Injectable Liposome Hemolysis Testing
Inquiry
Hemolysis is the breakdown or destruction of red blood cells (RBCS), resulting in the release of hemoglobin and other cellular contents into the surrounding environment. The analysis of cell hemolysis is very important for injectable liposomes because it fully represents the biocompatibility of injectable liposomes. The platform of CD Formulation supports the hemolysis experiments of injectable liposomes and provides systematic analytical services for the development and quality control of injectable liposomes.
Why Conduct Injectable Liposome Hemolysis Testing?
Hemolysis refers to the reaction of hemolysis and red blood cell aggregation caused by drug preparations. The hemolytic reaction includes immune and non-immune hemolysis, which is related to the safety of liposome preparations. Because liposome injection contains phospholipids and is complex in composition, blood cell aggregation can be produced after injection into blood vessels. Adverse reactions such as immune hemolysis and blood circulation dysfunction caused by immune reactions should also be excluded. Therefore, all injections and other drug preparations that may cause immune or non-immune immunoreaction should be subjected to hemolytic tests.
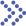
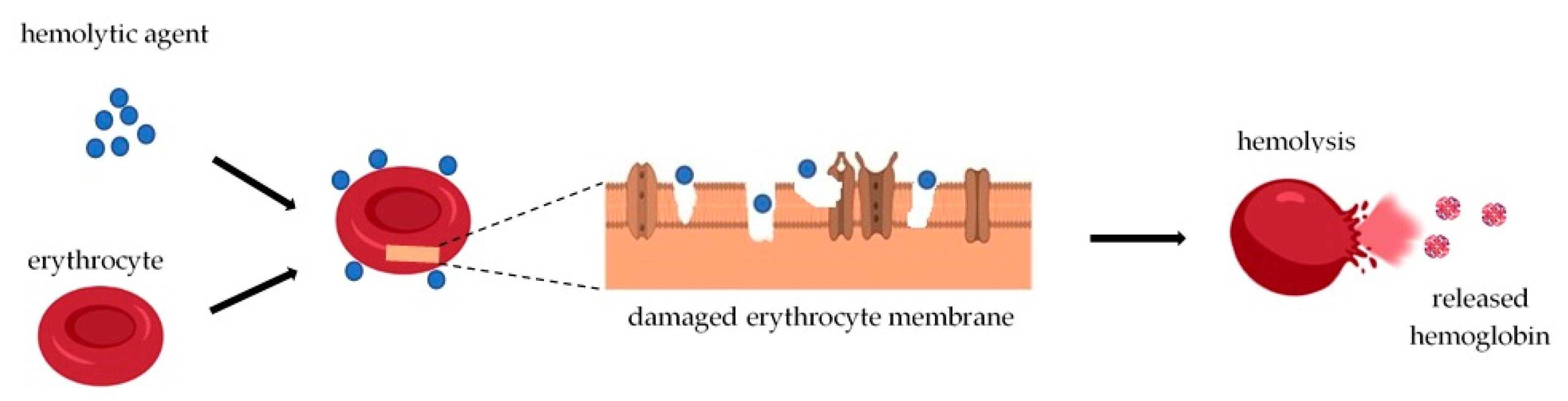 Fig.1 Basic mechanism of hemolysis. (Luna-Vázquez-Gómez R, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Basic mechanism of hemolysis. (Luna-Vázquez-Gómez R, et al., 2021)
Our Services for Injectable Liposome Hemolysis Testing
Hemolysis testing services include in vitro tests and in vivo tests.
In Vitro Hemolytic Testing
The mechanism of the hemolysis reaction is complex. Currently, there is no established preclinical in vivo test for comprehensive evaluation of the hemolytic response to liposomal injections. Therefore, we develop a serial program to investigate the hemolysis of such liposome injections without reference preparations in long-term toxicity studies. During the test, we will focus on the pertinent indicators and signs of hemolytic reaction (such as reticulocyte, red blood cell count, bilirubin, urine protein, nephritis, splenic congestion, etc.). If hemolysis occurs, further study should be conducted. For liposome injections already on the market with the same route of administration, we use the conventional in vitro test tube method to evaluate the hemolysis of the drugs. If the results of the in vitro test tube test are positive, further comparative studies will be conducted with the preparations on the market with the same route of administration, and if necessary, animal tests will be conducted in vivo.
