Liposome Phase Transition Temperature Analysis
Inquiry
The phase transition temperature of the lipid membrane affects the stability of the lipid bilayer membrane, and appropriate methods should be selected for study (such as differential scanning calorimetry, etc.). At CD Formulation, with years of experience in liposome research, our scientists are confident that they can provide comprehensive liposome products and services through our advanced liposome platform. Liposome phase transition temperature analysis plays an indispensable important role in the characterization of liposomes. We are committed to providing high-quality service to high-efficiency enterprise customers worldwide.
The Importance of Liposome Phase Transition Temperature Analysis
The phase transition temperature of liposomes is determined by the composition of phospholipids, and higher temperatures result in stiffer liposomes. Liposomes with different phase transition temperatures exhibit varying degrees of deformation during diffusion. When the phase transition temperature approaches ambient temperature, liposomes acquire an optimal level of stiffness and can adopt a "pseudo-rod-like" structure, which greatly enhances their ability to overcome multiple physiological barriers. Liposomes with excessively high phase transition temperatures lack deformability, while those with excessively low temperatures become trapped in the "mucin grid" due to excessive deformation.
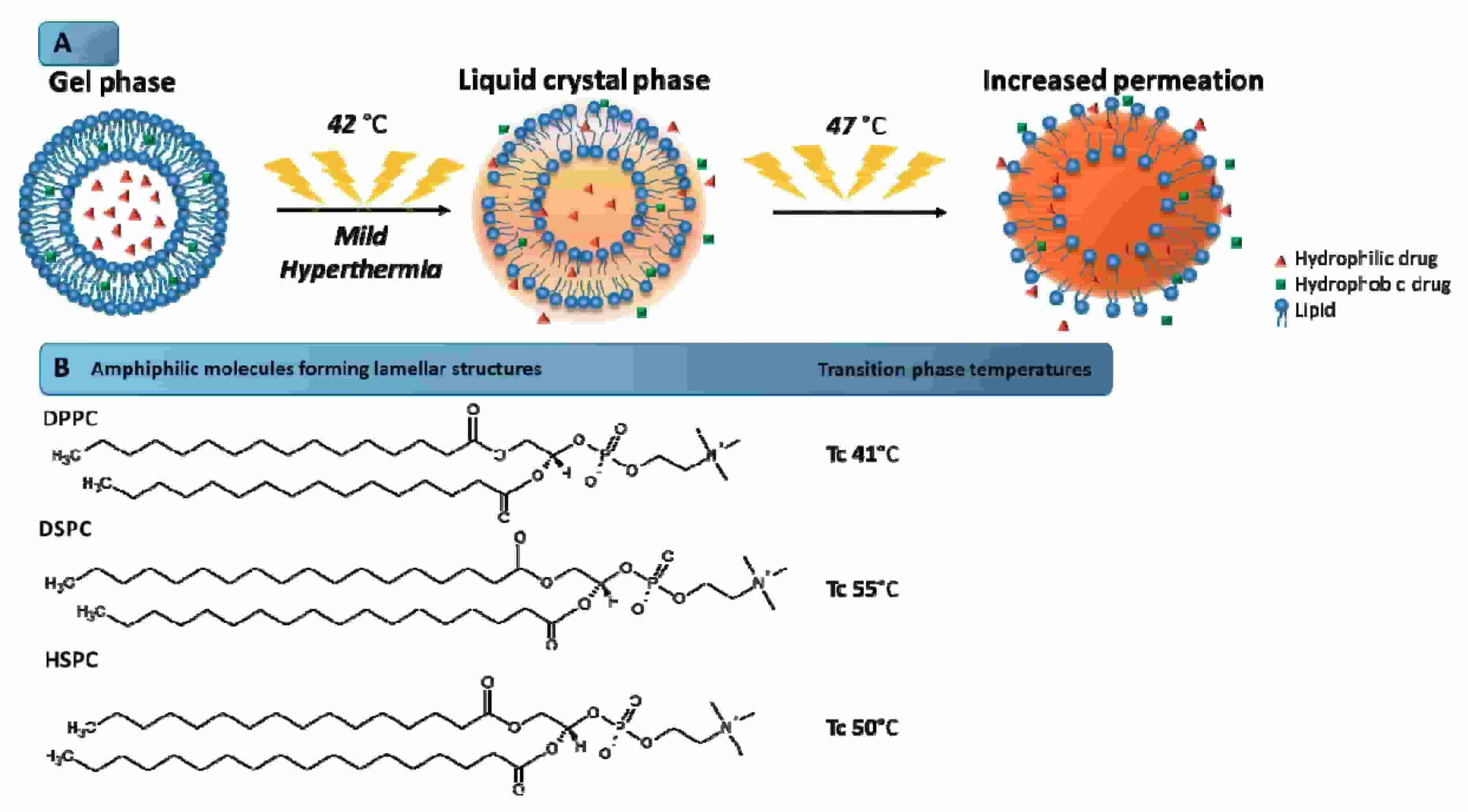 Fig.1 Schematic illustration of the mechanism of phase transition of the lipids that form the liposome bilayer. (Pereira Gomes I, et al., 2019)
Fig.1 Schematic illustration of the mechanism of phase transition of the lipids that form the liposome bilayer. (Pereira Gomes I, et al., 2019)
What Can We Do About Liposome Phase Transition Temperature Analysis?
Analysis of Phase Transition Temperature Analysis
