Nanosuspension Development for Nanomedicine
Inquiry
Nanosuspension consists of the pure poorly water-soluble drug without any matrix material suspended in dispersion. Preparation of nanosuspension is simple and applicable to all drugs which are water insoluble. CD Formulation has been dedicated to developing nanosuspensions for many years, utilizing nanosuspension technology to help researchers and pharmaceutical companies worldwide with the formulation and analysis of nanosuspensions.
Advantages of Nanosuspension
Nanosuspension is a submicron colloidal dispersion of pure drug nanoparticles with surfactant as a solubilizer. Nanosuspensions have their unique advantages:
- Nanosuspensions can successfully prepare drugs that are both poorly soluble in water and oil, overcoming the limitation of first dissolving the drug in preparing other formulations.
- Nanosuspensions have high drug loading capacity and are suitable for large-dose administration while reducing the administration volume.
- Through simple processes and prescriptions, the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs can be improved and the toxic side effects of a large number of additional ingredients on patients can be avoided.
- Nanosuspensions maintain the best crystallization state and have a sufficiently small drug particle size. At the same time, the particle characteristics of this dosage form can change the pharmacokinetic characteristics of intravenous injection of the drug, resulting in high efficiency and low toxicity.
- Making drugs into different particle sizes or performing surface modifications to prepare passively targeted and actively targeted nanosuspensions can increase the drug concentration at the lesion site, reduce the dosage, and reduce the toxic and side effects of the drug.
Our Nanosuspension Preparation Methods
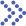
We are committed to the preparation methods of nanosuspension many years. These methods are mainly "bottom-up" and "top-down" technologies, and microemulsion as templates and emulsion as templates are also used for preparing nanosuspensions.
- "Bottom-up" technology involves using conventional precipitation methods to induce particle formation in a solution through chemical reactions. By manipulating different reaction conditions, the size of the precipitated particles is controlled to create nanosuspensions.
- "Top-down" technology uses external force to split drugs or carrier materials down to nanometer size. The technologies for reducing particle size include media milling (Nanocrystal), high-pressure homogenization (HPH), high-pressure homogenization in water (Dissocubes), high-pressure homogenization in nonaqueous media (Nanopure) and combination of precipitation and high-pressure homogenization (Nanoedge).
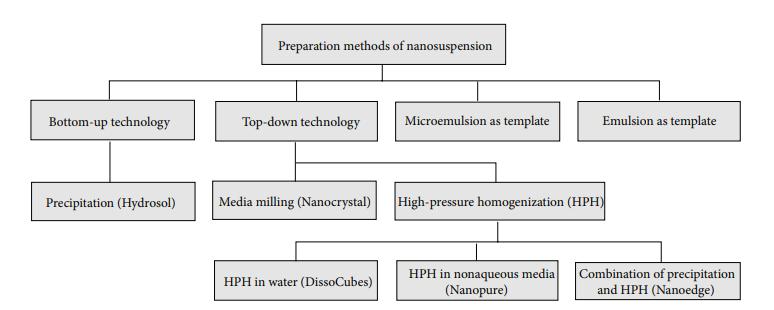 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of preparation methods of nanosuspension. (Kumar Bishwajit Sutradhar, et al. 2013)
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of preparation methods of nanosuspension. (Kumar Bishwajit Sutradhar, et al. 2013)
Our Solutions for Nanosuspension Development
Nanosuspensions are available for oral administration, intravenous injection, eye, lung, transdermal administration and other administration routes. We can provide our clients with nanosuspensions in the following drug delivery systems.
Oral Drug Delivery System
For active pharmaceutical ingredients classified as BCS Class II and IV, after we prepare them into nanosuspensions, they have small particle size, large specific surface area, and strong adhesion to mucous membranes. This can prolong the residence time of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract to improve its bioavailability.
Intravenous Drug Delivery System
For pharmaceutical active ingredients with poor water solubility, we prepare them into nanosuspensions. Because nanosuspensions have high drug loading capacity and suitable particle size, their distribution in the human body after intravenous injection has obvious passive targets. It mainly exists in the monocyte-macrophage system, such as liver, spleen, lung, lymph node and a small amount of bone marrow. Compared with solution formulations, nanosuspensions may alter the pharmacokinetic characteristics of intravenous administration of drugs, such as prolonging t1/2 and MRT.
