Transdermal Formulation Pharmacokinetic Study
Inquiry
Pharmacokinetics plays a vital role in understanding how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted in the body. It is essential for optimizing drug design and improving therapeutic efficacy. At CD Formulation, we have established a state-of-the-art pharmacokinetics research center dedicated to transdermal formulations. Our team comprises interdisciplinary experts and scientific leaders who utilize advanced experimental methods and big data analytics to explore the behavior of transdermal formulations in biological systems. We provide transdermal formulation pharmacokinetic study, offering innovative R&D services for pharmaceutical companies and research institutions.
About Transdermal Formulation
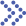
The technical advantages of patches make transdermal drug delivery more and more important, and gradually become the third major drug delivery route after injection and oral administration. However, transdermal drug delivery has limitations. These limitations restrict its market space. One limitation is that the drug effect is slow. It usually takes several hours for the drug to take effect. Another limitation is that many drugs fail to reach effective therapeutic concentrations. In addition, some drugs that are irritating and allergic to the skin themselves should not be designed as transdermal drug delivery formulations.
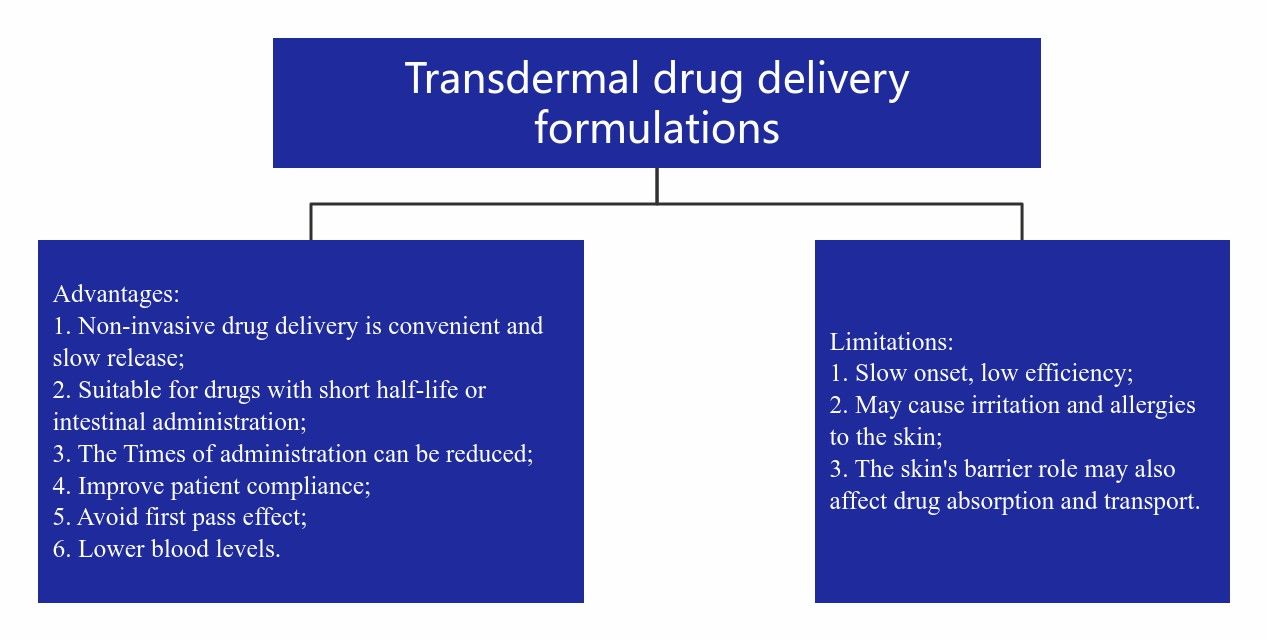 Fig.1 Advantages and limitations of transdermal formulations. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Advantages and limitations of transdermal formulations. (CD Formulation)
Absorption Properties of Transdermal Formulations
The skin has both chemical and physical barriers. Looking at its layers from outside to inside, we find the epidermal layer, which has the stratum corneum and active epidermis. Below that is the dermis, and then the subcutaneous layer. There are three main methods for drugs to infiltrate the body:
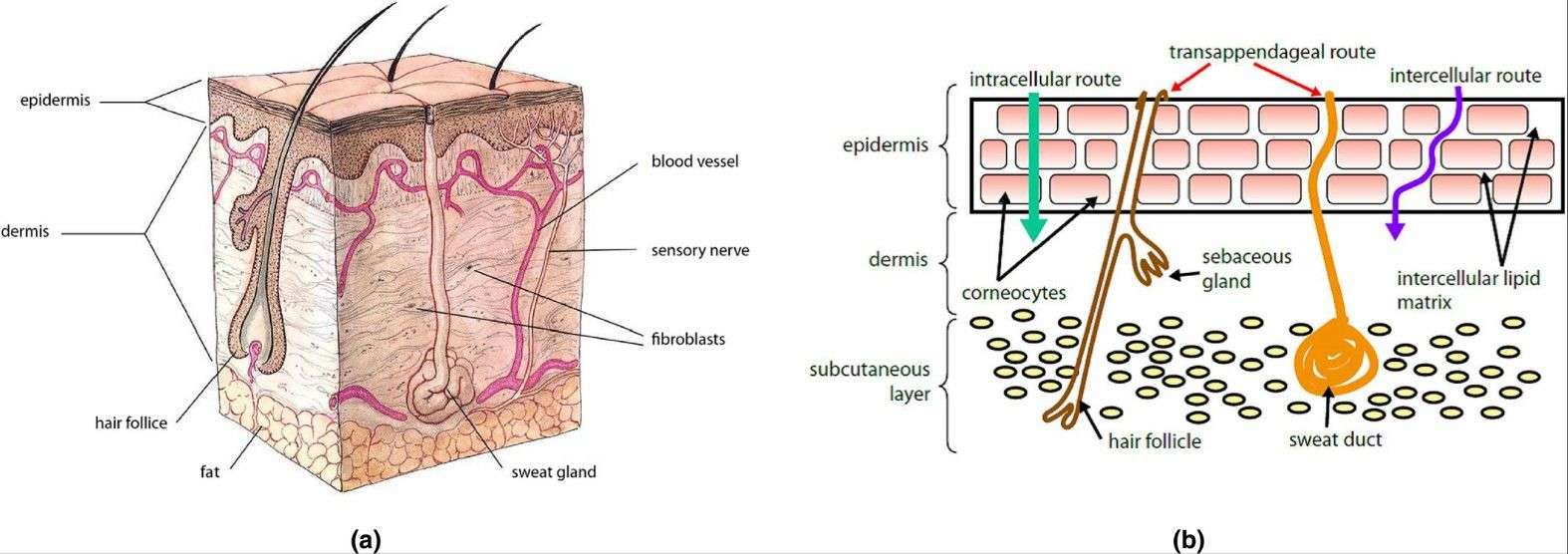 Fig.2 (a) Schematic representation of anatomical structure of the human skin. (b) Routes of percutaneous absorption. (André Luís Morais Ruela, et al. 2016)
