Nanoformulation Elemental Impurity Testing Service
Inquiry
Some elemental impurities may be introduced during the formulation development process of nanoformulations. These elemental impurities are an important part of drug quality control and assurance (QC/QA). Certain elemental impurities (especially heavy metal elements) not only affect the quality of nanoformulations. It has adverse effects on stability and shelf life, and it is also potentially toxic and can easily cause human diseases. Therefore, we need to control elemental impurities during the development and quality research of nanoformulations to ensure the drug safety of nanomedicines. CD Formulation has been committed to researching and developing elemental impurity testing of nanoformulations for years, and we also have rich experience in elemental impurity analytical method development and validation.
Classification of Elemental Impurities
The ICH Q3D guideline lists 24 elements and classify them according to risk levels. It is also determined whether the element needs to be controlled based on the route of administration and whether it is intentionally added.
- Class 1 elemental impurities: arsenic, cadmium, mercury and lead. These elements are obviously toxic and must not be used or restricted in drug production. All routes of administration must evaluate these 4 elements.
- Class 2A elemental impurities: cobalt, nickel, vanadium. These elements have a high probability of occurring in preparations and devices, and a risk assessment needs to be conducted on all potential sources and routes of administration.
- Class 2B elemental impurities: thallium, gold, palladium, iridium, osmium, rhodium, ruthenium, selenium, silver, platinum. These elements are less likely to occur in pharmaceutical products and may not be evaluated unless they are intentionally added during production.
- Class 3 elemental impurities: lithium, antimony, barium, molybdenum, copper, tin, chromium. These elements have low oral toxicity. For injection and inhalation drugs, if the PDE (permitted daily exposure) value of the administration route does not exceed 500 μg/d, they need to be evaluated. If such elements are intentionally added during production, they need to be evaluated.
- Other elemental impurities: aluminum, boron, calcium, iron, potassium, magnesium, manganese, sodium, tungsten, zinc and other elements. These elements have low toxicity, no PDE has been established, and risk assessment is subject to other guidance for the specific element and/or local regulations and specifications or quality standards for the drug product.
Our Strategy for Elemental Impurity Analytical Method Development
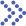
Based on our professional experience in nanoformulation quality research, we will mainly develop analytical methods for elemental impurities according to the process in the figure below.
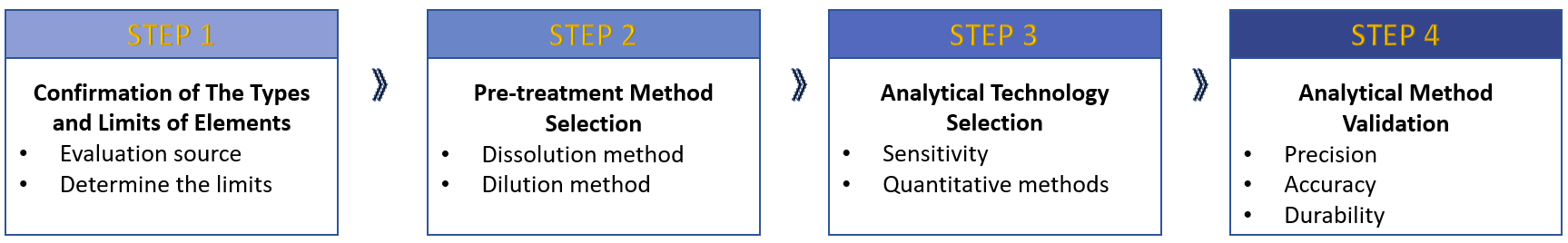 Fig.1 Our workflow of elemental impurity testing. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Our workflow of elemental impurity testing. (CD Formulation)
Confirmation of the types and limits of elements
Confirming the types of elements: According to ICH Q3D guideline, we will comprehensively evaluate potential sources of elemental impurities and identify known and potential elements. The main sources of elemental impurities include:
- Residues of elements (such as catalysts) intentionally added during the production of drug substances, excipients, or other pharmaceutical ingredients.
- Elemental impurities that are not intentionally added but may be present in raw materials, water or excipients used in drug production.
- Elemental impurities that may be introduced into the drug substance and/or drug product by manufacturing equipment.
- Packaging systems may leach elemental impurities into drug substances and drug products.
- Elemental impurities that may exist in the production environment of APIs, excipients and preparations.
Confirming the limits of elements: Generally, we refer to the element PDE values and calculation methods listed in ICH Q3D to determine the limits of each element.
