Self-emulsifying Drug Delivery System for Nanoformulations
Inquiry
Self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) is a formulation consisting of an oil phase, a surfactant, and a co-surfactant, designed to improve the solubility of poorly soluble drugs, enhance drug absorption rates and extents, and ultimately enhance bioavailability. This innovative lipophilic drug carrier shows promising potential in drug delivery. Leveraging our lipid drug delivery system platform, CD Formulation offers tailored self-emulsifying drug delivery system development services for nanoformulations to cater to diverse customer needs.
Advantages of Self-emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems
Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems include simple oil solutions, macroemulsions, multiple emulsions, and dry emulsions, as well as more complex self-emulsifying, microemulsifying, or nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems have the following significant advantages.
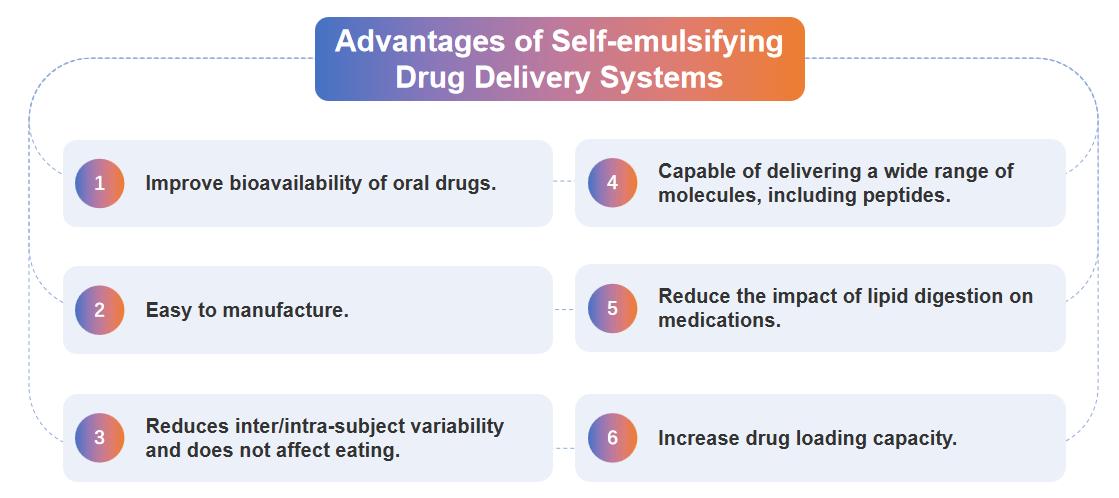 Fig.1 Advantages of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Advantages of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. (CD Formulation)
Mechanism of Self-emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems
Self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) or self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) consists of lipophilic or hydrophobic medications, an oil phase, surfactant, and co-surfactant. When exposed to the gastrointestinal peristalsis environment, it undergoes spontaneous emulsification to create an oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion with particle sizes smaller than 500 nm. The development of SEDDS is based on the drug lipid release system concept, where a blend of drugs dissolved in multiple excipients (such as triglycerides, surfactants, or co-emulsifiers) remains dissolved during gastrointestinal digestion, thereby enhancing the bioavailability of hydrophobic drugs.