Fig.2 (a) Schematic representation of anatomical structure of the human skin. (b) Routes of percutaneous absorption. (André Luís Morais Ruela, et al. 2016)
- Transcellular pathway: Through the keratinocyte through the transcellular pathway and into the skin. Keratinocytes containing highly hydrated keratin provide a hydrophilic environment that facilitates the passage of hydrophilic drugs.
- Intercellular pathway: Diffusion is mainly through the intercellular lipid matrix. This path is generally considered to be the most common route for small, uncharged drugs to pass through the skin.
- It is absorbed through skin appendages.
Percutaneous absorption of drugs mainly depends on the first two pathways, that is, drugs must pass through the stratum corneum before they can be absorbed to reach the target site. However, among all skin layers, the cuticle barrier effect is the strongest, in which the brick wall structure composed of cuticle cells and intercellular lipids blocks the transdermal absorption of drugs, directly or indirectly leading to the low bioavailability of these drugs.
Our Pharmacokinetic Solutions for Transdermal Formulations
In vitro release test (IVRT) and in vitro permeation test (IVPT)
The in vitro experiment is the transdermal process of the artificial membrane or in vitro skin simulation formulation under physiological conditions. By studying the release, transmission amount, and rate of the active ingredients in the external formulation, the clinical effectiveness of the formulation can be reflected to a certain extent, and it is beneficial to investigate the specific influencing factors of drug transdermal absorption. The diffusion cell method is used in the in vitro permeation test.
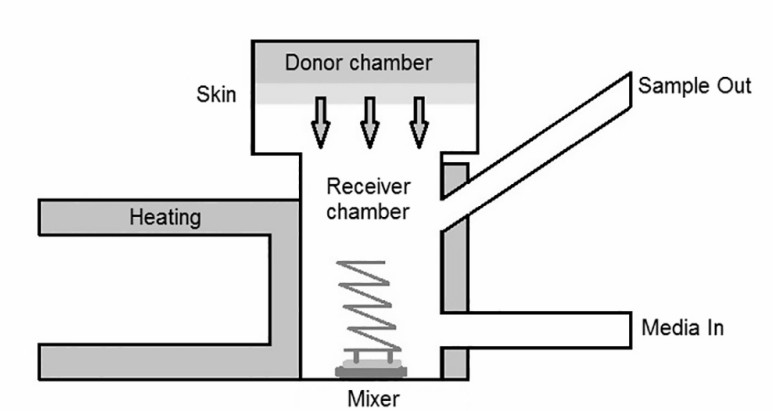 Fig.3 Vertical diffusion cell. (André Luís Morais Ruela, et al.2016)
Fig.3 Vertical diffusion cell. (André Luís Morais Ruela, et al.2016)
In vivo absorption and skin tissue distribution test
We offer skin dosing for large and small animals (mice, rats miniature pigs, etc.), including formulation types such as gels, creams, patches, nanoparticles, and microneedles.
