Exosome Development for Nanomedicine
Inquiry
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles that are released by many cell types. Exosomes are formed within intracellular endosomal compartments and secreted upon fusion of these compartments with the plasma membrane. CD Formulation offers exosome development services for nanomedicines to meet various needs by utilizing advanced exosome isolation and purification technology, as well as drug loading techniques. Our skilled nanoformulation development team can customize exosomes with different loads to support research on exosomes in nanomedicine.
Advantages of Exosomes as Drug Carriers
Exosomes are natural carriers for cell-to-cell transfer of genetic material and mediators of gene expression in early cells. They are found in a variety of body fluids and offer many advantages over traditional synthetic delivery vehicles, including better biocompatibility, greater stability, lower immunogenicity, high stability in the blood, and drugs can be delivered directly to cells. At the same time, the protein composition and lipid content of exosomes endow them with targeting capabilities to specific organs.
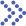
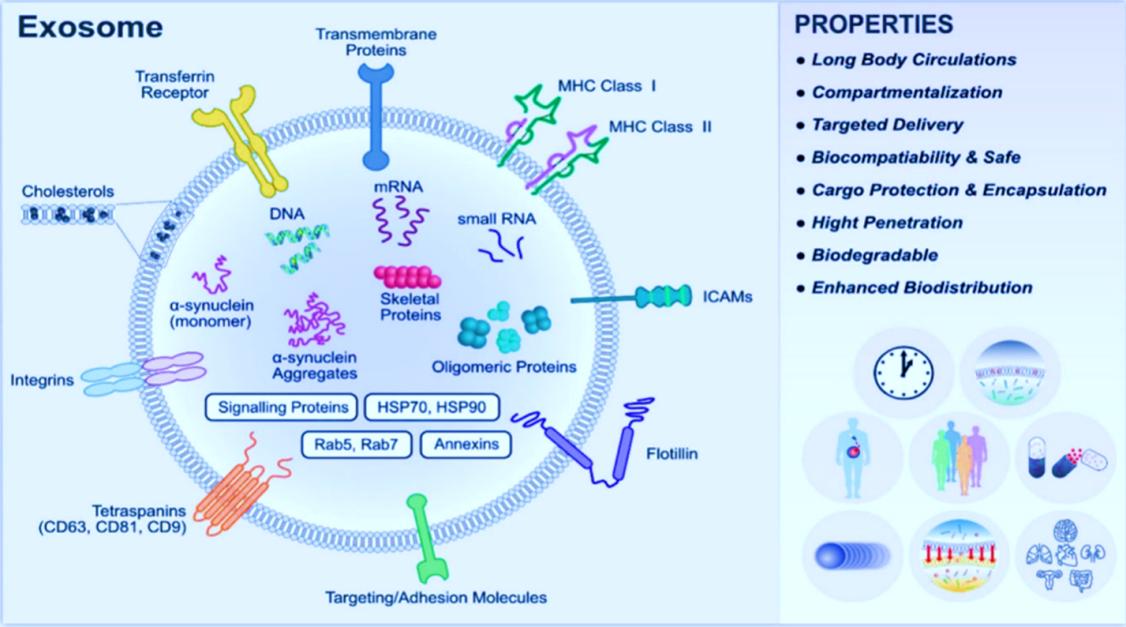 Fig.1 Typical structure of exosomes, properties, and functional attribution of various biomolecules present in exosome. (Amarjitsing Rajput, et al, 2022)
Fig.1 Typical structure of exosomes, properties, and functional attribution of various biomolecules present in exosome. (Amarjitsing Rajput, et al, 2022)
- Size of exosomes: The diameter of exosomes is approximately 40-150 nm.
- The number of exosomes: There are about 10^14 in the human body, which is close to the average of 1000-10000 produced by each cell.
- Cell source of exosomes: Almost all types of cells in the human body can produce exosomes.