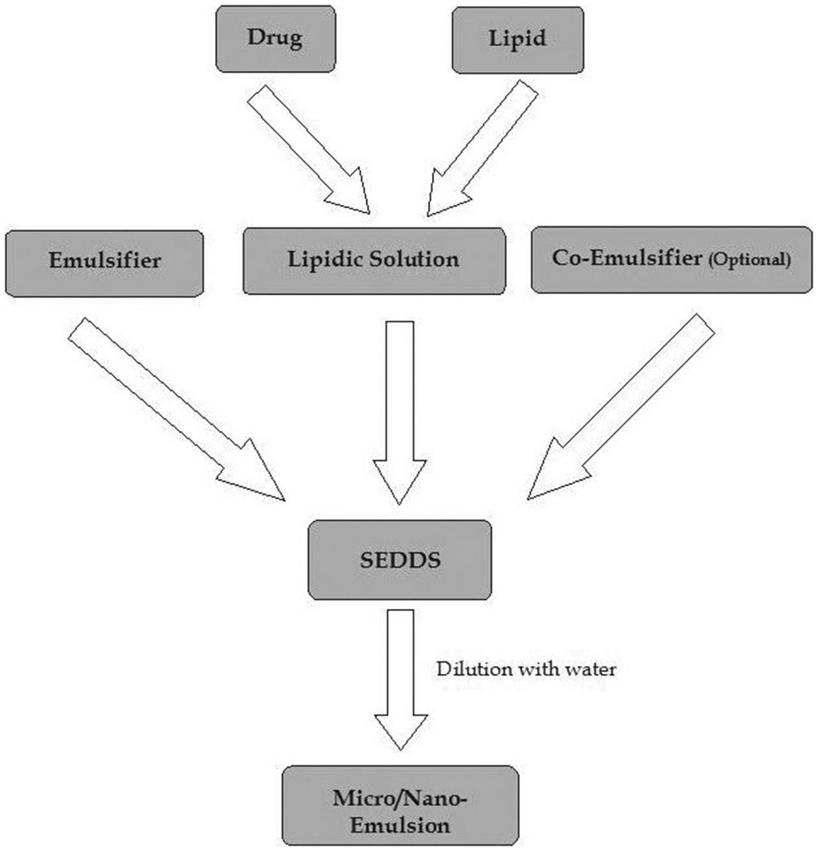 Fig.2 Mechanism of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. (Ahmad Salawi. 2022)
Fig.2 Mechanism of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. (Ahmad Salawi. 2022)
Our Strategies for Self-emulsifying Drug Delivery System Development
Based on the lipid drug delivery platform, CD Formulation has designed a specialized self-emulsifying drug delivery system development program. Through formulation screening optimization, quality evaluation, and new formulation research, it is expected to further promote the application of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems.
Formulation Screening and Optimization
The basic principle of formula design for self-emulsifying drug delivery systems is to select simple, effective, small amount, and low-toxic excipients to prepare the formula, under the premise of ensuring that the preparation can dissolve and emulsify the drug. The self-emulsification process is related to the properties and concentration of surfactant (SA), cosurfactant (CoSA), oil/SA ratio, SA/CoSA ratio, etc.
We have developed the following formulation optimization methods, including the pseudo-three phase diagram method, orthogonal experiment, response surface analysis method, etc.
Pseudo-three phase diagram method: The pseudo three-phase diagram replaces the pure substance in the ternary phase diagram with the mixture represented by the three vertices to determine the effective emulsion formation area. It is a basic tool for studying the microemulsion formation area.
Orthogonal experiment: We mostly apply the multi-factor and multi-level orthogonal experiment design method in the selection and optimization of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems.
Response surface analysis method (RSM): The most commonly used response surface analysis methods are central composite design and Box-Behnken design. We can use this method to analyze the interaction between various factors. This method is effective in experimental design and result expression and has good predictive ability.
Simplex grid method: We use the spatial graphic elimination method to optimize the prescription by influencing the indicators through the mutual constraints of the quantities between factors.
In addition, we have also developed other methods for formula optimization, such as d-optimal mixture design, quantitative structure-activity relationship, high-throughput screening, etc.
Quality Evaluation of Self-emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems
The quality evaluation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems mainly includes characterization indicators and drug release studies.
Characterization indicators: The characterization indicators of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems mainly include particle size, zeta potential, transmittance, drug loading, self-emulsification efficiency, stability, and oral bioavailability.
Drug release studies: Drug release studies of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems include in vitro and in vivo methods.
In vitro methods are used to study the mechanism of SEDDS and predict in vivo drug release behavior, including lipolysis, dialysis, and reverse dialysis.
In vivo method is to evaluate the degree of improvement in bioavailability by measuring pharmacokinetic parameters.
Furthermore, novel formulation technologies have been investigated for self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. These include solid self-microemulsification, supersaturated self-microemulsion, positively charged self-microemulsion, self-double emulsification drug delivery system, phospholipid complex self-microemulsion, and compound self-microemulsion.