Ophthalmic Drug Delivery System
Traditional ophthalmic dosage forms for poorly soluble drugs include suspensions, viscous solutions, ointments, etc. They are affected by factors such as tearing, conjunctival absorption, and tear dilution, making the drug less bioavailable. After we prepare the drug into a nanosuspension, reducing the particle size can increase the contact area and residence time between the drug and the cornea, increase the concentration of the drug in the infected tissue and the solubility of poorly soluble drugs, and enhance the efficacy.
Pulmonary Drug Delivery System
Due to the large surface area of the alveolar sacs in the lungs, abundant capillaries, and short transport distance, pulmonary administration can be absorbed rapidly, which can avoid the metabolic effects of gastrointestinal enzymes and the first-pass effect of the liver. After we make the drug into a nanosuspension, because the drug particle size is small and it has strong bioadhesion, it can make the drug difficult to be quickly cleared by ciliary movement, prolong the retention time of the drug in the nasal cavity, thereby improving the bioavailability of the drug.
Transdermal Drug Delivery System
Transdermal drug delivery preparations will be affected by drug solubility, stability, and dissolution rate. We prepare drugs into nanosuspensions. Because of their small particle size, they can increase the rate of drug penetration through the skin and increase their accumulation in the skin. This can improve the therapeutic effect, prolong the action time, reduce the frequency of medication, and increase patient medication compliance.
Other Drug Delivery Systems
Based on the characteristics of nanosuspensions, we can also develop nanosuspension quick-dissolving films, which can quickly disintegrate and release drugs in saliva when used for sublingual administration, which can improve the bio-availability of poorly water-soluble drugs. At the same time, we have also accumulated certain experience in the preparation of in-situ gel nasal spray preparations loaded with nanosuspensions and nasal drops loaded with nanosuspensions and can provide corresponding suspension development services for researchers.
Our Evaluation Capabilities for Nanosuspension Development
Our essential characterization parameters for nanosuspensions include appearance, color, odor, assay, related impurities, particle size, zeta potential, crystalline status, dissolution studies and in vivo studies.
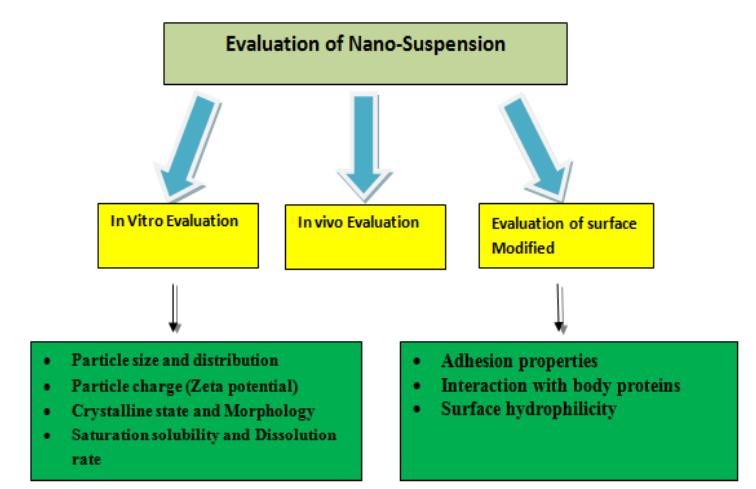 Fig.2 Flowchart showing various methods for characterization of nanosuspensions. (Neha Quadri, et al. 2023)
Fig.2 Flowchart showing various methods for characterization of nanosuspensions. (Neha Quadri, et al. 2023)
Why Choose Us to Develop Nanosuspensions?
- We have established a world-class nanosuspension technology platform, and our research team has rich professional knowledge and research experience in nanosuspension preparation technology.
- We can formulate personalized nanosuspension development proposals and strategies according to the specific needs of researchers or pharmaceutical companies, and vigorously promote the project process.
- Relying on our advanced instruments and equipment in the laboratory, we have rich experience in the evaluation of nanosuspension, such as characterization, in vivo evaluation, and evaluation of surface modification.
