Injectable Liposome Characterization
Inquiry
Liposomes are suitable for injection, including intravenous, intradermal and intratumoral injection, and can accurately deliver drugs to the target tissue. At present, most liposomal drugs are administered by injection. Characterization of liposome after production and storage is an essential part of its quality control. The physical and chemical properties of liposome can predict its behavior in vivo and in vitro. The CD Formulation utilizes a proprietary liposome platform to offer comprehensive analytical services for injectable liposome analysis.
Why You Need Injectable Liposome Characterization?
How do injectable liposomes react in the human body? Are injectable liposomes stable enough to ensure targeting? Is the particle size suitable for clinical use, or will they disappear in the bloodstream? Understanding the size, concentration, and zeta potential of liposomal formulations can help predict their trends in the body, and the relationship between charged liposomes and molecules of opposite charge can be monitored by measuring the zeta potential of the polymers produced by the two. These factors have a significant impact on the effectiveness of drug delivery, especially when pharmaceutical formulators believe that a particular liposome is suitable for a delivery vehicle. Therefore, an analytical system that provides comprehensive data is highly beneficial for the formulation design process.
Explore Our Services for Injectable Liposome Characterization
We provide liposome excipients distribution studies, liposome particle size distribution tests, Zeta potential tests, insoluble particles/visible foreign bodies detection and identification.
Liposome bacterial endotoxin test can be performed by USP prescribed methods, such as gel limit method, gel semi-quantitative method, dynamic color rendering method, endpoint color rendering method, dynamic turbidity method, endpoint turbidity method. The sterility test of injected liposomes was completed according to USP <43>.
Hemolysis refers to the reaction of hemolysis and red blood cell aggregation caused by drug preparations. Some small molecules, biologics or preparation excipients can also lyse red blood cells. Therefore, according to the FDA's recommendation, all injections including liposomal drugs and other topical preparations that may cause immune or non-immune hemolytic reactions should be subjected to hemolytic tests. The hemolytic test we provide includes in vitro test and in vivo test. The hemolytic test of the drug we offer is evaluated by in vitro test tube method first. If the result is positive, a comparative study will be conducted with the marketed preparation of the same drug administration route.
Our Platforms for Injectable Liposome Characterization
| Platforms |
Specifics |
| Particle characterization analysis platform |
- Platform for particle characterization and analysis, covering particle analysis instruments ranging from nano-scale, sub-micron to micron, stability characterization services for liposomes and other nanopreparations, and identification of insoluble particles and foreign bodies, etc.
- We can determine particle size distribution and develop and verify particle size distribution methods according to USP<429> and other pharmacopoeia methods to help customers establish particle size control quality standards.
|
| Sterility and Endotoxin Platform |
- PCR (Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR, qPCR);
- flow cytometer method;
- Stearic acid detection technology;
- Recombinant C factor endotoxin assay.
|
| Liposome Hemolysis Testing |
- In vitro hemolysis test
- Hemolysis test in vivo
|
Highlights for Injectable Liposome Characterization
- Rigorous testing standards. We can undertake the characterization needs of all stages from research and development to production, such as release standards and quality control standards for injectable liposomes.
- Flexibility. Our service model is not fixed, we can design a set of exclusive service process for each customer according to the specific background of each project.
- Advanced analysis platforms. Our facility caters to the characterization of injectable liposomes of a variety of specifications from the laboratory level to the clinical level.
Published Data
Technology: Injectable and In Situ-Formable Thiolated Chitosan-Coated Liposomal Hydrogels Technology
Journal: ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
IF: 9.5
Published: 2020
Results: In this study, to improve the water solubility and bioavailability of Cur, the authors encapsulated Cur in Cur-lip liposomes and then coated them with thiolated chitosan (CSSH) to form a liposome hydrogel (CSSH/Cur-lip gel). The hydrogel has thermosensitivity and in situ injection performance, being fluid at room temperature and rapidly gelatinizing at 37°C. The cumulative release ratio of CSSH/Cur-lip gel at 12 h was 31.57±1.34%, which can effectively delay the release of Cur. It is worth noting that the elastic hydrogel remains compressed even after five cycles of compression. The cytotoxicity experiment shows that the liposome hydrogel has good cell compatibility, but MCF-7 cells are significantly inhibited and killed after Cur encapsulation for 72 h. The in vivo breast cancer recurrence experiment shows that the CSSH/Cur-lip gel group can inhibit the recurrence of breast cancer tumors after resection and repair the damaged tissue. The results show that the drug-loaded liposome hydrogel can continuously deliver Cur and have good anti-tumor effects in vivo and in vitro. The injectable, context-shaped, thermosensitive CSSH/Cur-lip gel can be a promising new drug delivery carrier as a local and sustained drug delivery carrier to reduce the burst release and as an tissue engineering scaffold for tissue regeneration after tumor resection.
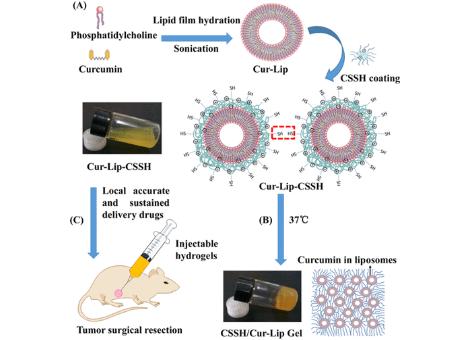 Fig.1 Cationic liposomes mediated transdermal delivery. (Kuznetsova DA, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Cationic liposomes mediated transdermal delivery. (Kuznetsova DA, et al., 2021)
Our CD Formulation team possesses extensive expertise and experience in the field of liposome injection. For numerous years, we have remained committed to delivering tailored and comprehensive solutions to our esteemed clientele, catering to their distinct requirements. Please do not hesitate to contact us promptly should you require any form of assistance.
References
- Riwang Li, Zhen Lin, et al. Injectable and In Situ-Formable Thiolated Chitosan-Coated Liposomal Hydrogels as Curcumin Carriers for Prevention of In Vivo Breast Cancer Recurrence. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2020, 12 (15), 17936-17948
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services


 Fig.1 Cationic liposomes mediated transdermal delivery. (Kuznetsova DA, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Cationic liposomes mediated transdermal delivery. (Kuznetsova DA, et al., 2021)