Our Methods for Constructing Self-emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems
Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) consist of a blend of oils, surfactants, and/or cosolvents that can emulsify without external agitation in the watery conditions of the gastrointestinal tract. These formulations enhance the oral bioavailability of drugs by enhancing the apparent solubility of highly hydrophobic compounds and mitigating metabolism or efflux mechanisms. Leveraging our innovative design approach, CD Formulation is proficient in developing self-emulsifying drug delivery systems through various preparation techniques.
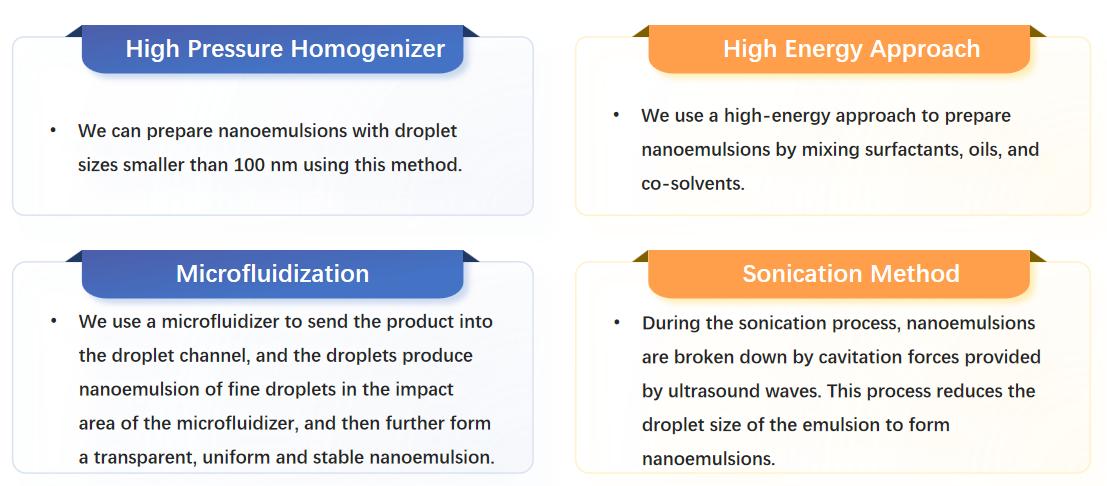 Fig.3 Our Methods of the preparation of Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. (CD Formulation)
Fig.3 Our Methods of the preparation of Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. (CD Formulation)
Highlights of Our Self-emulsifying Drug Delivery System Development
- With the help of our advanced and mature lipid drug delivery system platform, we have accumulated rich experience in the fabrication of Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. We can customize high-quality self-emulsifying drug delivery systems for our customers.
- We can provide customers with self-emulsifying drug delivery system services for nanoformulations, covering formulation screening and optimization and quality evaluation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems.
- We have also explored new formulation technologies for self-emulsifying drug delivery systems to meet customers' different needs, such as solid self-microemulsification, supersaturated self-microemulsion, positively charged self-microemulsion, self-double emulsification drug delivery system, phospholipid complex self-microemulsion, and compound self-microemulsion.
Custom Nanoemulsion Development Services
CD Formulation has extensive research on the development of targeting nanoformulation formulations. Based on our advanced targeted nanodelivery system, we provide customized formulation development services for targeting nanoformulations. Our professional team has conducted in-depth research on targeting nanoformulation delivery systems and applications and can develop targeting nanoformulations for different purposes, thereby promoting the clinical transformation and application of targeting nanoformulations.
Nanoemulsion Development for Nanomedicine
Using our advanced nanoemulsion technology and self-emulsifying drug delivery system, we can quickly develop and customize nanoemulsions to meet diverse customer needs. By thoroughly understanding the unique properties, preparation methods, and applications of nanoemulsions, we offer professional customization solutions.
Published Data
Technology: Integrated in silico formulation design of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems
Journal: Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B
IF: 14.5
Published: 2021
Results:
To integrate computational and experimental methods to rationally design self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) formulas, the authors achieved rational SEDDS formulation design by combining machine learning, central composite design, molecular modeling, and experimental methods. Research shows that integrated computer methods can reduce traditional drug formulation design work and can bring new ideas to future drug formulation design.