- Exosomes are heterogeneous: Even exosomes secreted by the same cell may have very different functions.
- Existence of exosomes: Exosomes are found in almost all tissues, intercellular spaces, and body fluids. Exosomes are produced from multivesicular bodies in cells.
Our Exosome Isolation and Purification Techniques
Exosomes can be secreted by almost all types of cells cultured in vivo or in vitro, and are widely found in plasma, bile, urine, breast milk, saliva, pleural effusion, lymph, gastric acid, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, tears, In body fluids such as semen, synovial fluid, amniotic fluid, ascites, nasal secretions and uterine aspirate fluid. CD Formulation relies on our advanced design concept to use the following isolation techniques for exosomes, such as ultrafiltration, ultracentrifugation, immunoaffinity purification, size exclusion chromatography (SEC), polymer-based precipitation, microfluidics-based isolation, magnetic separation, nanofluidic separation, dielectrophoretic separations, deterministic lateral displacement (DLD) separations, etc.
Apart from the isolation and separation methods mentioned earlier for exosomes, we are dedicated to studying new technologies for advanced isolation and separation of exosomes to offer expert assistance to researchers.
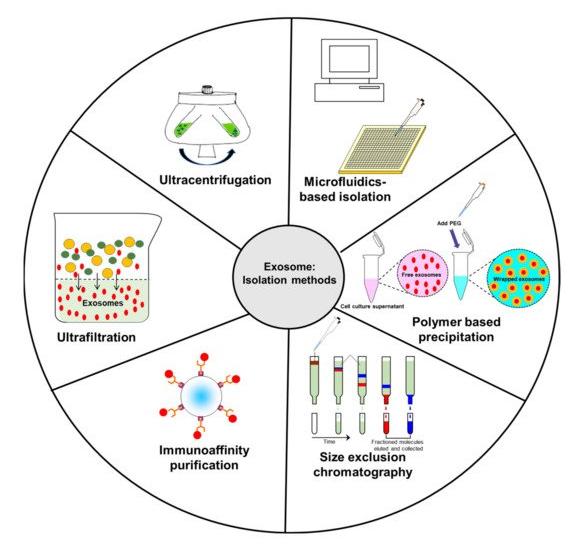 Fig.2 Schematic diagram representing common isolation methods for exosomes. (Andrew E. Massey, et al. 2021)
Fig.2 Schematic diagram representing common isolation methods for exosomes. (Andrew E. Massey, et al. 2021)
Our Exosome Drug Loading Techniques
We have been dedicated to exploring methods for loading exogenous drugs into exosomes for many years, including sonication, electroporation, transfection, incubation, extrusion, saponin-assisted loading, freeze-thaw cycles, heat shock, pH gradient method and low temperature osmosis analysis, etc. Based on the customer's target product needs, we can load drugs into exosomes through the following exosome drug loading technologies.
Sonication
During the ultrasound process, the exosome membrane deforms, the membrane permeability increases, and the drug enters the exosomes. After incubation, the recovery of exosome membranes was improved.
Electroporation Technology
Under the action of an electric field, small holes are formed on the exosome membrane, which facilitates the entry of drugs into the exosomes, and then the integrity of the exosome membrane is restored through incubation.
Transfection
The transfection reagent improves membrane permeability, allowing the drug to enter the vesicles.
Incubation
These methods are divided into direct incubation and indirect incubation. Direct incubation is to incubate drugs directly with exosomes. Indirect incubation is a process in which the drug is incubated with donor cells and then the drug-carrying exosomes are isolated and purified.
Extrusion
After the drug and exosomes are mixed, they are extruded using a small extruder. After repeated extrusion steps, the exosome membrane deforms to facilitate the entry of the drug, and the exosomes wrapped with the drug are obtained through the automatic recovery of the membrane.
Saponin-Assisted Loading
Saponin-mediated permeation, an adjunct method that can be used alone or in combination with ultrasonic electroporation. Saponins form complexes with the vesicle membrane, leading to pore formation and drug entry into exosomes.
