Nanoformulation Pharmacokinetic Studies
Inquiry
The study of nanoformulation pharmacokinetics plays a crucial role in drug delivery research by facilitating the development of suitable human clinical trials. It is imperative to comprehend the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) characteristics of potential drug compounds in order to gain insights into their pharmacokinetic and metabolic behaviors. CD Formulation offers comprehensive nanoformulation pharmacokinetic investigations encompassing aspects such as release, absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination.
What is Nanoformulation Pharmacokinetics?
Nanoformulation pharmacokinetics is a branch of pharmacology concerned with investigating the mechanisms by which nanoformulations are delivered to their target sites and eliminated from the body. The processes of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion govern the rate at which nanoagents accumulate and are removed from organisms.
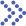
Absorption is the process by which a nanoformulation is carried from the point of administration (such as a tablet or capsule) into the systemic circulation. Absorption affects the speed and concentration at which a drug reaches the desired site of action (such as plasma).
Distribution is the spread of the nanoformulation in the body. This depends on the biochemical properties of the nanoformulations and the physiological condition of the individual taking it.
Metabolism is the process by which the body processes nanoformulations into subsequent compounds, that is, the nanoformulations are converted into substances that are more soluble in water through metabolism, making the drugs inactive for excretion from the body.
Excretion is the process of eliminating drugs from the body.
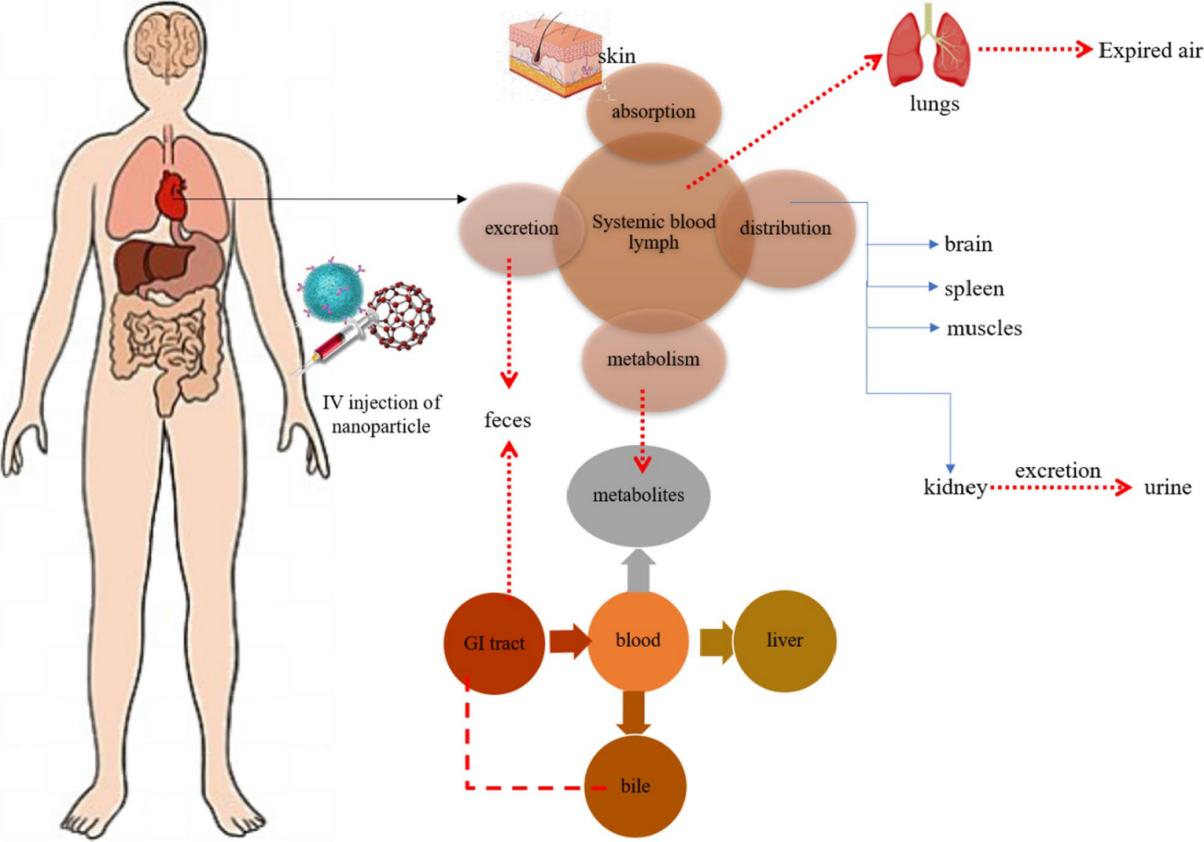 Fig.1 Overall ADME mechanism and fate of nanoparticles. (Muthukrishnan Haripriyaa, et al. 2023)
Fig.1 Overall ADME mechanism and fate of nanoparticles. (Muthukrishnan Haripriyaa, et al. 2023)
Clinical Significance of Nanoformulation Pharmacokinetic Studies
The objective of pharmacokinetic investigations on nanoformulations is to elucidate the distribution and metabolism of a drug within the body. A comprehensive comprehension of pharmacokinetics is imperative for the formulation of therapeutic strategies incorporating nanoformulations.
