Ocular Liposome Formulation Development
Inquiry

CD Formulation has accumulated extensive expertise in the development of liposome formulations. Currently, we possess the capability to encapsulate diverse drug molecules, including both small molecule drugs and macromolecular biological drugs, for various therapeutic categories. In our pursuit of ocular liposome development, we have consistently tackled challenges and successfully assisted numerous clients in resolving related issues. These include enhancing corneal adhesion and penetration of ocular liposomes, prolonging intravitreal half-life, as well as achieving targeted delivery through surface modification technology. Over the years, we have remained committed to innovation and leveraged cutting-edge technologies to explore the potential of next-generation liposome delivery systems in ocular formulations.
Why Develop Ocular Liposome Formulations?
The eye is a highly intricate organ with multiple protective barriers that maintain its integrity and prevent infection. These properties also pose challenges for drug delivery to the desired therapeutic targets. Despite the availability of effective ocular formulations in the market, their bioavailability is typically below 5%, resulting in unsatisfactory therapeutic efficacy. Therefore, developing ocular liposomes presents significant challenges, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of both static and dynamic ocular barriers. Common routes for delivering drugs to treat ocular diseases include topical, systemic, periocular, and intravitreal administration. Topical administration is preferred due to its high patient compliance and minimal invasiveness. However, it exhibits poor bioavailability in posterior ocular tissues. Intravitreal administration requires frequent dosing and carries risks such as vitreous hemorrhage, retinal detachment, and endophthalmitis. Systemic administration often necessitates high doses leading to serious side effects. The development of a long-acting targeted ocular liposome drug delivery system is currently imperative, as it can effectively mitigate side effects, enhance drug half-life, and facilitate precise drug delivery to the retina.
