Lyophilized Liposome Residual Moisture Analysis
Inquiry
Lyophilization, or freeze drying, is used to stabilize pharmaceutical formulations and increase shelf life by removing water from pharmaceutical products. During the freeze-drying process, the drug formulation is initially subjected to freezing, followed by ice removal through sublimation under vacuum in the primary drying stage. A secondary drying stage is then used to remove the unfrozen water molecules at a higher temperature than the primary drying. The drug freeze-drying cycle is designed to remove most of the loosely bound water. Liposomes must uphold a heightened level of functionality in the product. CD Formulation has rich experience and an advanced technology platform in water residue analysis of lyophilized liposomes, and we are committed to providing customers with professional technical support and accurate analysis results.
Why Conduct Lyophilized Liposome Residual Moisture Analysis?
Determining the residual moisture content of lyophilized liposomes is important for several reasons. First, residual water content is related to the formula stability during the product's shelf life. Liposomal preparations containing small molecules can have a direct degradation pathway triggered by water, and all end products must fall below the specified residual moisture specifications. In general, the degradation pathway of macromolecular liposomal preparations is more complex, and water often plays an indirect role. Secondly, moisture analysis of the statistically relevant sample set can provide insight into the freeze-drying process. Residual moisture determination can be used as a tool for process studies to confirm the efficiency, consistency, and robustness of a particular freeze-drying cycle designed for a particular drug formulation. A typical drug freeze-drying cycle typically targets 1% to 3% residual moisture content.
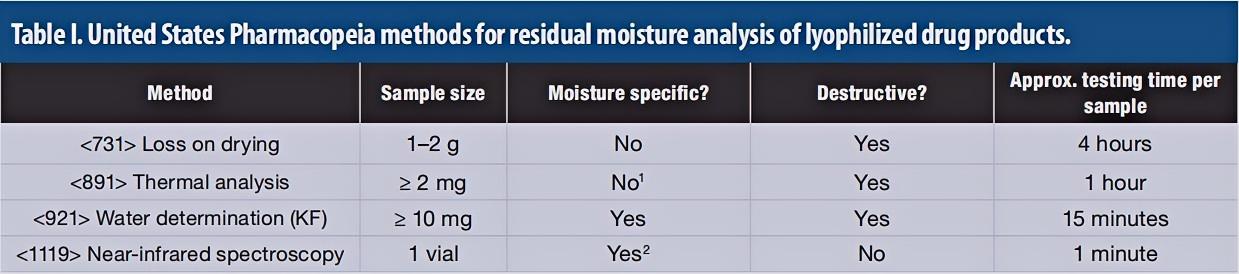 Table 1. USP methods for residual moisture analysis of lyophilized drugs. (Elizabeth Joseph, 2019)
Table 1. USP methods for residual moisture analysis of lyophilized drugs. (Elizabeth Joseph, 2019)
Our Services for Lyophilized Liposome Residual Moisture Analysis
The moisture content of the freeze-dried product will directly affect the glass transition of the sample. The glass transition will affect the softening of the material on a macro level, which will affect the long-term stability of the product and the maximum storage temperature of the product. At the same time, the control of moisture in the product and the pursuit of uniformity of moisture content are of great significance for quality control and beneficial to the subsequent documentation work. We will provide you with the following types of services:
- Lyophilized liposome moisture analysis. We offer traditional methods, such as Karl Fisher coulometric titration, thermo-gravimetric analysis (TGA), near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy, and frequency modulation spectroscopy (FMS). We also offer new technologies: headspace vapor measurement method.
- Study on water release standard of lyophilized liposome products. Freeze-drying machine on-line sampling method.
- Rubber plug moisture test. Freeze-dried powder bottles are often easily atomized, so we offer humidity testing at the plug.