Pre-treatment Method Selection
Sample pretreatment is a key step before elemental impurity analysis.
Direct dissolution: For trace and trace element impurity analysis, simple dissolution with inorganic acid or water is preferred for sample preparation. Methods that directly dissolve the sample are preferred for the analysis of liquid preparations.
Indirect dissolution: For raw materials, some excipients, such as binders, colorants, pigments, and preparations that are difficult to find suitable solvents to dissolve, it is difficult to prepare samples using direct dissolution methods, so indirect dissolution methods are needed. Indirect dissolution method is the first choice for active pharmaceutical ingredients, poorly soluble excipients and solid preparations.
Analytical Techniques Selection
There are a variety of analysis techniques for inorganic elements, including conventional heavy metal inspection methods, ultraviolet spectrophotometry (UV), atomic absorption spectrophotometry (AAS), X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF), and inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS).
Analytical Method Validation
Elemental impurity analytical method validation includes but are not limited to the following aspects.
- System suitability
- Linearity and range
- Limit of quantitation
- Accuracy
- Repeatability
- Specificity
- Limit of detection
- Intermediate precision
- Durability (including solution stability)
Why Choose Us to Test Elemental Impurity?
- Relying on our advanced equipment, we can offer elemental impurity testing services by UV, AAS, ICP-MS, etc.
- Our core technical team have rich experience in elemental impurity analytical method development, analytical method validation.
- We have complete analysis and testing service management specifications, a relatively fast sample circulation cycle, and can quick response to your detailed requirements for elemental impurity testing of nanoformulations.
Published Data
Technology: Single-particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (spICP-MS) Technique
Journal: TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry
IF: 13.1
Published: 2022
Results:
The authors compared the principles of single-particle multi-element/isotopic analysis using ICP-MS systems equipped with different types of mass analyzers (quadrupole, TOF and sector mass analyzer). The authors also highlight recent advances in the qualitative characterization and quantitative measurement of NPs and the resulting applications, including differentiation of engineered and natural NPs and their origin tracing. The authors also discuss single-cell multi-element analysis, as its principles and applications are very similar to single-particle analysis. Based on current progress and limitations, the authors also propose future trends, including hyphen technology to provide complementary information, enriched isotope labeling to track environmental transformation and bioaccumulation of NPs, and real-time monitoring of NPs through internal standard calibration.
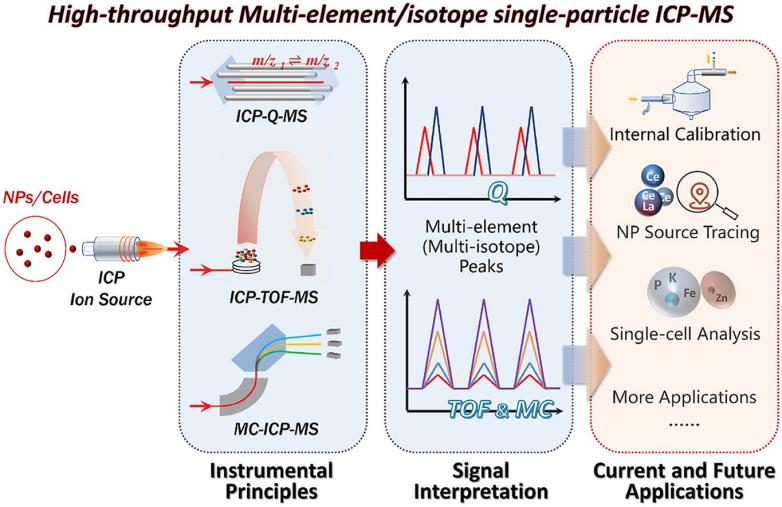 Fig.2 High-throughput multi-elment/isotope single-particle ICP-MS. (Xiangwei Tian, et al. 2022)
Fig.2 High-throughput multi-elment/isotope single-particle ICP-MS. (Xiangwei Tian, et al. 2022)
CD Formulation has a variety of analytical equipment and a expert team with rich experience to provide elemental impurity testing services for nanoformulations. If you are interested in our elemental impurity testing services, please contact us for detailed information.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services


 Fig.1 Our workflow of elemental impurity testing. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Our workflow of elemental impurity testing. (CD Formulation) Fig.2 High-throughput multi-elment/isotope single-particle ICP-MS. (Xiangwei Tian, et al. 2022)
Fig.2 High-throughput multi-elment/isotope single-particle ICP-MS. (Xiangwei Tian, et al. 2022)