Therapeutic Proteins & Peptides - CD Formulation
Call Us:
- Home
- Services
- Therapeutic Peptide Synthesis and Production
- Therapeutic Peptide Chemical Synthesis
- Therapeutic Peptide Biosynthesis
- Custom Specialty Peptides Synthesis
- Multiple Antigenic Peptide (MAP) Synthesis
- Cyclic Peptide Synthesis
- Stapled Peptide Synthesis
- Long Peptide Synthesis
- Cell Penetrating Peptide (CPP) Synthesis
- Linear Peptide Synthesis
- Peptoid Synthesis
- Disulfide-Rich Peptide (DSR) Synthesis
- Peptide Antigens Synthesis
- D-Amino Acid-Containing Peptide Synthesis
- Bicyclic Peptide Synthesis
- Custom Modified Peptide Synthesis
- C-Terminal Modified Peptide Synthesis
- N-Terminal Modified Peptide Synthesis
- Unusual & Non-natural Amino Acids Modified Peptide Synthesis
- Phosphorylated Peptide Synthesis
- Prenylated Peptide Synthesis
- Sulphated Peptide Synthesis
- PEGylated Peptide Synthesis
- Biotinylated Peptide Synthesis
- Glycosylated Peptide Synthesis
- Acetylated Peptide Synthesis
- Amidated Peptide Synthesis
- Methylated Peptide Synthesis
- Peptide Dimer Synthesis
- Fatty Acid Modified Peptide Synthesis
- Custom Labeled & Conjugated Peptide Synthesis
- Enzyme Labeled Peptide Synthesis
- Isotope Labeled Peptide Synthesis
- Imaging Agent Labeled Peptide Synthesis
- Quenched Fluorescent Peptide (FRET Peptide) Synthesis
- Fluorescence Labeled Peptide Synthesis
- Carrier Protein-Conjugated Peptide Synthesis
- DNA-Conjugated Peptide Synthesis
- RNA-Conjugated Peptide Synthesis
- siRNA-Conjugated Peptide Synthesis
- Nanoparticle-Conjugated Peptide Synthesis
- Gold Nanoparticle-Conjugated Peptide Synthesis
- Therapeutic Peptide Library
- Therapeutic Peptide Array
- Large Scale Therapeutic Peptide Synthesis
- Neoantigen Peptide Service
- Therapeutic Protein Production & Engineering
- Therapeutic Protein Production
- Yeast Expression System-Based Therapeutic Protein Production
- Baculovirus-Insect Cell Expression System-Based Therapeutic Protein Production
- Escherichia Coli Expression System-Based Therapeutic Protein Production
- Mammalian Cell Expression System-Based Therapeutic Protein Production
- Glyco-Engineering-Based Therapeutic Protein Production
- Eukaryotic Algae Engineering-Based Therapeutic Protein Production
- Therapeutic Protein Engineering
- Therapeutic Protein Production
- Therapeutic Proteins & Peptides Process Development
- Cell Line Development for Therapeutic Proteins & Peptides
- Therapeutic Proteins & Peptides Upstream Cell Culture Process Development
- Therapeutic Proteins & Peptides Upstream Fermentation Process Development
- Therapeutic Peptides Upstream Synthetic Process Development
- Therapeutic Proteins Downstream Purification Process Development
- Therapeutic Peptides Downstream Purification & Isolation Process Development
- Therapeutic Proteins & Peptides Formulation Process Development
- Therapeutic Proteins & Peptides Process Characterization and Process Validation
- Therapeutic Proteins & Peptides Production Process Scale-up
- Therapeutic Proteins & Peptides Technology Transfer
