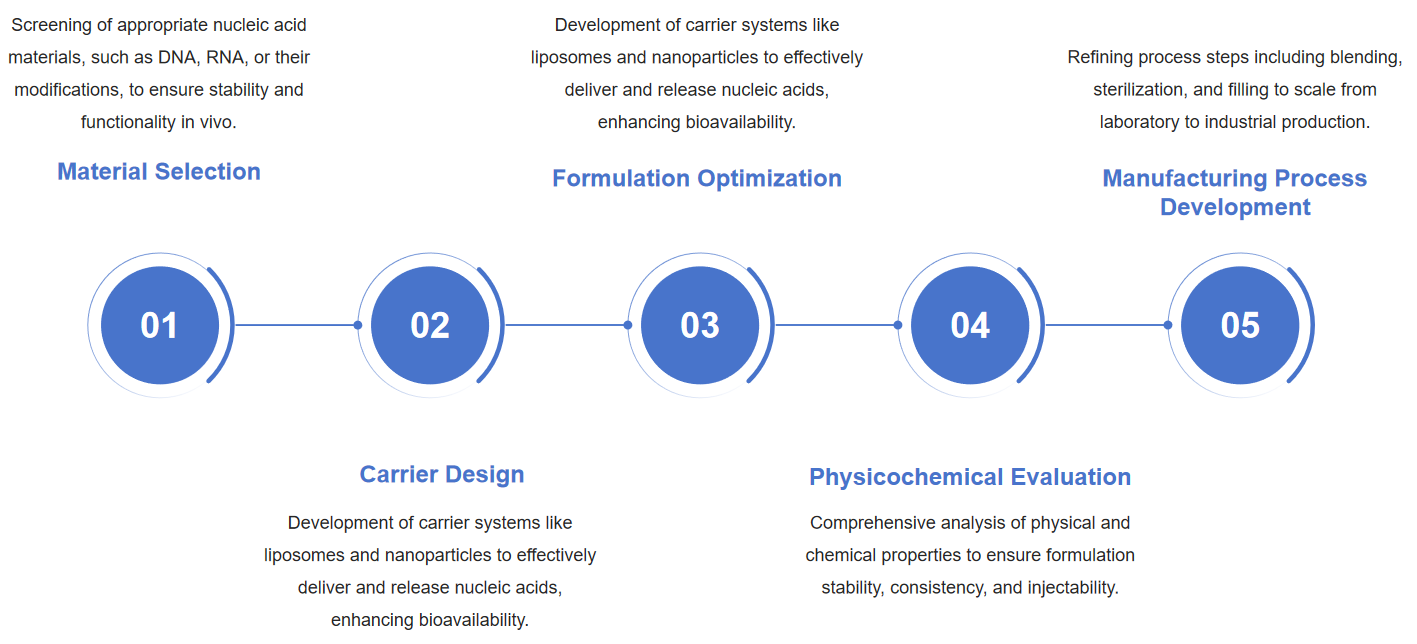 Fig.1 Flow chart of injectable nucleic acid formulation development. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Flow chart of injectable nucleic acid formulation development. (CD Formulation)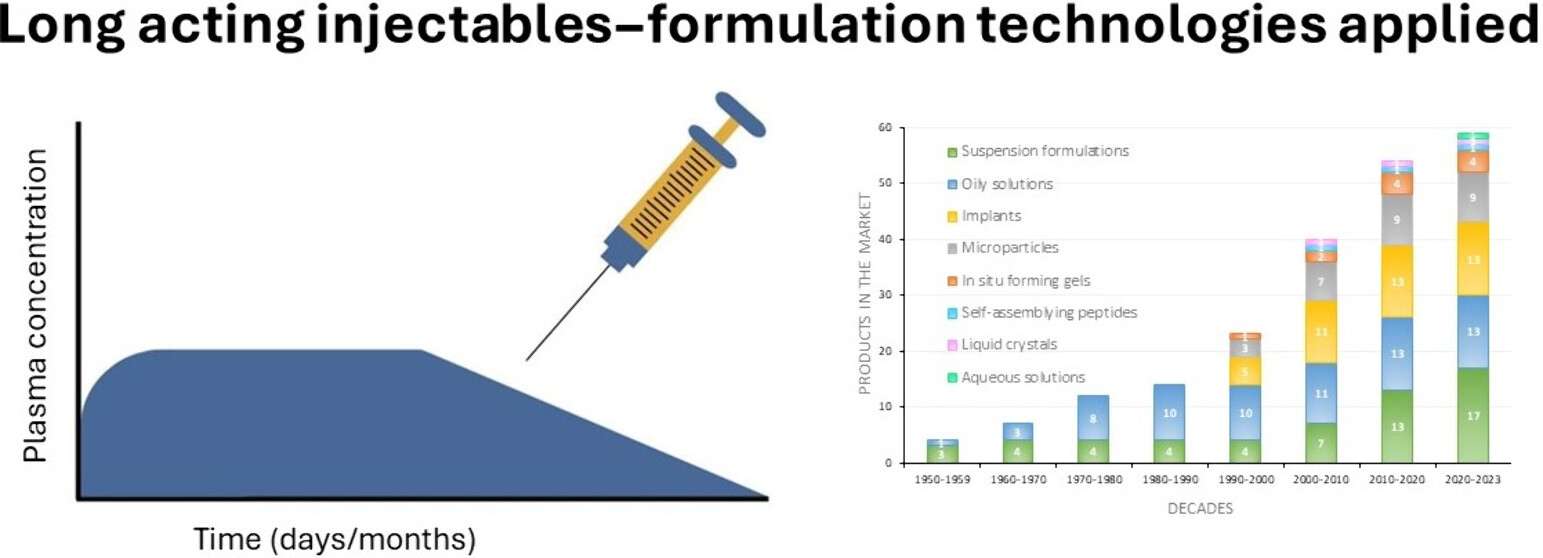 Fig.2 Patient-centric long-acting injectable and implantable platforms. (Alidori S, et al., 2024)
Fig.2 Patient-centric long-acting injectable and implantable platforms. (Alidori S, et al., 2024)