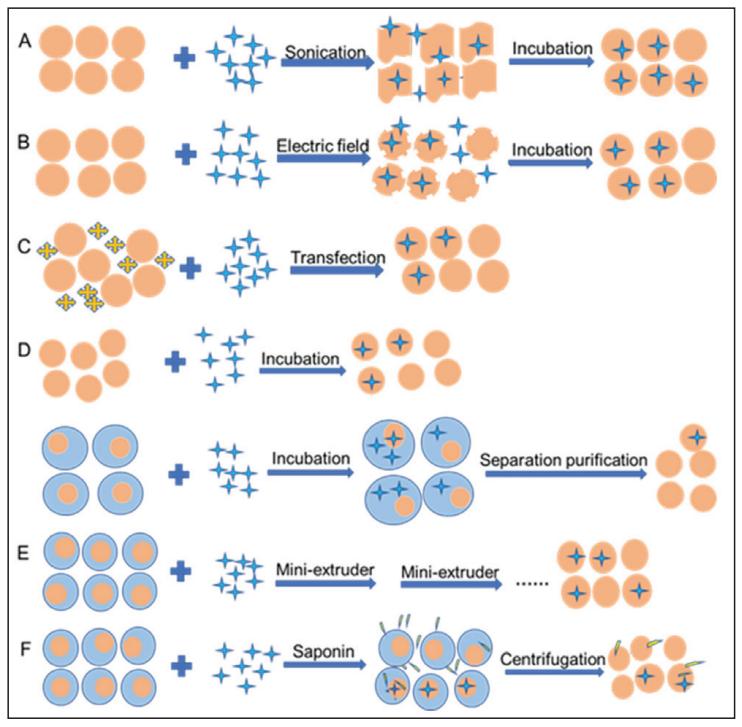 Fig.3 Exosome loading methods. (XIAO-MING XI, et al. 2021)
Fig.3 Exosome loading methods. (XIAO-MING XI, et al. 2021)
Our Analytical Capabilities for Exosomes
The physical stability of exosomes during prolonged storage can be determined by monitoring changes in particle size, zeta potential and appearance as a function of time. We can provide you with the following analysis and characterization of exosomes including,
- Particle Size
- Zeta Potential
- Encapsulation Efficiency
- Drug Loading
- In Vitro Release
- Stability
Why Choose Us to Develop Exosomes?
- Relying on our first-class exosome research and development platform, we have core technologies for exosome-related research and development, including exosome isolation and purification technology and exosome drug loading technology.
- We have a skilled and specialized team of professionals for exosome development and can provide high-quality customization and analysis services for exosomes.
- We have successfully created a comprehensive and integrated service model, which comprehensively covers the research and development processes such as exosome preparation, isolation, purification, drug loading, and characterization, showing the service advantages of strict planning, efficient collaboration, and orderly advancement. We can empower the research and development of exosomes more, faster, better, and more economically.
Published Data
Technology: Methods for drug loading into engineered exosomes: CRISPR/Cas9 technology
Journal: Journal of Nanobiotechnology
IF: 10.2
Published: 2024
Results:
The authors review the latest liposome preparation technologies, excipients for liposome formulations used in various new studies, and administration routes used to deliver exosomes to target disease areas. The authors also describe the optimization of liposome-based drug delivery systems, preparation techniques with higher reproducibility, and broader new modal applications including nucleic acid therapy, CRISPR/Cas9 therapy, and immunotherapy.
Here is the methods for drug loading into engineered exosomes.