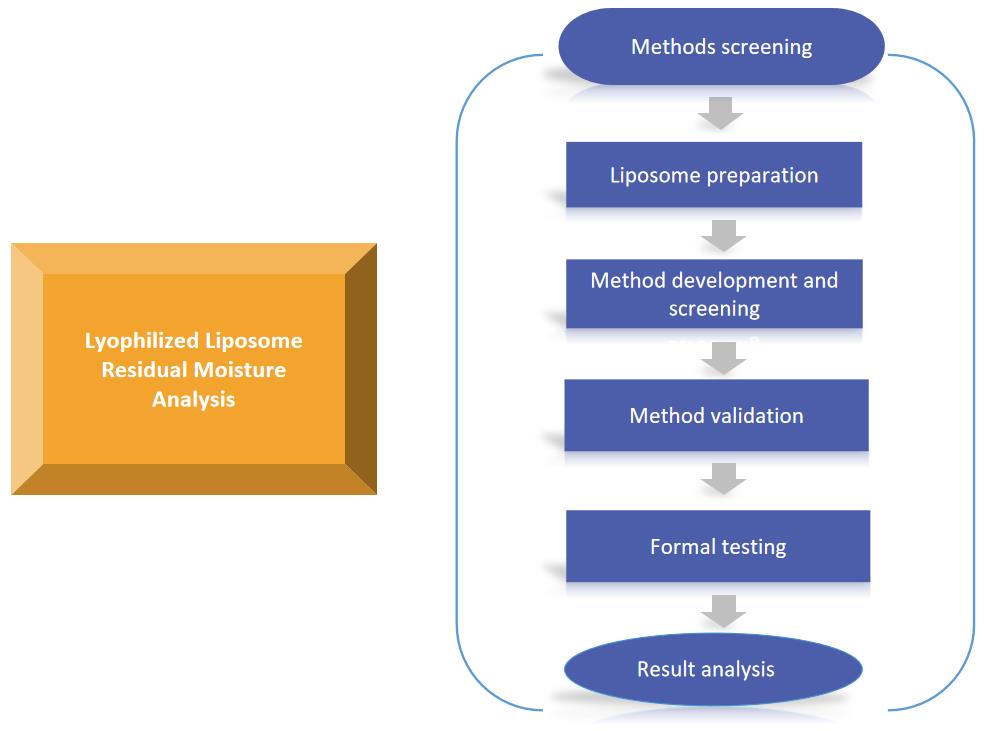 Fig.2 Workflow of lyophilized liposome residual moisture analysis. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 Workflow of lyophilized liposome residual moisture analysis. (CD Formulation)
Our Platforms for Lyophilized Liposome Residual Moisture Analysis
| Techniques |
Detailed Information |
| Karl Fisher coulometric titration technique |
- Chemical analysis method
- It targets water molecules, so it's more accurate.
- The principle is a REDOX reaction, which involves the chemical measurement of equal amounts of iodine and water and then measurement by volume or coulomb to get the result.
|
| Thermo-gravimetric analysis (TGA) technique |
- Measures weight-related quantities (such as mass, solids residue or residue rate, etc.) of the sample being analyzed as a function of temperature or time within a temperature range controlled by a specified procedure.
- Used in conjunction with KF titration to ensure that the weight change must be caused by moisture.
|
| Near-infrared (NIR) technique |
- By comparing the reflected radiation of a sample with a standard reference of the same wavelength, the analysis of residual moisture can be quickly completed.
- This method requires calibration work, and once calibrated, NIR is a very efficient analysis method.
|
| Frequency modulation spectroscopy (FMS) technique |
- By tuning the FMS instrument's near-infrared laser to 1382 nm (the internal absorption frequency of the selected vibrational transition of water vapor).
- By measuring the headspace vapor pressure inside the sample bottle and creating a moisture prediction model.
- The result represents active water, and this technique can be used to explore various forms of water.
- Compared with NIR, the accuracy of FMS under 1% moisture is more reliable.
|
| Headspace technique |
- Fast nondestructive analysis method
- Related to the degradation of API, which means that the stability of the freeze-dried product can be defined in terms of the water vapor pressure in the sealed vial.
|
Our Key Advantages in Lyophilized Liposome Residual Moisture Analysis
- Scientific and comprehensive. Scientific and comprehensive management system, rigorous experimental program to ensure accurate analysis results for customers.
- Rapid. To deliver accurate results in the shortest possible time.
- Advanced. The provision of professional facilities and technology platforms is a cornerstone of our commitment to customer satisfaction.
Published Data
Technology: Lyophilized liposome residual moisture analysis technique
Journal: Food Bioscience
IF: 5.6
Published: 2023
Results: Water content is an important index of "dry" plant bodies, and the decrease of water content will lead to the increase of stability of plant bodies. The ROPA: PC ratios used in this study were 1:2, 1:4, and 1:6, respectively. The authors performed statistical comparisons of RNP samples. The moisture content of RNP powder is between 4.42% and 5.46%. As the concentration of phospholipids increases, the water content decreases, and the study identified several freeze-dried liposome drug formulations with water content ranging from 1.5% to 6.5%. In contrast to water content, the water solubility index increased with the increase of phospholipid ratio (p > 0.05), but the difference was insignificant.
