Transdermal Delivery - CD Formulation
Call Us:
- Home
- Services
- Transdermal Formulation Development
- Gel Transdermal Formulation Development
- Cream Transdermal Formulation Development
- Ointment Transdermal Formulation Development
- Spray Transdermal Formulation Development
- Transdermal Patch Development
- Single-Layer Drug-In-Adhesive Transdermal Patch Development
- Multi-Layer Drug-In-Adhesive Transdermal Patch Development
- Matrix Transdermal Patch Development
- Reservoir Transdermal Patch Development
- Vapor Transdermal Patch Development
- Active Gel Transdermal Patch Development
- Controlled Release Transdermal Patch Development
- Transdermal Microneedle Patch Development
- Nano Transdermal Patch Development
- Nanofiber/Microfiber Transdermal Patch Development
- Microemulsion/Nanoemulsion Transdermal Patch Development
- Metal Nano Transdermal Patch Development
- Solid Lipid Nano Transdermal Patch Development
- Polymer Nano Transdermal Patch Development
- Vesicle Nano Transdermal Patch Development
- Nano Gel Transdermal Patch Development
- Liposome Transdermal Patch Development
- Nanocrystal Transdermal Patch Development
- Ethosomes Transdermal Patch Development
- Peptide Transdermal Formulation Development
- Protein Transdermal Formulation Development
- Nucleic Acid Transdermal Formulation Development
- Transdermal Formulation Analysis and Testing Services
- Conventional Characterization for Transdermal Formulation
- Transdermal Formulation Appearance Analysis
- Transdermal Formulation Rheological Properties Analysis
- Transdermal Formulation Weight Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Thickness Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Folding Endurance Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Moisture Absorption Rate Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Moisture Content Percentage Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Surface pH Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Swelling Index Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Tensile Strength Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Drug Content and Excipient Content Assays
- Transdermal Formulation Drug Content Uniformity Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Crystal Structure Analysis
- Transdermal Formulation Peel Adhesion Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Shear Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Release Liner Removal Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Tack Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Cold Flow Evaluation
- Transdermal Formulation Residual Drug Analysis
- In Vitro Penetration Testing of Transdermal Formulation
- In Vitro Release Testing of Transdermal Formulation
- Nanoproperty Characterization for Transdermal Formulation
- Quality Control and Release Testing for Transdermal Formulation
- Transdermal Formulation API and Excipient Characterization
- Transdermal Formulation Analytical Method Development and Validation
- Transdermal Formulation Analytical Method Transfer
- Transdermal Formulation Batch Release Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Residual Solvents Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Extractables and Leachables Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Elemental Impurities Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Impurity Analysis
- Transdermal Formulation Stability Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Temperature Cycling Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Forced Degradation Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Packaging Integrity Testing
- Transdermal Formulation Bioequivalence Evaluation
- Conventional Characterization for Transdermal Formulation
- Biological Evaluation for Transdermal Formulation
- GMP Manufacturing Services of Transdermal Formulation
- Transdermal Formulation Development
- Technologies
- Applications
- Order Online
- Company
- Inquiry

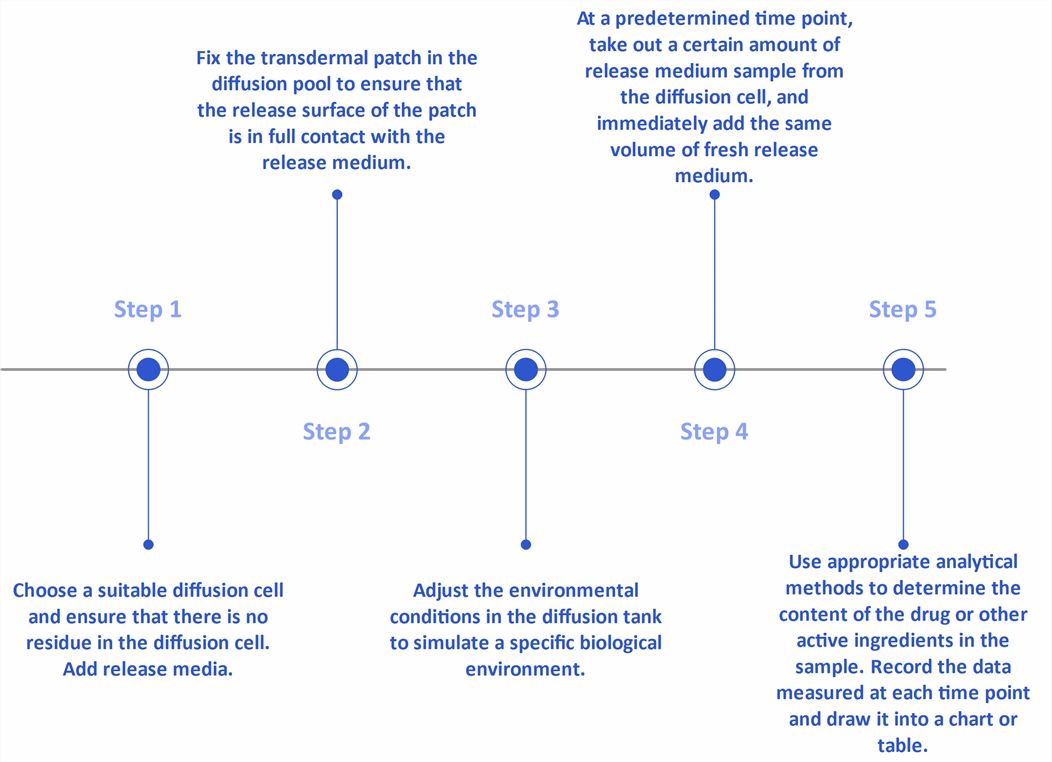 Fig.1 Flow chart of in vitro release testing (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Flow chart of in vitro release testing (CD Formulation)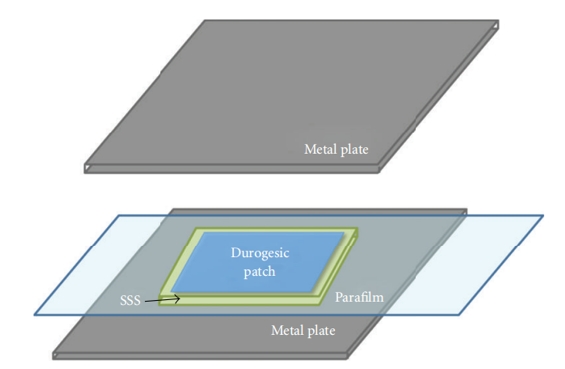 Fig.2 Illustration of the SSS method setup (Bing Cai, et al., 2012)
Fig.2 Illustration of the SSS method setup (Bing Cai, et al., 2012)