Laboratory analysis enables the identification of optimal concentrations for desired therapeutic outcomes and the determination of dosages associated with increased risk of adverse events. This information aids healthcare providers in predicting safe drug dosing regimens and understanding the pharmacokinetics of drug clearance from the patient's system.
Our Services for Nanoformulation Pharmacokinetic Studies
Pharmacokinetic and toxicokinetic studies of nanoformulations involve examining their absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties. A thorough understanding of the biokinetics of nanoformulations through detailed analysis of their ADME properties and comprehensive kinetics is essential to ensure the development of safe and effective products. Our team can conduct customized nanoformulation pharmacokinetic studies based on specific customer needs, facilitating the evaluation of nanoformulations for clinical translation and accelerating their use in disease treatment and diagnosis.
Absorption
Absorption is the process by which the drug loaded on the nanoparticles enters the bloodstream from the site of administration through a variety of pathways. Nanoparticles are primarily administered orally and intravenously, the latter allowing the nanoparticles to enter the bloodstream without absorption. Nanoparticles move through the system, the pH changes from 3 to 7, and contain a variety of intestinal enzymes that metabolize the functional groups so that they can be absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract.
Bioavailability is the proportion of the initially administered nanoparticles that enter the systemic circulation, which depends on the properties of the nanoparticles and the route of administration. Bioavailability can directly reflect the absorption of the nanoparticles.
Distribution
Distribution is the mechanism by which nanoparticles and their therapeutic nanoformulation payloads are transported from the blood circulation to tissues, interstitial fluids, and cells. Once absorbed, the nanoformulations are distributed throughout tissues and other organisms via blood circulation. The volume of distribution is the amount of drug in the body divided by the plasma concentration. We use the volume of distribution to assess dosing regimens.
Metabolism
When nanoparticle carriers are present, they are required to maintain normal energy balance in the body. The liver, kidneys, skin and placenta can metabolize foreign compounds to a certain extent.
Elimination
Nanoformulations can be excreted via the liver and gallbladder and in feces as well as urine. Clearance is the ratio of drug elimination rate to plasma drug concentration. We calculated clearance to confirm the appropriate nanoformulation dosing rate.
 Fig.2 Overall process of ADME in the human body. (Muthukrishnan Haripriyaa, et al. 2023)
Fig.2 Overall process of ADME in the human body. (Muthukrishnan Haripriyaa, et al. 2023)
Why Choose Us for Studying Nanoformulation Pharmacokinetics?
- Our core professional team has multidisciplinary backgrounds in nanoformulation, biology, clinical medicine, industrial pharmacy, etc., and can provide necessary technical support for customers' requirements for nanoformulation pharmacokinetic research.
- We have a fully equipped preclinical research laboratory that can respond quickly to your detailed requirements and conduct the nanoformulation pharmacokinetic research trials in a timely manner.
- We have abundant experimental animal resources and clinical researchers with extensive experience in nanoformulation pharmacokinetic studies. We can quickly customize a feasible research plan based on your nanoformulation pharmacokinetic study requirements.
Published Data
Technology: In vivo pharmacokinetic model
Journal: European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences
IF: 4.6
Published: 2021
Results:
The objectives of this work included the development and evaluation of long-acting isomitidine chloride (ISMM)-docusate sodium (DS) composite-loaded lipid nanoparticles (LA ISMM-DS LNP). In vivo pharmacokinetic studies of long-acting isomitidine chloride-docusate sodium composite-loaded lipid nanoparticles were also conducted. Composite-loaded lipid nanoparticles can prolong plasma drug concentrations in vivo for seven days, with enhanced AUC0-∝, MRT0-∝ and t1/2, while Cl is reduced. In vitro and in vivo studies predict that composite-loaded lipid nanoparticles have higher safety and efficacy. The results show that the successfully developed composite-loaded lipid nanoparticles will have great clinical potential in the treatment and prevention of trypanosomiasis.
