Environmentally Responsive Nanoparticle Development for Nanomedicine
Inquiry
With the help of our word-leading nanoparticle preparation technology, CD Formulation can provide our clients with environmentally responsive nanoparticle formulation development services to meet the needs of different customers, including but not limited to endogenous stimuli responsive nanoparticles, exogenous stimuli responsive nanoparticles and multiple responsive nanoparticles.
Classification and Advantages of Environmentally Responsive Nanoparticles
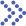
Environmentally responsive nanoparticles are nanodelivery systems designed by responding to tumor microenvironment endogenous stimuli (including low pH, high-level reactive oxygen species, overexpressed enzymes, etc.) and exogenous stimuli (light, ultrasound, temperature, etc.). They can achieve rapid release of drugs at the lesion site.
 Fig.1 Classification of environmentally responsive nanoparticles. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Classification of environmentally responsive nanoparticles. (CD Formulation)
Environmentally responsive nanoparticles possess properties such as low pH, high reactive oxygen species levels, high shear stress, multi-enzymes, etc. Therefore, they can achieve precise and controllable drug release and increase drug accumulation at the lesion site, thereby improving therapeutic effects and reducing drug side effects.
Our Design Strategies for Environmentally Responsive Nanoparticles
Our design goals of environmentally responsive nanoparticles are mainly to accelerate drug release, promote drug uptake by lesion cells, and improve drug penetration. We are committed to the environmentally responsive nanoparticles design strategies based on abnormal physiological indicators of micro-environment. And our design strategies for environmentally responsive nanoparticles is as follows.
- Responsive to the breaking of chemical bonds and the cleavage of carriers.
The cleavage of sensitive chemical bonds triggers the release of drugs or the cleavage of carriers, thereby achieving controlled release of drugs.
- Response to achieve removal of PEG layer and Responsive charge reversal.
The outer protective layer of the carrier is removed through microenvironmental response to increase the uptake efficiency of the carrier by cells, such as the removal of the polyethylene glycol (PEG) shell or through the reversal of charge on the carrier surface.
- Response to achieve activation of functional molecules.
Re-exposure of functional molecules promotes cellular drug uptake.
- Responding to nanoparticle size changes.
By changing the size of the carrier's responsiveness, the enrichment and penetration of the carrier in the tumor site can be regulated.
Explore Our Construction for Environmentally Responsive Nanoparticles
We can provide our clients with our construction and customization services for various environmentally responsive nanoparticles, including pH-responsive nanoparticles, redox-responsive nanoparticles, ROS-responsive nanoparticles, hypoxia-responsive nanoparticles, etc.
pH-Responsive Nanoparticles
We have two strategies for constructing pH-responsive nanoparticles. One strategy is to utilize polymers with ionizable groups that exhibit conformational and solubility changes at different pH values. Another strategy is to introduce structures with acid-sensitive cleavage that can respond to cleavage in slightly acidic environments.
Redox-Responsive Nanoparticles
We have expertise in developing GSH-responsive nanoparticles based on disulfide bonds, ditelluride bonds and metal ions. And we can tailor them to your specific needs.
ROS-Responsive Nanoparticles
Our team created a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive polymer nanoparticle platform, and successfully encapsulated drugs in ROS-responsive nanoparticles with the help of this platform.
Hypoxia-Responsive Nanoparticles
Our team utilized hypoxia-responsive amphiphilic polymers to create hypoxia-responsive nanoparticles in water that can specifically release drugs in low-oxygen conditions.
Enzyme-Responsive Nanoparticles
We use enzyme-sensitive nanoparticles to bind particular enzyme substrates at desired locations. When these nanoparticles are activated by enzymes found in tumor cells, they undergo alterations in function or appearance, like exposing functional ends or distinct morphological changes. This method boosts targeting, penetration, and drug retention, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness of anti-tumor treatments.
Magnetically Responsive Nanoparticles
We have developed techniques for preparing magnetically responsive nanoparticles, in situ synthesis and direct composites. In the in-situ approach, nanoparticle precursors and/or monomers are first mixed and then the nanoparticle formation and/or polymerization are sequentially activated via physicochemical triggers or chemical initiators. In the direct compounding approach, nanofillers and polymers are prepared separately and then they are mixed together, usually by mechanical force or melting.
Furthermore, aside from the environmentally sensitive nanoparticles mentioned earlier, we also offer tailored environmentally responsive nanoparticles such as ATP-responsive nanoparticles, photon-responsive nanoparticles, and GSH/ROS dual responsive nanoparticles.
Our Analytical Capabilities for Environmentally Responsive Nanoparticles
We can also provide our customers with characterization services for various physicochemical characteristics of environmentally responsive nanoparticles, including size, shape, charge distribution, stability, diffusion properties, surface functionalization, and interactions with organisms, etc.
- Particle Size
- Particle Shape
- Diffusion Properties
- Surface Charge and Zeta Potential
- Surface Functionalization
- Drug Loading
- Encapsulation Efficiency
- Drug Release
- Stability
Why Choose Us to Develop Environmentally Responsive Nanoparticles?
- Based on nanoformulation development technology and different environmental stimuli, we can produce various environmentally responsive nanoparticles for research and development, such as pH-responsive nanoparticles, redox-responsive nanoparticles, ROS-responsive nanoparticles, hypoxia-responsive nanoparticles, pH and GSH-responsive nanoparticles, etc.
- We offer a comprehensive solution that includes designing and constructing environmentally responsive nanoparticles and analyzing and characterizing them based on the customer's requirements.
- We hold well-equipped instruments and equipment and a team with strong professional skills to ensure accurate, timely, and efficient responses to your project needs.
Published Data
Technology: The preparation process of tumor microenvironment (TME)-responsive nanomedicines
Journal: Advanced Science
IF: 15.1
Published: 2022
Results:
The authors summarize recent advances in tumor microenvironment (TME)-responsive nanomedicines for cancer immunotherapy. The nanomedicine responds to signals in the TME such as weak acidity, reducing environment, high levels of reactive oxygen species, hypoxia, overexpressed enzymes and high levels of adenosine triphosphate. Furthermore, the authors discuss the potential of establishing platforms that combine nanomedicine-based therapeutics and immunotherapeutic strategies to overcome each step of the cancer immune cycle and enhance antitumor effects.
CD Formulation has been researching environmentally responsive nanoparticle formulations for many years. If you need our assistance, please feel free to contact us for detailed conversations, and our team will get back to you within three business days.
References
- Shaojun Peng, Fengfeng Xiao, Meiwan Chen, et al. Tumor-Microenvironment-Responsive Nanomedicine for Enhanced Cancer Immunotherapy. Advanced Science. 2022,9,2103836.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Classification of environmentally responsive nanoparticles. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Classification of environmentally responsive nanoparticles. (CD Formulation)