- Proteins & Peptides Formulation Research and Development
- Proteins & Peptides Pre-formulation Studies
- Proteins & Peptides Formulation Development
- Proteins & Peptides Liquid Formulation Development
- Proteins & Peptides Sterile Formulation Development
- Proteins & Peptides Buffer-free Lyophilized Formulation Development
- Proteins & Peptides High-concentration Formulation Development
- Protein & Peptide Lyophilization Formulation Development
- Proteins & Peptides Spray Drying Formulation Development
- Proteins & Peptides Drug Delivery System Development
- Proteins & Peptides Oral Delivery System Development
- Proteins & Peptides Transdermal Delivery System Development
- Proteins & Peptides Injectable Delivery System Development
- Proteins & Peptides Inhaled Delivery System Development
- Proteins & Peptides Intranasal Delivery System Development
- Proteins & Peptides Innovative Delivery System Delivery Development
- Proteins & Peptides Liposomal Delivery System Development
- Proteins & Peptides Microneedle Delivery System Development
- Proteins & Peptides Microspheres Delivery System Development
- Proteins & Peptides Nanoparticles Delivery System Development
- Proteins & Peptides Microemulsion Delivery System Development
- Proteins & Peptides Hydrogels Delivery System Development
- Packaging Material Screening and Testing Services for Protein & Peptide Formulation
- Proteins & Peptides Characterization and Analytical Testing Services
- Therapeutic Proteins & Peptides Characterization
- Proteins & Peptides Primary Structure Characterization
- Higher-Order Structures (HOS) Proteins & Peptides Characterization
- Peptide Mapping Analysis
- Proteins & Peptides Particle and Aggregation Characterization
- Proteins & Peptides Viscosity Analysis
- Proteins & Peptides Quantitative Analysis
- Proteins & Peptides Sequencing Analysis
- Amino Acid Analysis
- Post-translational Modifications (PTMs) Analysis
- Proteins & Peptides Stability and Thermal Denaturation Analysis
- Proteins & Peptides Crystal Structure Elucidation
- Proteins & Peptides Druggability Assessment
- Proteins & Peptides Formulation Analysis
- Proteins & Peptides Quality Control and Release Testing
- Proteins & Peptides Analytical Method Development
- Proteins & Peptides Analytical Method Validation and Transfer
- Proteins & Peptides Product-related Impurity Analysis
- Proteins & Peptides Process-related Impurity Analysis
- Proteins & Peptides Elemental-related Impurity Analysis
- Proteins & Peptides Residual Solvent and Volatile Impurity Analysis
- Proteins & Peptides Extractables and Leachables Analysis
- Proteins & Peptides Residual Host Cell DNA Testing
- Proteins & Peptides Residual Host Cell Protein (HCP) Analysis
- Virus Clearance Testing
- Cell Line Characterization
- Proteins & Peptides Biosimilarity Studies
- Proteins & Peptides Comparability Studies
- Proteins & Peptides Stability Testing
- Proteins & Peptides Forced Degradation Studies
- Proteins & Peptides Batch-release Testing