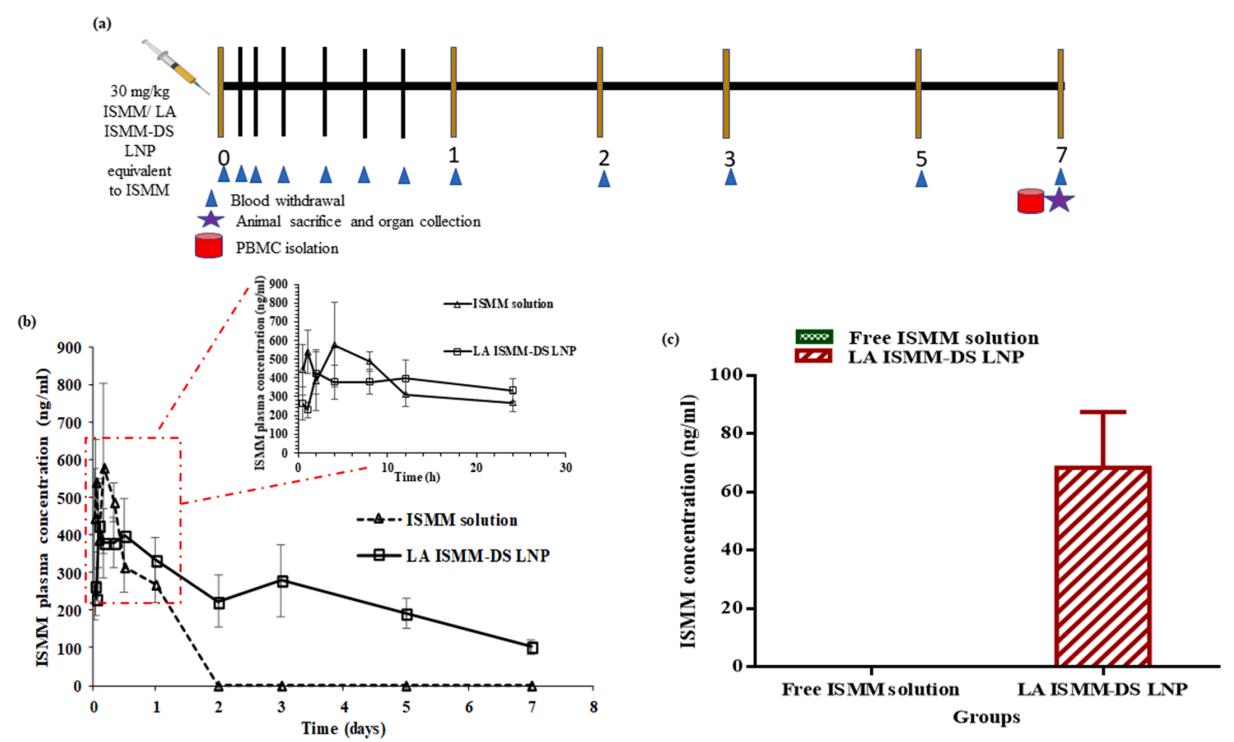 Fig.3 In vivo pharmacokinetic studies. (Dhanashree H Surve, et al. 2021)
Fig.3 In vivo pharmacokinetic studies. (Dhanashree H Surve, et al. 2021)
Through the study of the nanoformulation pharmacokinetics (absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion), it can provide necessary technical support for clinicians to calculate and evaluate the dosage and frequency of administration. CD Formulation is a leading expert in nanoformulation pharmacokinetic studies, depending on our professional expert team and rich experience. If you need any assistance with nanoformulation pharmacokinetic studies, please feel free to contact us for detailed communication.
References
- Muthukrishnan Haripriyaa, Krishnamurthy Suthindhiran. Pharmacokinetics of nanoparticles: current knowledge, future directions and its implications in drug delivery. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2023, (9):113.
- Dhanashree H Surve, Anil B Jindal. Development of cationic Isometamidium chloride loaded long-acting lipid nanoformulation: optimization, cellular uptake, pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and immunohistochemical evaluation. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2021,167:106024.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services


 Fig.1 Overall ADME mechanism and fate of nanoparticles. (Muthukrishnan Haripriyaa, et al. 2023)
Fig.1 Overall ADME mechanism and fate of nanoparticles. (Muthukrishnan Haripriyaa, et al. 2023) Fig.2 Overall process of ADME in the human body. (Muthukrishnan Haripriyaa, et al. 2023)
Fig.2 Overall process of ADME in the human body. (Muthukrishnan Haripriyaa, et al. 2023) Fig.3 In vivo pharmacokinetic studies. (Dhanashree H Surve, et al. 2021)
Fig.3 In vivo pharmacokinetic studies. (Dhanashree H Surve, et al. 2021)