We can offer a wide range of instruments for the analysis of liposomal phase transition temperature, primarily encompassing various spectroscopic and optical techniques, including nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), X-ray diffraction, electron microscopy, infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, fluorescence analysis, and differential thermal analysis.
Solutions for Liposome Phase Transition Temperature
Temperature-sensitive liposomes consist of temperature-sensitive phospholipids. In order to avoid premature drug release, the phase transition temperature of the liposomes should be higher than the normal body temperature of 37 °C. In order to avoid damage to human health tissue caused by excessive temperature, the phase transition temperature of liposomes should be lower than 45 °C. In the design of heat-sensitive liposomes, hemolytic lipids can also be added to reduce the phase transition temperature of the liposomes to 39-40 °C, and the average 20-30s mild high heat can complete 50% drug release. In this service, we screen for clients the phospholipid ratio suitable for the phase transition temperature, to meet the your requirements for the liposome phase transition temperature. The preservation condition, in vivo process and drug release behavior of liposomes will be fully considered to select phospholipids with suitable phase transition temperature. We also can design temperature-sensitive liposomes for you.
Our Workflow of Liposome Phase Transition Temperature Analysis
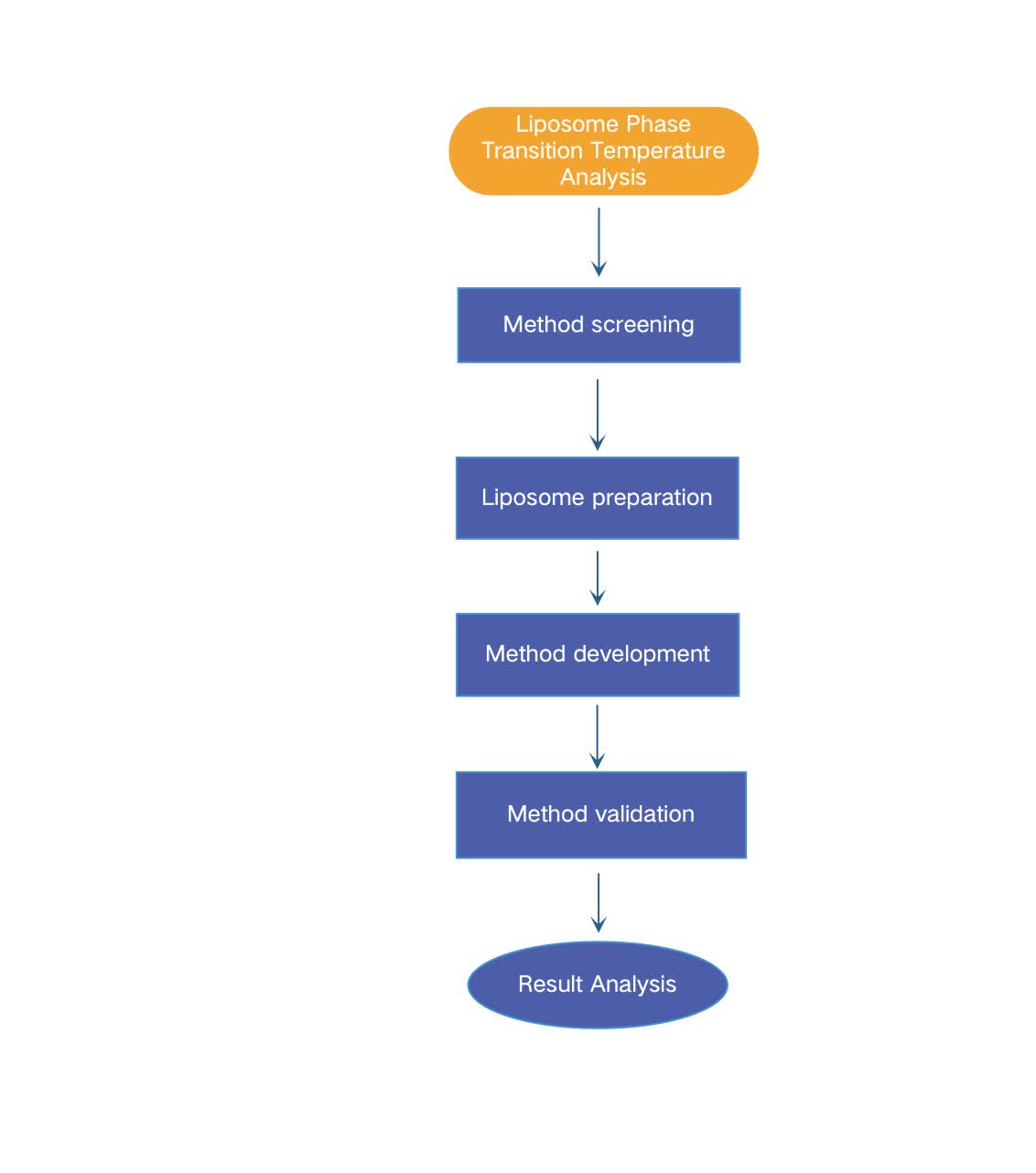 Fig.2 Workflow of liposome phase transition temperature analysis. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 Workflow of liposome phase transition temperature analysis. (CD Formulation)
Our Platform for Liposome Phase Transition Temperature Analysis
| Platforms |
Specifics |
| Analysis Platform |
- nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR),
- electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR),