- Proteins & Peptides Biological Evaluation
- Therapeutic Proteins & Peptides Characterization
- Proteins & Peptides cGMP Manufacturing
- Therapeutic Peptide Synthesis and Production
- Technologies
- Prtoein & Peptide Characterization Technologies
- Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Technology
- Differential Scanning Fluorescence (DSF) Technology
- Analytical Ultracentrifugation (AUC) Technology
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Technology
- Asymmetrical Flow Field-Flow Fractionation (AF4) Technology
- Hollow Fiber Flow-Field-Flow Fractionation (HF5) Technology
- Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) Technology
- Micro-Flow Imaging (MFI) Technology
- Multi-angle Light Scattering (MALS) Technology
- Multi-angle Dynamic Light Scattering (MADLS) Technology
- X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Technology
- UV-Vis Spectrophotometry Technology
- Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy Technology
- Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy Technology
- Cryo-electron Microscopy (cryo-EM) Technology
- Small-angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) Technology
- Mass Spectrometry (MS)-Based Sequencing Technology
- Hydrogen-Deuterium Exchange Mass Spectrometry (HDX-MS) Technology
- Isoelectric Focusing (IEF) Technology
- Capillary Isoelectric Focusing (cIEF) Technology
- Capillary Zone Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry (CZE-MS) Technology
- SDS-PAGE Technology
- Capillary Gel Electrophoresis (CGE) Technology
- Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Technology
- Viral Titers Determination Using TCID50
- Liquid Chromatography (LC) Technologies
- Ion Exchange Chromatography (IEX) Technology
- Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (HIC) Technology
- Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) Technology
- Affinity Chromatography (AC) Technology
- Reversed-phase Chromatography (RP-HPLC / RP-UPLC) Technology
- Mixed Mode Chromatography (MMC) Technology
- Fast Protein Liquid Chromatography (FPLC) Technology
- Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF) Technology
- Membrane Filtration Technology
- Protein Expression Technologies
- Peptide Synthesis Technologies
- Prtoein & Peptide Characterization Technologies
- Online Order
- Company
- Inquiry

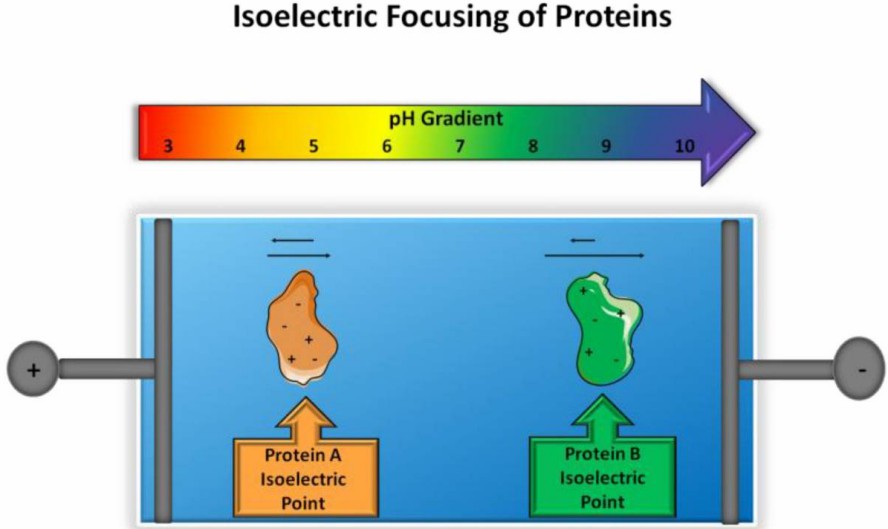 Fig. 1 Principle of isoelectric focusing. (Pergande MR, et al., 2017)
Fig. 1 Principle of isoelectric focusing. (Pergande MR, et al., 2017)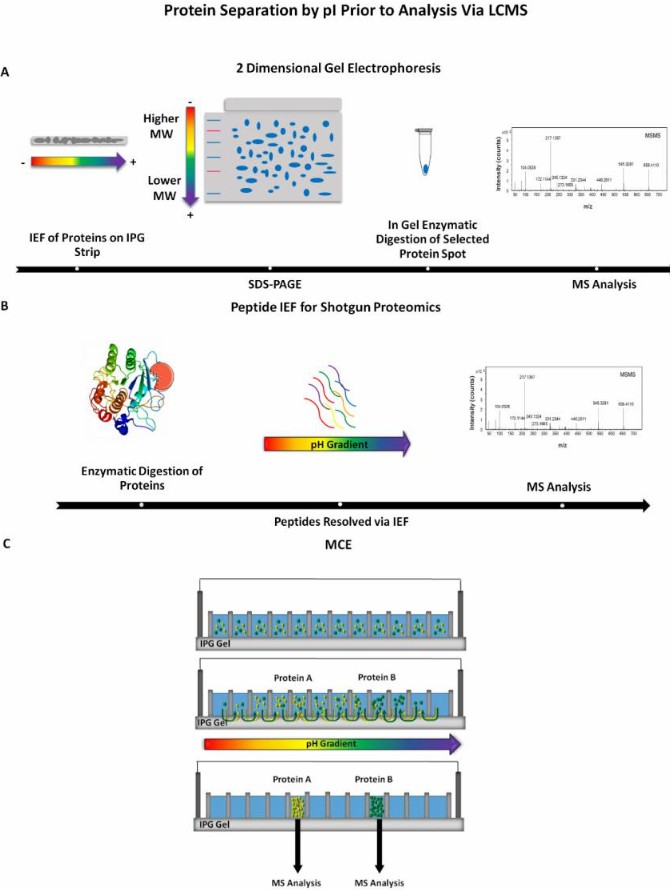 Fig.2 Examples of isoelectric focusing (IEF) methods incorporated prior to mass spectrometry (MS) detection. (Pergande MR, et al., 2017)
Fig.2 Examples of isoelectric focusing (IEF) methods incorporated prior to mass spectrometry (MS) detection. (Pergande MR, et al., 2017)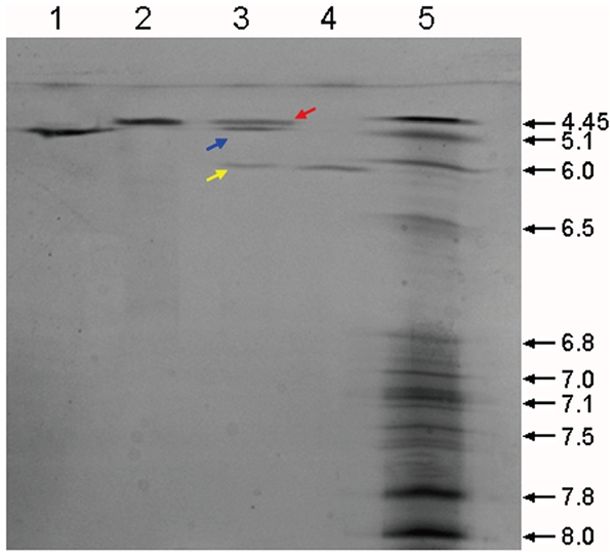 Fig. 3 Isoelectric focusing electrophoresis analysis of HMG. (Huang YS, et al., 2014)
Fig. 3 Isoelectric focusing electrophoresis analysis of HMG. (Huang YS, et al., 2014)