Oral Nanoformulation Development Based on Organic Nanomaterials
Inquiry
Organic nanomaterials can be used as candidates for oral delivery carriers. They have various advantages such as biodegradability, biocompatibility, non-immunogenicity, extended delivery, and easy modification, and have been widely used in multiple oral nanoformulations. CD Formulation can provide you with formulation development services for organic nanomaterial-based oral nanoformulation to meet different requirements.
Our Services for Organic Nanomaterial-Based Oral Nanoformulation Development
We offer comprehensive, innovative, and timely solutions and help you quickly develop the organic nanomaterial-based oral nanoformulations. Our technical team has many years of practical experience in the development of the following organic nanomaterial-based oral nanoformulations. And we support all phases of the formulation development and even commercialization process of the organic nanomaterial-based oral nanofomulations through our extensive technical expertise in the organic nanocarrier technology.
Polymeric Nanoparticle-Based Oral Nanoformulation
Polymers are often used as delivery vehicles for oral nanoformulations due to their modifiable groups (such as carboxyl, hydroxyl, amino, etc.).
Micelle-Based Oral Nanoformulation
Micelles are amphiphilic colloidal structures with particle sizes ranging from 5 to 100 nm. Micelles are used as drug carriers in oral nanoformulations because they can carry lipophilic drugs within their core, while the micelle surface binds polar molecules. Polymer micelles are used therapeutically because they provide better solubility, thereby improving intestinal permeability of the micelles.
Liposome-Based Oral Nanoformulation
Liposomes, with a size range of 100-500 nm, are considered the most used nanocarriers for various potentially active hydrophobic and hydrophilic molecules because of their high biocompatibility, biodegradability, and low immunogenicity. Liposomes have also been shown to enhance drug solubility and controlled distribution, as well as their surface modification capabilities for targeting, prolonged and sustained release. Therefore, liposomes as nanocarrier materials have also been widely used in oral nanoformulations.
Dendrimer-Based Oral Nanoformulation
Dendrimers have open cavities and high surface charge densities, which facilitate their customization into oral nanoformulations by incorporating targeting molecules, enhancers, or stabilizers.
Metal-Organic Framework-Based Oral Nanoformulation
Due to the unique crystalline porous structure of metal organic framework (MOF), MOF has emerged as a promising nanomaterial candidate in oral nanoformulation.
Protein-Polymer Complex-Based Oral Nanoformulation
Protein polymers are naturally occurring macromolecules derived from plants and animals, making them an easily available renewable resource. In addition to being biodegradable and tunable, nanoparticles made from protein-based materials are often bio-compatible and easy to process. There are several different protein polymers suitable for nanoparticle-based drug delivery, each with its own unique structure-function relationship. Therefore, protein polymers have been widely used as nanomaterials in oral nanoformulation.
Our Strategies for Oral Nanoformulation Development Based on Organic Nanomaterials
Common dosage forms of oral nanoformulations include nanosuspensions, nanoparticles, tablets, capsules, nanoemulsions, etc. Typically, nanosuspensions can be either final oral nanoformulations or formulation intermediates for final oral nanoformulations. CD Formulation relies on our advanced design concept to use different preparation methods according to different organic nanomaterial-based oral nanoformulation properties to prepare organic carriers that meet your requirements. Our solutions for organic nanomaterial-based oral nanoformulations are as follows.
Fabrication of Nanosuspensions
There are various methods for preparing nanosupensions, including grinding method, high pressure homogeneous method, emulsification method, etc. If nanosuspensions are final oral nanoformulations, our fabrication of nanosuspensions is used by nanocrystal technology. If nanosuspensions are formulation intermediates for final oral nanoformulations, it is just the first step of the fabrication of oral nanoformulations.
Fabrication of Organic Nanoparticles
We will use spray drying and freeze-drying techniques to solidify the nanosuspension into nanoparticles.
Fabrication of Organic Nanomaterial-Based Oral Nanoformulation
- If the dosage form is capsule, we will use our advanced equipment to prepare the nanoparticles together with other excipients into pellets, and then fill the pellets into capsules.
- If the dosage form is nanoparticle, we mix the nanoparticles with other excipients for granulation, then dry, granulate, and mix to prepare oral nanoparticles.
- If the dosage form is a tablet, we mix the nanoparticles with other excipients and granulate them, then dry, granulate, mix, and compress them into oral tablets.
Our Analytical Capabilities for Organic Nanomaterial-Based Oral Nanoformulation
The physiochemical stability of the organic nanomaterial-based oral nanoformulations during the fabrication and storage can be determined by monitoring changes in particle size, zeta potential, drug content, appearance, and In vitro dissolution evaluation of organic nanomaterial-based oral nanoformulation, ect. We can provide you with the following analysis and characterization of organic nanomaterial-based oral nanoformulation including:
- Particle Size
- Zeta Potential
- API Assay
- In Vitro Dissolution Evaluation
- Stability
Why Choose Us to Develop Organic Nanomaterial-Based Oral Nanoformulations?
