Thin-Film Hydration Method for Liposome Preparation
Inquiry
Also known as the Bangham method, the thin-film hydration (TFH) technique is widely recognized for its versatility in preparing liposomes with various structural and functional properties. This method is highly effective for creating heterogeneous liposomes, meeting a broad range of research and development requirements. CD Formulation excels in leveraging this technique to support R&D initiatives in the pharmaceutical industry.
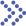
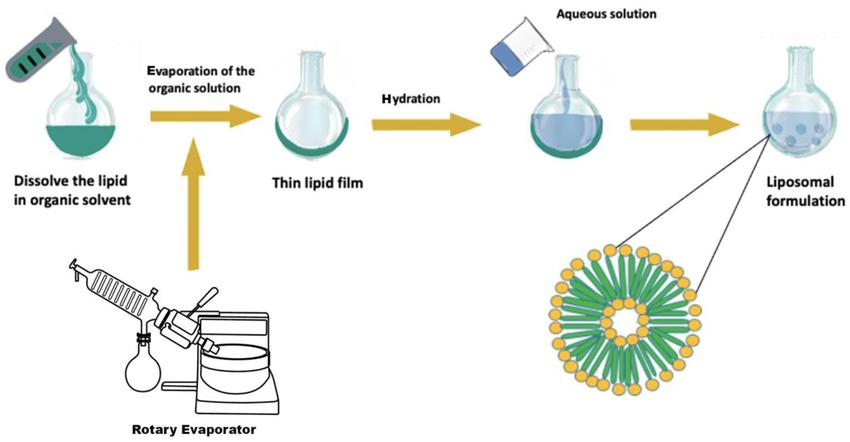 Fig.1 Thin film hydration method for empty liposome preparation. (Jaradat, Eman, et al, 2021)
Fig.1 Thin film hydration method for empty liposome preparation. (Jaradat, Eman, et al, 2021)
What is the Thin-Film Hydration Method for Liposome Preparation?
The thin-film hydration method commonly refers to as the Bangham method. This technique represents the most established approach for liposome preparation. This process begins by dissolving the phospholipids in an organic solvent. The solvent is evaporated under reduced pressure to form a thin lipid membrane. Next, a suitable aqueous medium is introduced. When the temperature reaches the phase transition point of the phospholipids, the lipid membrane absorbs water and separates, naturally assembling into a closed spherical structure, which we call a liposome. This method is straightforward and easily executed, achieving nearly 100% encapsulation efficiency for most lipophilic drugs. However, it tends to produce liposomes with a heterogeneous size distribution; thus, necessitating size control measures such as polycarbonate membrane extrusion or homogenization techniques. Furthermore, maintaining sterile conditions throughout the procedure is essential to ensure product sterility.
Our Thin-Film Hydration Services for Liposome Development
Based on this method, we first systematically study the properties of drugs and then carry out formulation development research.
The liposomes generated by this method exhibit a heterogeneous size distribution. We employ size control techniques, such as polycarbonate membrane extrusion and homogenization, to regulate the dimensions of the liposomes while maintaining sterility throughout the process to ensure product sterility.
We provide professional and systematic analysis for liposomes such as size, potential, encapsulation efficiency, viscosity, etc.
Our Expertise in Thin-Film Hydration Liposome Preparation
| Techniques and Platforms |
Specifics |
| Freeze-thaw Techniques |
- Temperature, humidity, time, frequency of screening
- Curve study
- Freezing point study
- Effects of freeze-thaw on physicochemical properties of liposome samples
|
| Analysis Platform |
- Size
- Potential
- Condensation phenomenon
- The rupture of liposomes and the changes in the encapsulation rate
|
Why Choose CD Formulation?
Liposome Thin-Film Hydration Techniques
- Proficient in liposome thin-film hydration (TFH) preparation technique
- Formulation development capability
- Process optimization capability
- Size control capability
Powerful Thin-Film Hydration Platforms
- Advanced process equipment to meet all stages of research and development
- Systematic analysis platform to meet the physical, chemical, and biological characterization
A Great and experienced Team
- Successfully provided vital support to numerous corporations and academic institutions, enabling them to delve deeply into liposome thin-film hydration (TFH) preparation techniques.
- We have a great team for liposome preparation and physical and chemical analyses.
Published Data
Technology: modified thin film hydration (MTFH) technique
Journal: International Journal of Pharmaceutics
IF: 10.7
Published: 2022
Results: In this study, the authors developed a straightforward industrial method to produce ART-GPC liposomes. Conventional techniques for synthesizing ART-GPC liposomes, such as thin-film hydration, ethanol injection (EI), and freeze-drying (FD), have yielded products with suboptimal physical and chemical properties. The authors validated the scalability and reproducibility of the MTFH technology. This represents the first report demonstrating that the MTFH method can effectively preserve liposomes in a dry film state while allowing in situ rehydration within the injection bottle, exhibiting excellent performance. In conclusion, the MTFH method emerges as a promising technology for the large-scale production of ART-GPC liposomes. The structural integrity of liposomes produced in small-scale bottles indicates significant potential for commercial manufacturing. Quality design strategies—including solvent selection, pressure application, hydration duration, and temperature control—were implemented to achieve optimal physical and chemical characteristics along with favorable production conditions.