- We can also provide customization services for nanosuspensions based on different drug delivery systems including oral, intravenous injection, eye, lung, and transdermal drug delivery systems, etc.
Published Data
Technology: Ultrasonic precipitation method for preparing paclitaxel nanosuspension (PTX) NS
Journal: Bioactive Materials
IF: 18.9
Published: 2021
Results:
The authors prepared paclitaxel nanosuspension (PTX) NS by ultrasonic precipitation method, which has the characteristics of simple preparation and good repeatability. With the help of the homologous targeting mechanism, a glioma C6 cancer cell membrane (CCM)-coated (PTX) NS was developed and modified with DWSW peptide to obtain DWSW-CCM-(PTX) NS with BBB penetration and tumor targeting. function. This study provides a comprehensive solution to improve the targeting of nanosuspensions and demonstrates the encouraging potential of biomimetic nanosuspensions suitable for tumor treatment.
Here are preparation and characterization of paclitaxel nanosuspension shown in this article:
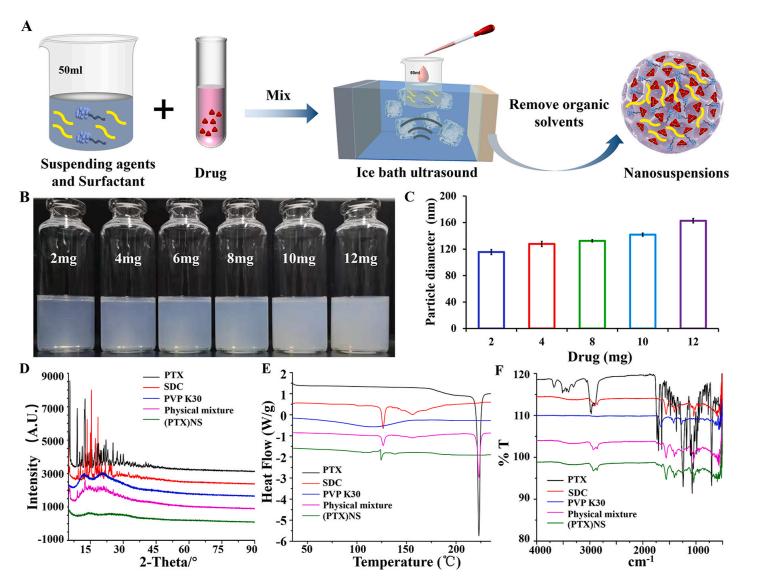 Fig.3 Preparation and characterization of paclitaxel nanosuspension. (Yueyue Fan, et al. 2021)
Fig.3 Preparation and characterization of paclitaxel nanosuspension. (Yueyue Fan, et al. 2021)
CD Formulation has always been at the forefront of nanosuspension development. If you have a requirement about our services, please feel free to contact us by phone or email, and we will reply to you within three working days.
References
- Kumar Bishwajit Sutradhar, Sabera Khatun, and Irin Parven Luna. Increasing Possibilities of Nanosuspension. Journal of Nanotechnology. 2013, doi.org/10.1155/2013/346581
- Neha Quadri, Review on Polyherbal Nanosuspension and Approaches to Enhance Solubility of Drugs. Dr. Mohd. Mustaqeem Abdullah. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 2023,12(10): 313-335.
- Yueyue Fan, Yuexin Cui, Wenyan Hao, et al. Carrier-free highly drug-loaded biomimetic nanosuspensions encapsulated by cancer cell membrane based on homology and active targeting for the treatment of glioma. Bioactive Materials. 2021, (6): 4402-4414.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of preparation methods of nanosuspension. (Kumar Bishwajit Sutradhar, et al. 2013)
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of preparation methods of nanosuspension. (Kumar Bishwajit Sutradhar, et al. 2013) Fig.2 Flowchart showing various methods for characterization of nanosuspensions. (Neha Quadri, et al. 2023)
Fig.2 Flowchart showing various methods for characterization of nanosuspensions. (Neha Quadri, et al. 2023) Fig.3 Preparation and characterization of paclitaxel nanosuspension. (Yueyue Fan, et al. 2021)
Fig.3 Preparation and characterization of paclitaxel nanosuspension. (Yueyue Fan, et al. 2021)