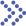
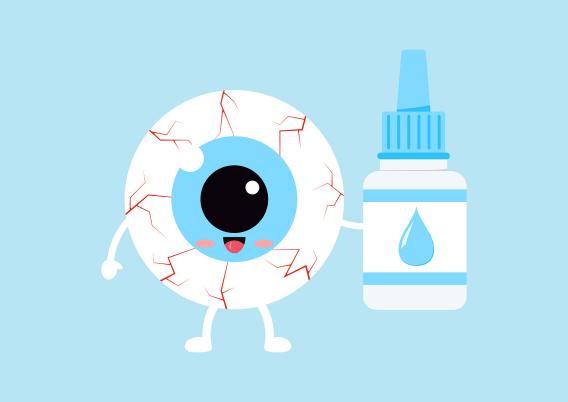
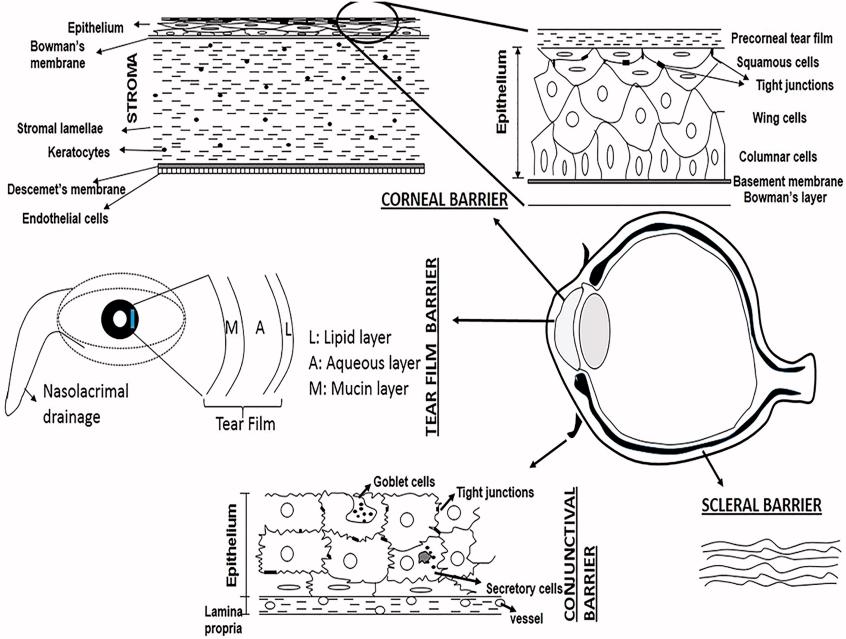 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the barriers for absorption of topically administered drugs. (Agarwal, R., et al., 2016)
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the barriers for absorption of topically administered drugs. (Agarwal, R., et al., 2016)
Explore Our Ocular Liposome Formulation Development Services
When designing ocular liposome formulations, it is crucial to consider the physiological and physicochemical properties of different components in the intraocular environment. Our development services encompass all aspects of ocular liposome formulation development, including design, preparation, characterization, and tolerance assessment. We aim to provide customers with comprehensive solutions through our professional team and advanced equipment for efficient high-quality ocular liposome formulation development. Our services include but are not limited to:
- Screening for an ocular liposome delivery system: the liposomes are categorized into unicellular and multicellular types. Based on the customer's provided information, we screen and recommend the appropriate type of liposome.
- Formulation development and optimization: based on various delivery routes, the formulation design is tailored to specific raw material ratios and surface modification screening preparation schemes.
- Evaluating and characterizing services: comprehensively to deliver high-quality and efficient ocular liposomes.
- Consulting and technical support: our team of scientists can provide you with professional technical support services or answer your questions about your project.
General Workflow of Ocular Liposome Formulation Development
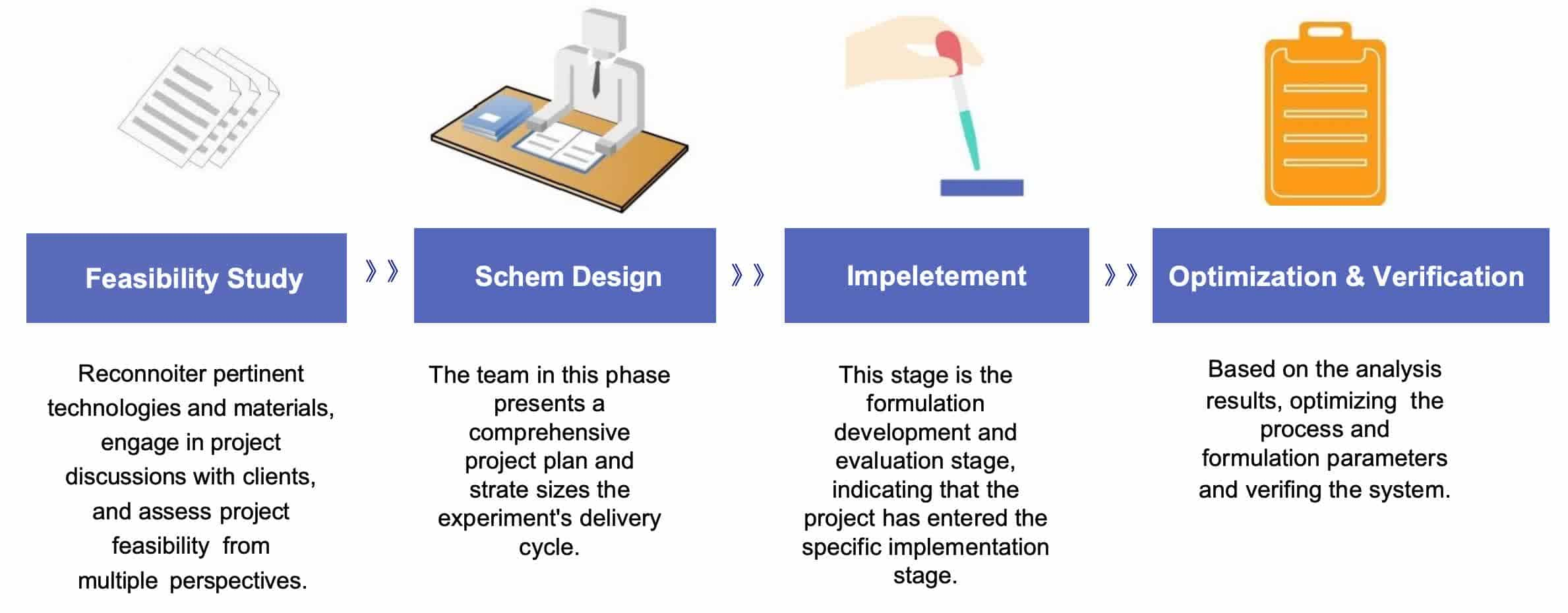 Fig.2 The workflow of ocular liposome formulation development. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 The workflow of ocular liposome formulation development. (CD Formulation)
Our Platforms for Ocular Liposome Formulation Development
| Penetration Enhancement Technology |