In Vivo Hemolysis Testing
If the results of hemolysis in vitro are positive, we will conduct hemolysis tests in animals or combine them with repeated drug toxicity tests to evaluate the hemolysis effect of drugs in vivo and further explore the hemolysis mechanism according to the requirements of the guiding principles for the development of injection liposomes. In addition, we infer the correlation between hemolysis response in animals and hemolysis response in humans, thus suggesting the risk of clinical trials with an injection of liposomes.
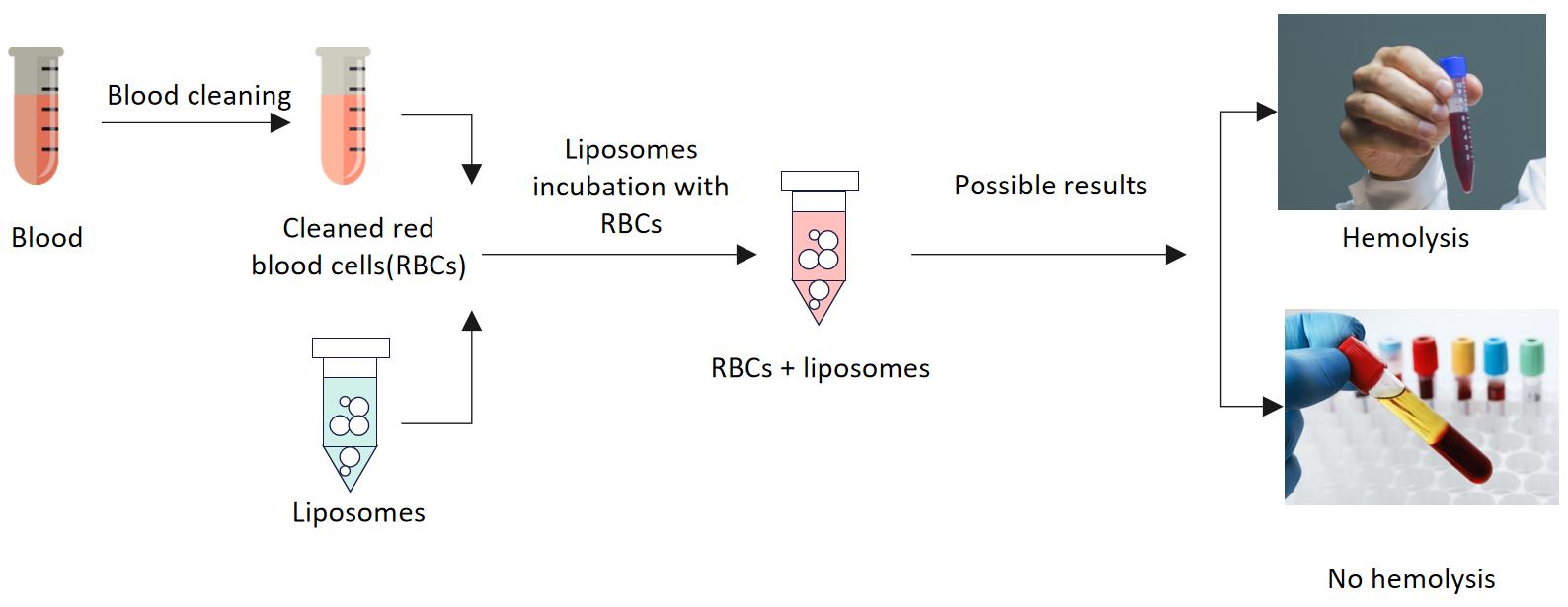 Fig.2 Workflow of injectable liposome hemolysis testing. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 Workflow of injectable liposome hemolysis testing. (CD Formulation)
Our Platforms for Injectable Liposome Hemolysis Testing
We offer professional facilities and technology platforms for customers to meet their needs and requirements.