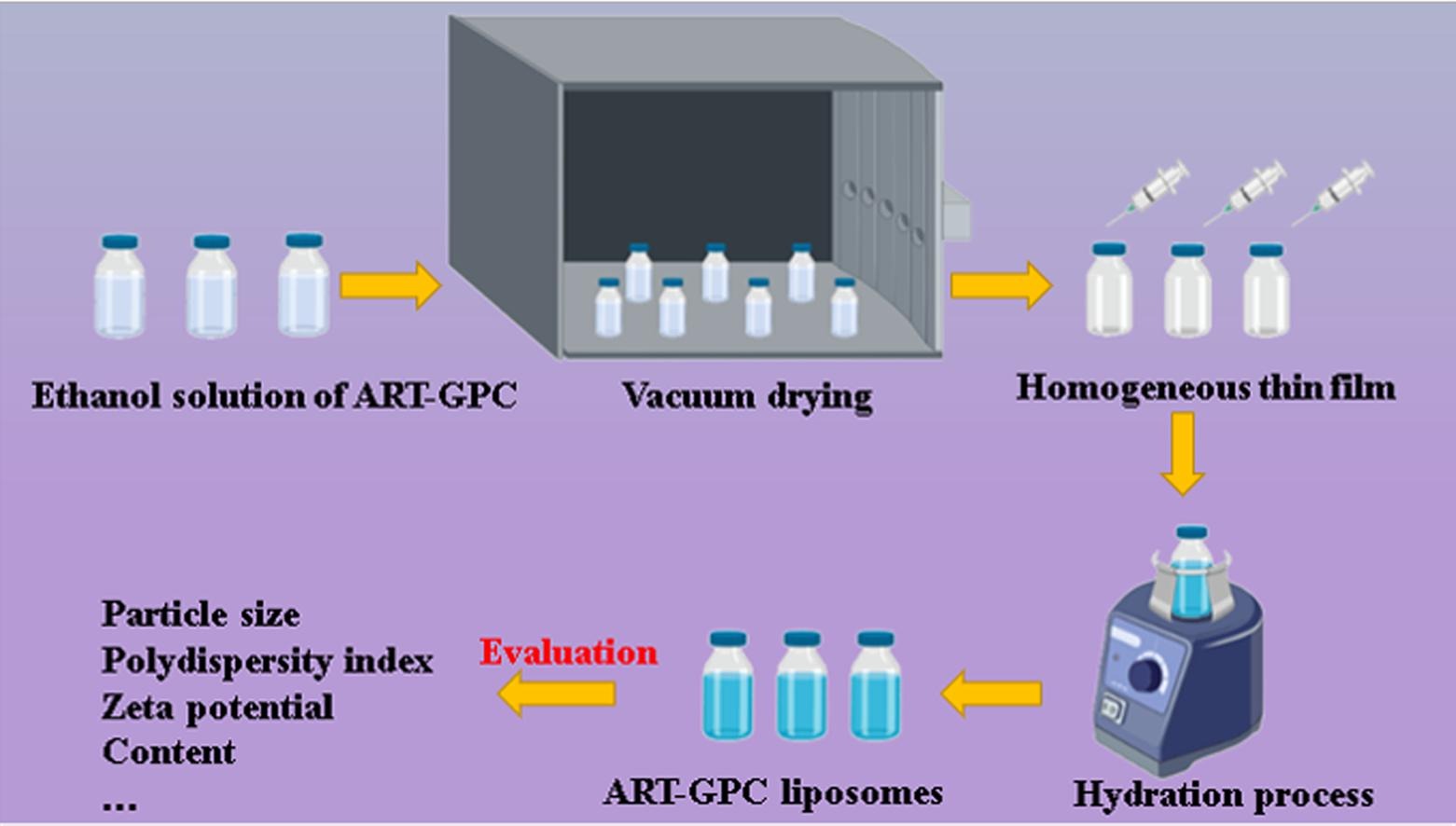 Fig.2 A modified thin film method for large-scale production of dimeric artesunate phospholipid liposomes and comparison with conventional approaches. (Wang J, et al. 2022)
Fig.2 A modified thin film method for large-scale production of dimeric artesunate phospholipid liposomes and comparison with conventional approaches. (Wang J, et al. 2022)
CD Formulation specializes in providing customized solutions for liposome preparation using the thin-film hydration technique. Our services are designed to meet the unique demands of pharmaceutical companies and research institutions, ensuring high-quality liposome production for diverse applications. Contact us for expert assistance in your liposome development projects.
References
- Jaradat, Eman & Weaver, Edward & et al. Microfluidics Technology for the Design and Formulation of Nanomedicines. Nanomaterials. 2021. 11. 3440. 10.3390.
- Wang J, He W, et al. A modified thin film method for large scale production of dimeric artesunate phospholipid liposomes and comparison with conventional approaches. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2022 May 10; 619: 121714.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services


 Fig.1 Thin film hydration method for empty liposome preparation. (Jaradat, Eman, et al, 2021)
Fig.1 Thin film hydration method for empty liposome preparation. (Jaradat, Eman, et al, 2021) Fig.2 A modified thin film method for large-scale production of dimeric artesunate phospholipid liposomes and comparison with conventional approaches. (Wang J, et al. 2022)
Fig.2 A modified thin film method for large-scale production of dimeric artesunate phospholipid liposomes and comparison with conventional approaches. (Wang J, et al. 2022)