Screening of viscosifying polymers or penetration enhancer such as polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), methylcellulose, hydroxyethyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and hydroxypropyl cellulose, buffer screening, etc. |
| Particle Size and Charge Control |
The drug delivery efficiency of liposomes is influenced by their size and charge, which can be regulated through particle size control technology or the selection of liposome systems with varying particle sizes to cater to different therapeutic requirements. |
| Aseptic Technology |
The quality and safety of ocular formulations are subject to stricter control measures. Aseptic technique stands as a pivotal factor in this regard. |
| In Vitro and In Vivo Assessment |
In vitro and in vivo pharmacodynamics, tolerance, stability assessment. In vitro evaluation mainly evaluates the liposome dosage form of eye from the perspective of model and cell. |
Our Advantages in Ocular Liposome Formulation Development
- Comprehensive Expertise. Our team of highly skilled scientists and engineers has extensive experience in the development and manufacturing of ocular liposome formulations.
- Cutting-edge Technology. Our facility is equipped with advanced liposome production systems, analytical instruments, and clean rooms, enabling us to deliver products that are both efficient and cost-effective.
- Customized Solutions. Our team works closely with customers to understand their goals and deliver optimal results.
- Stringent Quality Control. We apply strict quality control measures throughout the development and manufacturing process.
- High efficiency. Our project management and streamlined processes enable us to efficiently deliver.
Published Data
Technology: Cationic liposome Technology in Ocular Liposome Formulation
Journal: Drug Delivery and Translational Research
IF: 5.4
Published: 2022
Results: In this study, the author prepared liposomal formulations containing timolol maleate (TM) and brimonidine tartrate (BT) using thin-layer hydration. After necessary evaluation, such as drug loading percentage, particle size, pH, zeta potential, and drug release, the optimal formulation was selected. And finally, the study on lowering intraocular pressure was conducted for the optimized formulation.