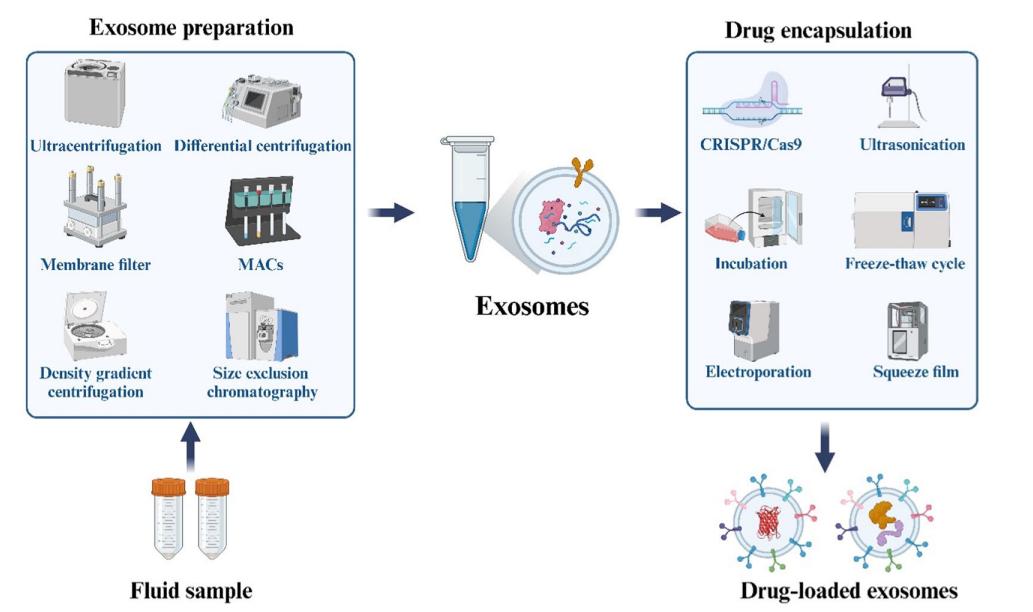 Fig.4 Methods for drug loading into engineered exosomes. (Zhen Chen, et al. 2024)
Fig.4 Methods for drug loading into engineered exosomes. (Zhen Chen, et al. 2024)
As an emerging research field, exosomes have entered a period of intense research. CD Formulation has always been at the forefront of exosome research and development by leveraging its internal and external technical resources. Please feel free to contact us for detailed conversations and communication if you are interested in our services.
References
- Amarjitsing Rajput, Akansh Varshney, Rashi Bajaj, et al. Exosomes as New Generation Vehicles for Drug Delivery: Biomedical Applications and Future Perspectives. Molecules. 2022, 27, 7289.
- Andrew E. Massey, Shabnam Malik, Mohammad Sikander, et al. Clinical Implications of Exosomes: Targeted Drug Delivery for Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22(10), 5278
- XIAO-MING XI, CHEN-MENG, SHU-JUN XIA, et al. Drug loading techniques for exosome-based drug delivery systems. Pharmazie. 2021, 76: 61-67.
- Zhen Chen, Min Xiong, Jiaqi Tian, et al. Encapsulation and assessment of therapeutic cargo in engineered exosomes: a systematic review. Journal of Nanobiotechnology. 2024,22,18.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Typical structure of exosomes, properties, and functional attribution of various biomolecules present in exosome. (Amarjitsing Rajput, et al, 2022)
Fig.1 Typical structure of exosomes, properties, and functional attribution of various biomolecules present in exosome. (Amarjitsing Rajput, et al, 2022) Fig.2 Schematic diagram representing common isolation methods for exosomes. (Andrew E. Massey, et al. 2021)
Fig.2 Schematic diagram representing common isolation methods for exosomes. (Andrew E. Massey, et al. 2021) Fig.3 Exosome loading methods. (XIAO-MING XI, et al. 2021)
Fig.3 Exosome loading methods. (XIAO-MING XI, et al. 2021) Fig.4 Methods for drug loading into engineered exosomes. (Zhen Chen, et al. 2024)
Fig.4 Methods for drug loading into engineered exosomes. (Zhen Chen, et al. 2024)