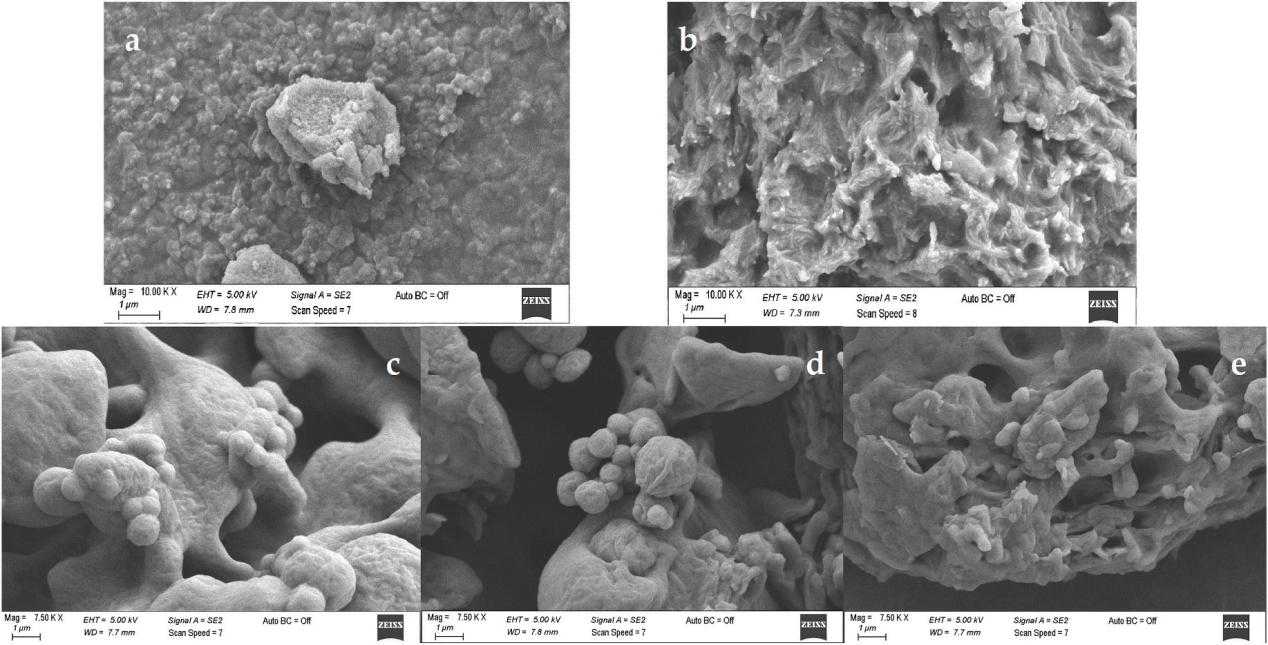 Fig.3 SEM photographs of liposomes. (Oya Irmak Sahin, et al., 2021)
Fig.3 SEM photographs of liposomes. (Oya Irmak Sahin, et al., 2021)
CD Formulation has developed a complete lyophilized liposome analysis platform and process to provide customers with tailor-made comprehensive analysis solutions and accurate and reliable data. If you need any help, please contact us immediately.
References
- Elizabeth Joseph. Residual Moisture Determination in Lyophilized Drug Products. Pharmaceutical Technology. 2019, November. Vol. 43. No. 11. Pages: 30–39, 56.
- Oya Irmak Sahin, Ayse Neslihan Dundar, et al. Lyophilized nano-liposomal system for red onion (Allium cepa L.) peel anthocyanin: Characterization, bioaccessibility and release kinetics. Food Bioscience. 2023. Volume 53. 102702.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services


 Table 1. USP methods for residual moisture analysis of lyophilized drugs. (Elizabeth Joseph, 2019)
Table 1. USP methods for residual moisture analysis of lyophilized drugs. (Elizabeth Joseph, 2019) Fig.2 Workflow of lyophilized liposome residual moisture analysis. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 Workflow of lyophilized liposome residual moisture analysis. (CD Formulation) Fig.3 SEM photographs of liposomes. (Oya Irmak Sahin, et al., 2021)
Fig.3 SEM photographs of liposomes. (Oya Irmak Sahin, et al., 2021)