Nanoformulation Critical Aggregation Concentration Testing Service
Inquiry
Critical aggregation concentration (CAC) determines the assembly behavior of supramolecular peptide-based nanoformulations. Once the critical aggregation concentration is exceeded, amphiphilic block copolymers can form various types of aggregates through hydrophobic interactions in water. CD Formulation can perform the critical aggregation concentration of nanoformulations through different technical methods such as static light scattering, dynamic light scattering, surface tension measurements, etc.
What is Critical Aggregation Concentration (CAC)?
The minimum concentration at which polymer molecules associate to form polymer micelles is the critical aggregation concentration (CAC). When the monomer concentration reaches a certain amount, the critical aggregation concentration (CAC) is an important indicator to measure it. It can form micelles or vesicles in a self-assembled manner (hydrophobic interaction), and its structure also shows diversity, including spherical shape, oval, rod and sheet.
The critical aggregation concentration (CAC) is the most important parameter for studying the aggregation behavior of biological macromolecules and supramolecular peptide-based nanomedicines. Therefore, it is necessary for us to conduct in-depth research on CAC measurement technology to facilitate the formulation development of supramolecular peptide-based nanomedicines.
Our Critical Aggregation Concentration Testing Techniques
CD Formulation explore and research critical aggregation concentration (CAC) testing techniques including static light scattering (SLS), dynamic light scattering (DLS), tensiometric, conductometric, fluorometric, and calorimetric methods.
Static Light Scattering (SLS)
CAC is the compound concentration at which molecular aggregation begins to form. At this transition point, it is easy to observe the sudden change in SLS intensity (non-linearity) as the compound concentration increases.
Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
Dynamic light scattering is one of the simple methods to measure CAC. DLS intensity is related to aggregate size. As monomers and clusters begin to assemble, the intensity in DLS grows exponentially with increasing concentration.
Surface Tension Measurements
We used the pendant drop method to determine the critical aggregation concentration (CAC) value of water-soluble synthetic amphiphilic reagents. The samples were vigorously stirred in deionized water with a concentration of 5 mg/ml for 20 hours, and then serially diluted twice to form solutions with different concentrations. Then, record the surface tension value of the sample at 25±5℃ until the deviation in this value stabilizes. The CAC value is obtained by plotting the surface tension value versus the concentration of the amphiphilic substance.
Fluorometric Measurements
In the determination process of critical aggregation concentration (CAC), pyrene is used as a fluorescent probe to measure the fluorescence value of the sample solution added with pyrene.
Apart from the above CAC measurement techniques, we also have developed conductometric to meet customers’ different CAC determination requirements.
Our Workflow of Nanoformulation Critical Aggregation Concentration Testing
Our team can quickly respond to customers’ critical aggregation concentration testing requirements to support their nanoformulation development needs, and we can perform the CAC test in just following four steps.
 Fig.1 Our workflow of nanoformulation critical aggregation concentration testing. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Our workflow of nanoformulation critical aggregation concentration testing. (CD Formulation)
Why Choose Us to Test Nanoformulation Critical Aggregation Concentration?
- We are committed to different CAC determination methods to support researchers’ nanoformulation development and studying the assembly behavior of nanomedicines, including SLS, DLS, tensiometric, conductometric, fluorometric, and calorimetric methods, etc.
- Our core team have rich experience in critical aggregation concentration (CAC) determination for the evaluation of the assembly behavior of supramolecular peptide-based nanomedicines.
- We also can help customers design and explore the new critical aggregation concentration determination technology to meet their special requirements.
Published Data
Technology: Dual-emissive gold nanocluster labeling
Journal: Biosensors
IF: 5.743
Published: 2022
Results:
The authors studied fluorescence visualization of the interaction between cationic hyperbranched polyethylenimine and anionic sodium dodecyl sulfonate surfactant via dual-emission gold nanocluster labeling. The sensing mechanism is due to interaction-induced conformational changes in the polymer, thereby regulating the molecular structure of gold nanoclusters and subsequent light radiation processes. The authors obtained three critical concentration points for polymer-surfactant interaction, namely critical aggregation concentration (CAC), charge neutralization concentration (CNC), and polymer saturation point (PSP), through changes in the fluorescence emission ratio of designed dual-emitting gold nanoclusters. And these three critical concentration points were verified through hydrodynamic diameter and zeta potential measurements. Fluorescence visualization is of great significance for improving product performance and/or processing technology in related fields.
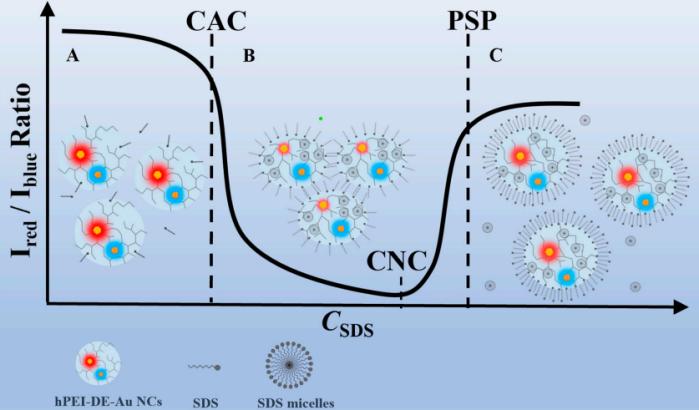 Fig.2 Schematic illustration of hPEI-SDS interaction visualization by DE-AuNC labeling. (Jiaojiao Zheng, et al. 2022)
Fig.2 Schematic illustration of hPEI-SDS interaction visualization by DE-AuNC labeling. (Jiaojiao Zheng, et al. 2022)
As a loyal partner of researchers developing nanoformulations, CD Formulation not only has extensive experience in the development of critical aggregation concentration (CAC) determination methods, but also has in-depth exploration in using CAC to study the assembly behavior of supramolecular peptide-based nanomedicines and the aggregation behavior of biological macromolecules. If you have any questions about CAC determination or research on the assembly behavior of nanomedicines, please do not hesitate to contact us at any time.
References
- Jiaojiao Zheng, Jing Zhang, Fengniu Lu, et al. Visualization of Polymer–Surfactant Interaction by Dual-Emissive Gold Nanocluster Labeling. Biosensors. 2022,12,686.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services


 Fig.1 Our workflow of nanoformulation critical aggregation concentration testing. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Our workflow of nanoformulation critical aggregation concentration testing. (CD Formulation) Fig.2 Schematic illustration of hPEI-SDS interaction visualization by DE-AuNC labeling. (Jiaojiao Zheng, et al. 2022)
Fig.2 Schematic illustration of hPEI-SDS interaction visualization by DE-AuNC labeling. (Jiaojiao Zheng, et al. 2022)