Monoclonal Antibody Preparation Services
InquiryMonoclonal antibodies are antibodies secreted by a single B lymphocyte clone. Since B lymphocytes can only produce a proprietary antibody against one antigenic determinant, they have highly specific physical and chemical properties, single biological activity, and antigen binding specificity and other characteristics. Monoclonal antibody technology is an important tool in modern life science research. It plays an indispensable role in the study of the structure and function of genes and proteins. It is also the fastest growing and most promising development direction in the medical field. CD Formulation will provide you with a cost-effective solution for monoclonal antibody preparation services.
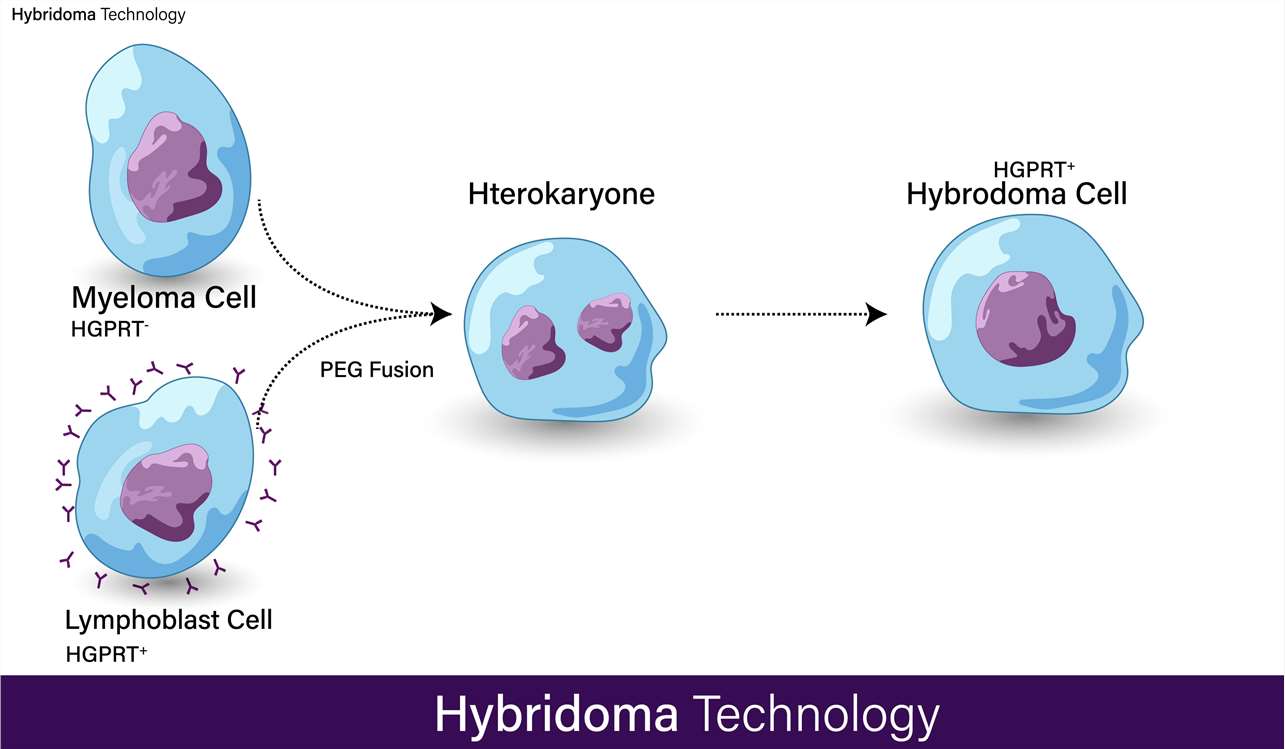 Fig.1 Hybridoma technology. Steps in monoclonal antibody production.
Fig.1 Hybridoma technology. Steps in monoclonal antibody production.
Our Serves
Commonly used methods for preparing monoclonal antibodies: single B cell technology, hybridoma monoclonal antibody technology and phage display technology. We have mastered these technologies and methods to prepare monoclonal antibodies.
Single B Cell Antibody Technology: Single B cell technology is a newly developed technology for rapid preparation of monoclonal antibodies. This technology takes advantage of the fact that each B cell produces only one specific antibody, and can directly amplify the antibody gene from a single B cell to obtain a monoclonal antibody.
Hybridoma monoclonal antibody technology: also known as monoclonal antibody preparation technology. B cells are fused with myeloma cells to obtain hybridoma cells that can produce antibodies and proliferate indefinitely. Monoclonal antibodies can be obtained by culturing the hybridoma cells.
Phage antibody library technology: First, the antibody gene library is amplified from B cells and inserted into the phage genome, so that the antibody fragments are fused with the phage capsid protein and displayed on the surface of the phage to form a phage display antibody library. Multiple rounds of panning are then used to screen out high-affinity antibodies that bind to the target antigen.
Advantages of Monoclonal Antibodies
- Monoclonal antibodies specifically detect a single epitope and are not prone to cross-reaction with other proteins.
- Due to their high specificity, monoclonal antibodies are very suitable for use as primary antibodies in experiments, and the background staining signals they produce are usually significantly lower than polyclonal antibodies.
- Compared with polyclonal antibodies, monoclonal antibodies have very high homogeneity. Under the same experimental conditions, the reproducibility of results between monoclonal antibody experiments is very high, easy to prepare on a large scale, and has high batch stability.
- Thanks to their high specificity, monoclonal antibodies are able to bind antigens extremely efficiently in mixtures of related molecules (for example, during affinity purification).
CD Formulation's Service Advantages
- Multiple antigen types: recombinant proteins, natural proteins, peptides, cells and DNA, etc.
- Mature antibody development platform: rapid immunization, high-efficiency electrofusion, hybridoma serum-free culture and various purification methods, etc.
- Comprehensive antibody verification system: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, etc.
Related Services



 Fig.1 Hybridoma technology. Steps in monoclonal antibody production.
Fig.1 Hybridoma technology. Steps in monoclonal antibody production.