- Relying on our advanced instruments and equipment, such as rapid nanomedicine preparation system, we can provide organic nanomaterial-based oral nanformulation development services for polymeric nanoparticle-based, micelle-based, liposome-based, dendrimer-based, metal-organic framework-based, and protein-polymer complex-based oral nanoformulation.
- Our professional and technical personnel have accumulated rich experience in the preparation of oral nanoformulations and can quickly respond to your specific requirements and design our professional research and development proposals and oral nanoformulation preparation strategies based on organic nanomaterials according to your requirements.
- We also highly focused on quality control research and control of nano-preparations based on organic materials. The basic monitoring indicators include particle size, zeta potential, API assay, in vitro dissolution evaluation and stability.
Published Data
Technology: Non-physical technologies
Journal: Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology
IF: 46.802
Published: 2022
Results:
The authors discussed emerging technologies that seek to address remaining obstacles to successful gastrointestinal-based drug delivery. Scientists are developing non-physical technologies such as molecular modifications, nanoparticles, microparticles, large patches and devices that can be used clinically. At the molecular level, stability is improved by modifying drug molecules. For example, the diameter of nanoparticles is usually 1-100 nm, up to several hundred nanometers. These particles encapsulate the drug via excipients. Excipients are biodegradable or biocompatible polymers, lipids, surfactants, and mixtures thereof. Nanoparticles are more stable and absorbent, allowing for targeted drug delivery through the addition of surface ligands. Oral semaglutide combined with enhancer molecules (SNAC) to prepare pharmaceutical formulations is a typical example.
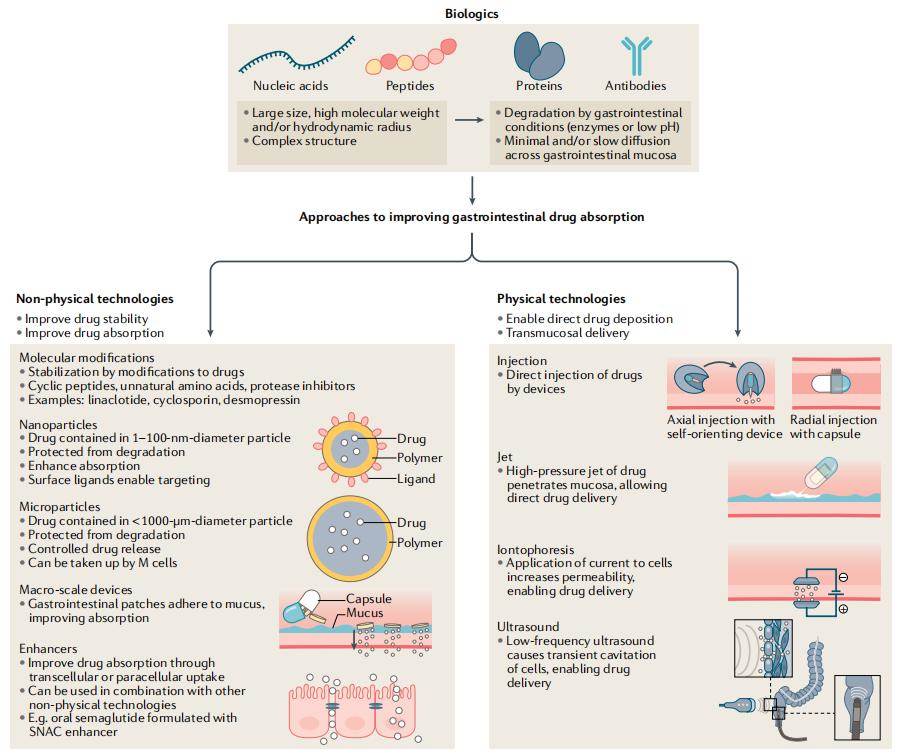 Fig.1 Emerging technologies for gastrointestinal delivery of biologics. (Jacqueline N. Chu, et al,2022)
Fig.1 Emerging technologies for gastrointestinal delivery of biologics. (Jacqueline N. Chu, et al,2022)
CD Formulation, as a professional research service company providing nanoformulation development services, can design and prepare different oral nanoformulations based on organic materials to meet the different needs of customers. If you have a requirement about our services, please feel free to contact us, we will reply to you immediately.
References
- Jacqueline N. Chu, Giovanni Traverso. Foundations of gastrointestinal-based drug delivery and future developments. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2022, 19:219-238.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Emerging technologies for gastrointestinal delivery of biologics. (Jacqueline N. Chu, et al,2022)
Fig.1 Emerging technologies for gastrointestinal delivery of biologics. (Jacqueline N. Chu, et al,2022)