- X-ray diffraction,
- electron microscopy,
- infrared spectroscopy,
- Raman spectroscopy,
- fluorescence analysis,
- differential thermal analysis.
|
Our Advantages in Liposome Phase Transition Temperature Analysis
- Efficient service. Our whole process of liposome phase transition temperature analysis service is completed efficiently and quickly.
- Rigorous standard. Our aim is to establish rigorous and scientifically sound test standards for the analysis of liposomal phase transition temperature, and effectively implement them.
- Advanced technologies. Our platform is equipped with all the relevant advanced equipment and technology platforms for liposomal phase transition temperature analysis.
Published Data
Technology: Combination techniques of ATR-FTIR, CD, DSC and fluorescence spectra
Journal: Chemistry and Physics of Lipids
IF: 7.4
Published: 2023
Results: In this study, the authors combined spectral methods, including ATR-FTIR spectroscopy, circular dichroism, ultraviolet spectroscopy, and fluorescence spectroscopy, to determine the fine structure of the moxifloxin-liposome complex, the location of the drug in the bilayer, and the major sites of MOX-lipid membrane interaction. The lipid composition of liposomes plays a key role in the interaction with moxifloxacin, greatly influencing the loading efficiency, strength and characteristics of drug binding, lipid phase separation and phase transition parameters. The behavior of moxifloxin-liposome complex during double-layer phase transition by DSC showed that in the DPPC/CL2− liposome system, two microphases with different CL2- content coexist, and Mox interacts with these two microphases, resulting in the formation of two microphases. Complex types with different structures and phase transition temperatures. This binding stabilizes the gel state of the lipid bilayer and increases the phase transition temperature Tm to 3−5 °C.