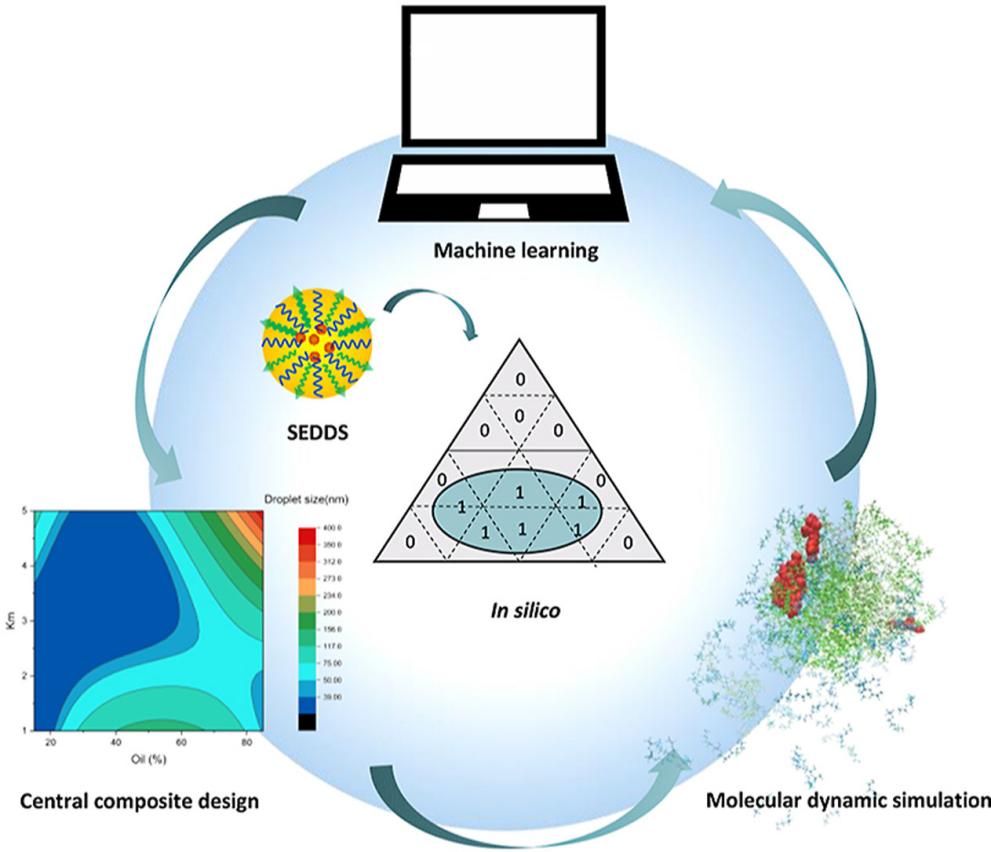 Fig.4 Integrated in silico formulation design of selfemulsifying drug delivery systems. (Haoshi Gao, et al. 2021)
Fig.4 Integrated in silico formulation design of selfemulsifying drug delivery systems. (Haoshi Gao, et al. 2021)
With the continuous deepening of research on self-emulsifying drug delivery systems, the emergence of natural emulsifiers with mild properties, good stability, low irritation, and high safety will accelerate the development of this dosage form. As a professional services company in nanoformulation research, CD Formulation is keen on exploring and further optimizing the formulation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. If you require our self-emulsifying drug delivery system services, please kindly contact us for in-depth discussions.
References
- Ahmad Salawi. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: a novel approach to deliver drugs. Drug Delivery. 2022,29(1):1811-1823.
- Haoshi Gao, Haoyue Jia, Jie Dong, et al. Integrated in silico formulation design of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. 2021, 11(11):3585-3594.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services


 Fig.1 Advantages of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Advantages of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. (CD Formulation) Fig.2 Mechanism of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. (Ahmad Salawi. 2022)
Fig.2 Mechanism of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. (Ahmad Salawi. 2022) Fig.3 Our Methods of the preparation of Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. (CD Formulation)
Fig.3 Our Methods of the preparation of Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. (CD Formulation) Fig.4 Integrated in silico formulation design of selfemulsifying drug delivery systems. (Haoshi Gao, et al. 2021)
Fig.4 Integrated in silico formulation design of selfemulsifying drug delivery systems. (Haoshi Gao, et al. 2021)