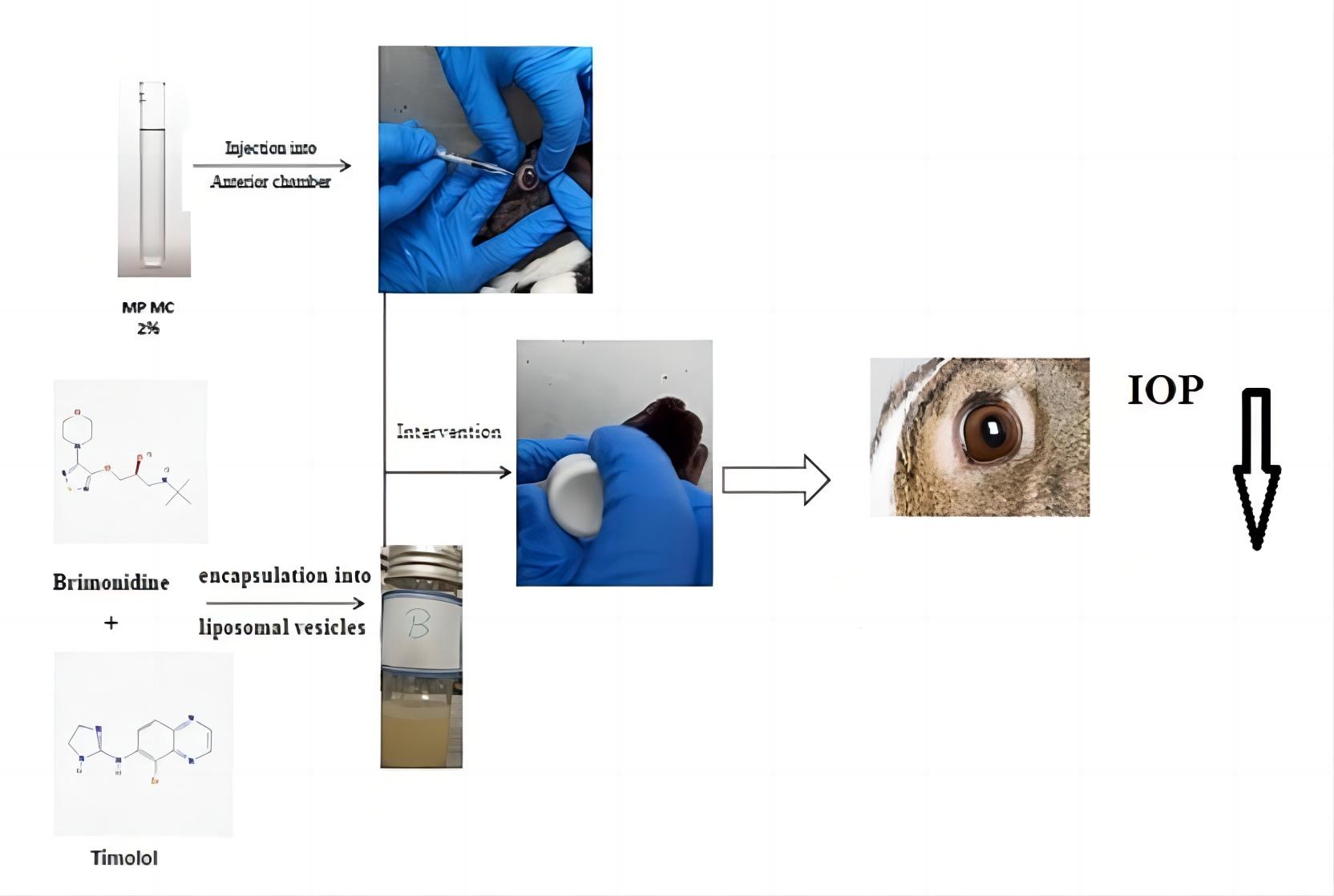 Fig.3 Development process for ocular liposome formulation with timolol maleate and brimonidine tartrate. (bigdeli, A., et al., 2022)
Fig.3 Development process for ocular liposome formulation with timolol maleate and brimonidine tartrate. (bigdeli, A., et al., 2022)
CD Formulation is composed of a group of scientists who are dedicated to research and are dedicated to overcoming various difficulties that may arise during the development of ocular liposomes. If you have any specific needs, feel free to contact us. Our team is available to assist you with consultations.
References
- Mishra GP, Bagui M, et al. Recent applications of liposomes in ophthalmic drug delivery. J Drug Deliv. 2011, 2011: 863734.
- Agarwal, R., Iezhitsa, I., et al. Liposomes in topical ophthalmic drug delivery: an update. Drug Delivery, 2016, 23(4), 1075–1091.
- bigdeli, A., Makhmalzadeh, B.S., et al. Cationic liposomes as promising vehicles for timolol/brimonidine combination ocular delivery in glaucoma: formulation development and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. 2023, 13, 1035–1047.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services