| Techniques & Platforms |
Detailed Information |
| Equipment |
- Centrifuge tube and centrifugal machine
- 96-well plate
- Ultra-clean workbench
- Biosafety cabinet
- Micropipette
- Enzyme marker
- Incubator
- UV spectrophotometry
|
| Qualitative analysis and quantitative analysis techniques |
- For the qualitative study of hemolysis: After incubation and centrifuge, visual observation of hemolysis. If the solution in the hole is clear red and no cells or a small amount of red blood cells remain at the bottom of the tube, it indicates that hemolysis has occurred. If all red blood cells settle, the supernatant appears colorless and clear, indicating the absence of hemolysis.
- Quantitative study of hemolysis: Carefully absorbing supernatant to detect OD450nm.
|
Our Key Advantages in Injectable Liposome Hemolysis Testing
- Scientific experimental scheme. According to customer requirements, our professional scientists customize scientific and reasonable experimental programs to meet the hemolysis testing requirements of various injectable liposomes.
- Advanced technologies and platforms. Utilizing advanced techniques and platforms to meet the various needs of customers. Our laboratory can meet different requirements of hemolysis experiments in vivo and in vitro to support for liposome drug development.
Published Data
Technology: Toxin removal technique by long-circulating liposomes
Journal: Membranes
IF: 4.2
Published: 2021
Results: The effectiveness of liposomes as bait targets depends on their availability in the host and how quickly they are cleared from the cycle. While pegylation of liposomes may improve their cycle times, little is known about how this modification affects their interaction with anti-virulence factors. To fill this knowledge gap, the authors investigated the ability of conventional and long-circulating liposomes to prevent in vitro hemolysis of red blood cells caused by two potent hemolysins (hemolysin and streptolysin O). Their exploration showed that both conventional and long-circulating liposomes were equally capable of preventing hemolysis caused by streptolysin O. Conversely, pegylation reduces the effectiveness of hemolysin-induced hemolysis and alters the binding kinetics. These findings indicate that the elimination of toxins through long-circulating liposomes is achievable, contingent upon the specific virulence factors under investigation.
 Fig.3 Hemolysis abrogation by increasing amounts of regular liposomes produced by sonication. (Ayllon M, et al., 2021)
Fig.3 Hemolysis abrogation by increasing amounts of regular liposomes produced by sonication. (Ayllon M, et al., 2021)
CD Formulation has formulated a complete program of formulation optimization, drug administration, in vivo sample collection, and quantitative analysis of biological samples from skin, which can efficiently complete experiments, provide accurate and reliable data, and facilitate the drug development process of skin administration. If you need any kind of assistance, please contact us immediately.
References
- Luna-Vázquez-Gómez R, Arellano-García ME, et al. Hemolysis of Human Erythrocytes by Argovit™ AgNPs from Healthy and Diabetic Donors: An In Vitro Study. Materials. 2021; 14(11):2792.
- Ayllon M, Abatchev G, et al. Liposomes Prevent In Vitro Hemolysis Induced by Streptolysin O and Lysenin. Membranes. 2021. 11(5):364.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services


 Fig.1 Basic mechanism of hemolysis. (Luna-Vázquez-Gómez R, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Basic mechanism of hemolysis. (Luna-Vázquez-Gómez R, et al., 2021) Fig.2 Workflow of injectable liposome hemolysis testing. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 Workflow of injectable liposome hemolysis testing. (CD Formulation) Fig.3 Hemolysis abrogation by increasing amounts of regular liposomes produced by sonication. (Ayllon M, et al., 2021)
Fig.3 Hemolysis abrogation by increasing amounts of regular liposomes produced by sonication. (Ayllon M, et al., 2021)