Animal Model Construction
According to the mechanism of drug action, we select the animal disease model of corresponding pathogenesis. CD Formulation provides breeding and modeling services for animals ranging from ordinary rats to immunocompromised mice.
| Species |
Collectable and Analyzable Sample Types |
| Mice |
Plasma, cuticle, epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous tissue, muscle |
| Rats |
Plasma, cuticle, epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous tissue, muscle |
| Miniature pigs |
Plasma, cuticle, epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous tissue, muscle |
Our Pharmacokinetic Analysis
CD Formulation specializes in preclinical pharmacokinetic analysis. Our pharmacokinetic analysis included the following:
| Items |
Specific Information |
| Absorption characteristics |
- Transdermal rate: We assess how quickly a drug enters the body through the skin.
- Skin penetration: The total drug amount absorbed into the body through the skin within a specific time frame is measured.
- Site of absorption: Know where the drug is mainly absorbed.
|
| Distribution characteristics |
- Tissue distribution: Study the distribution of drugs in the skin and various tissues in the body.
- Plasma protein binding rate: The degree to which a drug binds to plasma proteins is assessed.
|
| Metabolic characteristics |
- Metabolites: Identify the metabolites of the drug in the body. Its pharmacological activity and toxicity are also studied.
- Metabolic pathways: Understand the main metabolic pathways of drugs in the body.
|
Why Choose CD Formulation?
- Professional equipment and instruments: We have advanced transdermal absorption experimental equipment. This includes a diffusion cell system, HPLC, and MS. These tools can accurately measure drug permeability and pharmacokinetic parameters in the skin.
- Standardization of experimental methods: We use standardized experimental methods. The Franz diffusion cell method is our industry gold standard for in vitro transdermal experiments. It can simulate the penetration process of drugs on human skin, providing reliable data support.
- Multi-species models: We have various experimental animal models, including rats, rabbits, guinea pigs, and miniature pigs. These animals have good similarities to human skin in anatomical structure and physiological state. They help us predict drug behavior in the human body more accurately.
Publication Data
Technology: Transdermal Formulation Pharmacokinetic Study
Journal: Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences
IF: 0.264
Published: 2016
Results: Bioactive compounds have been successfully administered via cutaneous administration because of advances in the design of topical and transdermal formulations. In vitro and in vivo evaluations of these novel drug delivery systems are necessary to characterize their quality and efficacy. This review covers the most well-known methods for assessing the cutaneous absorption of drugs as an auxiliary tool for pharmaceutical formulation scientists in drug delivery systems. In vitro methods such as skin permeation assays using Franz-type diffusion cells, cutaneous retention, and tape-stripping methods to study the cutaneous penetration of drugs, and in vivo evaluations as pre-clinical pharmacokinetic studies in animal models are discussed. Alternative approaches to cutaneous microdialysis are also covered. Recent advances in research on skin absorption of drugs and the effect of skin absorption enhancers, as investigated using confocal laser scanning microscopy, Raman confocal microscopy, and attenuated total reflectance Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, are reviewed.
Through comprehensive pharmacokinetic studies, CD Formulation accurately simulates drug penetration across skin layers and systemic distribution. Our services include evaluating the effects of various formulations and excipients on drug release rates and bioavailability. These precise evaluations enhance drug efficacy and safety while minimizing potential side effects. For tailored solutions to your research needs, contact us, and our team will respond within three business days to assist you.
References
- André Luís Morais Ruela, Aline Gravinez Perissinato, et al. Evaluation of skin absorption of drugs from topical and transdermal formulations. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2016. vol. 52, n. 3.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services


 Fig.1 Advantages and limitations of transdermal formulations. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Advantages and limitations of transdermal formulations. (CD Formulation) Fig.2 (a) Schematic representation of anatomical structure of the human skin. (b) Routes of percutaneous absorption. (André Luís Morais Ruela, et al. 2016)
Fig.2 (a) Schematic representation of anatomical structure of the human skin. (b) Routes of percutaneous absorption. (André Luís Morais Ruela, et al. 2016) Fig.3 Vertical diffusion cell. (André Luís Morais Ruela, et al.2016)
Fig.3 Vertical diffusion cell. (André Luís Morais Ruela, et al.2016)