Albumin Nanoparticle Development for Nanomedicine
Inquiry
Albumin, as a multifunctional drug target carrier and a functional carrier that improves the pharmacokinetic properties of peptide and protein drugs in vivo, plays an increasingly important role in the clinical application of drugs. CD Formulation, a top formulation development service provider, offers our clients albumin nanoparticle formulation development services using our advanced technology. Our professional nanoformulation team can design and create our high-quality albumin nanoparticles tailored to your various needs, supporting research and potential commercialization in the field of nanomedicine.
Advantages of Albumin Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Carriers
Albumin, also known as serum protein, has a wide range of sources. Albumin is extracted from different sources such as Ovalbumin (OVA), Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA), Human Serum Albumin (HSA) and Rat Serum Albumin (RSA). Albumin can be bound to a variety of molecules and substances, including therapeutic drugs, antibodies and peptides.
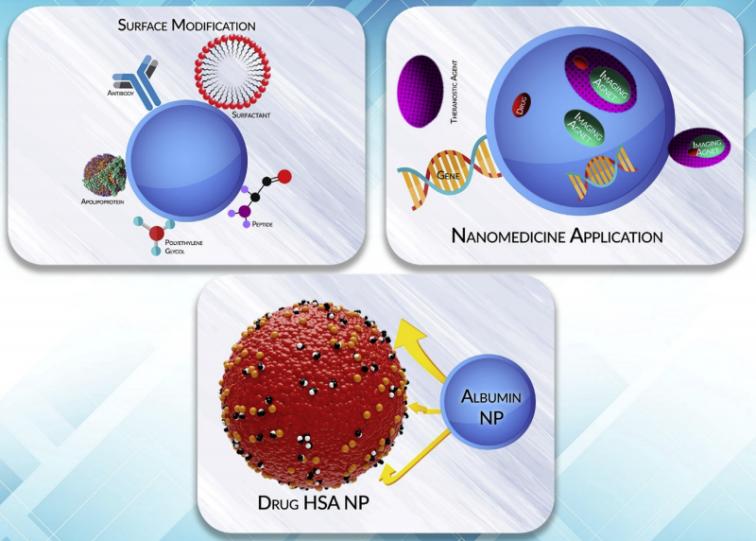 Fig.1 Albumin can bind to a broad range of molecules. (Elmira Karami, et al. 2020)
Fig.1 Albumin can bind to a broad range of molecules. (Elmira Karami, et al. 2020)
Albumin has the characteristics of good biocompatibility, non-toxicity, and non-immunogenicity, and its application in new drug delivery carriers continues to increase. Especially for tumor treatment, albumin nanoparticles, as drug delivery carries, have the following advantages:
 Fig.2 Advantages of albumin nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 Advantages of albumin nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers. (CD Formulation)
What Can We Provide for Albumin Nanoparticle Development?
Albumin nanoparticles encapsulate drugs in albumin nanoparticle delivery systems. Drugs can be covalently bound to the spatial structure of albumin or attached to the surface of the delivery system through physical adsorption. Currently, there are also more advanced technologies to incorporate drugs into the matrix of nanoparticles. We are committed to albumin nanoparticle research and development. we can provide you with comprehensive and professional solutions and helps you quickly develop the formulation of high-quality albumin nanoparticles for nanomedicine.
- Formulation design/ fabrication/ formulation optimization/ modification.
- Analysis and characterization of albumin nanoparticles.
Explore Our Preparation Methods for Albumin Nanoparticles
We can choose appropriate physical and chemical methods to prepare albumin nanoparticles based on the characteristics of the active drugs. In the preparation of albumin nanoparticles, chemical methods include desolvation, emulsification and self-assembly. At the same time, we can also use thermal gelation, nanoparticle albumin binding (NAB) technology and nanospray drying to produce albumin nanoparticles using physical techniques. In addition, we can also use some special methods (e.g., covalent bonding, surface coating, and electrostatic adsorption) to load albumin nanoparticles onto targeted drugs.
- Coacervation or Desolvation
- Emulsification
- Self-assembly
- Thermal Gelation
- Nanoparticle Albumin-Bound Technology (NAB-technology)
- Nanospray Drying
In addition to the special methods mentioned earlier, we offer additional techniques for creating albumin nanoparticles as needed. We can also customize the surface of these nanoparticles with modifications such as altered cell-penetrating peptides, adjustments using natural substances, and other functional changes.
Our Analytical Capabilities for Albumin Nanoparticle
The durability of albumin nanoparticles over an extended period of storage can be assessed by observing alterations in their form, size, zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, drug content, in vitro drug release, and overall appearance over time. We offer an array of analyses and characterizations for albumin nanoparticles including:
- Shape
- Particle Size and Distribution
- Zeta Potential
- Encapsulation Efficiency
- Drug Loading
- In Vitro Drug Release
- Stability
Why Choose Us to Develop Albumin Nanoparticles?
- We have profound professional knowledge in the exploration and research of preparation methods of albumin nanoparticles, including coacervation or desolvation, emulsification, self-assembly, thermal gelation, NAB-technology, nanospray drying, etc.
- Our team of experts utilizes advanced equipment and instruments to deliver high-quality and impactful solutions for albumin nanoparticle development, including formulation design and optimization, albumin nanoparticle fabrication and modification, and quality control and evaluation.
- Our excellent project management process is a major guarantee for the rapid advancement of your project. During the process of advancing the project, we have a dedicated person feedback on the project's progress to you as soon as possible, so that you can always have control of the project.
Published Data
Technology: Chemometric technique for preparation of human serum albumin nanoparticles (HSA)
Journal: Journal of Nanostructure in Chemistry
IF: 10.7
Published: 2017
Results:
The authors applied chemometric methods for size optimization of human serum albumin (HSA) nanoparticles. The influence of three experimental parameters, such as pressure (P) or power, organic solvent volume (V) and time (T), under sonication and high-pressure homogenization, was studied using multivariate analysis. The method was optimized in response to the size of the nanoparticles.
CD Formulation is a leader in the development of albumin nanoparticle formulations. And our team can quickly respond to the different needs of customers in albumin nanoparticle development services. If you need our services, please contact us via phone or email, and our team will respond to you within three business days.
References
- Elmira Karami, Mahdi Behdani, Fatemeh Kazemi-Lomedasht. Albumin nanoparticles as nanocarriers for drug delivery: Focusing on antibody and nanobody delivery and albumin-based drugs. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology. 2020, 55:101471.
- Nastaran Hosseinifar, Amir Abdolah Mehrdad Sharif, Navid Goodarzi, et al. Preparation of human serum albumin nanoparticles using a chemometric technique. Journal of Nanostructure in Chemistry. 2017,7:327-335.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Albumin can bind to a broad range of molecules. (Elmira Karami, et al. 2020)
Fig.1 Albumin can bind to a broad range of molecules. (Elmira Karami, et al. 2020) Fig.2 Advantages of albumin nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 Advantages of albumin nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers. (CD Formulation)