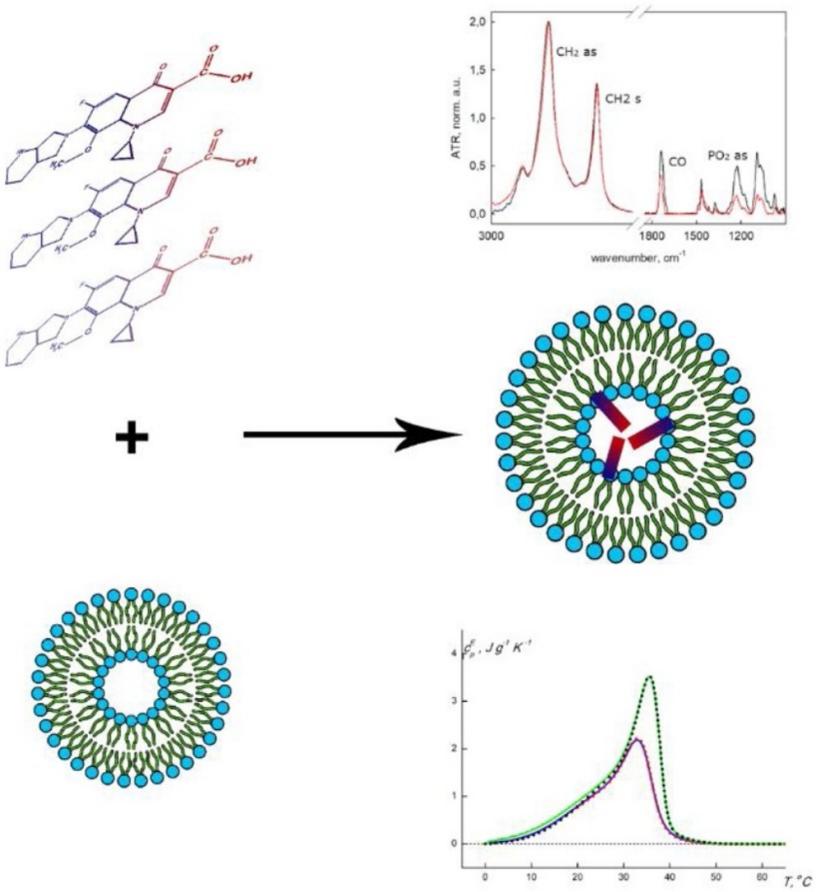 Fig.3 Schematic illustration mechanism of interaction between Mox and lipid bilayer. (Irina M. Le-Deygen, et al., 2023)
Fig.3 Schematic illustration mechanism of interaction between Mox and lipid bilayer. (Irina M. Le-Deygen, et al., 2023)
CD Formulation offers a complete toolbox for the temperature analysis and characterization of liposomal phase transitions, including all of the above methods. Our services are highly cost-effective and have a fast turnaround time. For each project, we will generate a comprehensive documentation package to provide publishable images and experimental steps. Please contact us to share more information about your research.
References
- Pereira Gomes I, Aparecida Duarte J, et al. Thermosensitive Nanosystems Associated with Hyperthermia for Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceuticals. 2019; 12(4):171.
-
Irina M. Le-Deygen, Anna A. Skuredina, et al. Yakimov, Ilya M. Kolmogorov, Daria M. Deygen, Tatiana V. Burova, Natalia V. Grinberg, Valery Y. Grinberg, Elena V. Kudryashova, Moxifloxacin interacts with lipid bilayer, causing dramatic changes in its structure and phase transitions. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids.2020. Volume 228, 104891.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services


 Fig.1 Schematic illustration of the mechanism of phase transition of the lipids that form the liposome bilayer. (Pereira Gomes I, et al., 2019)
Fig.1 Schematic illustration of the mechanism of phase transition of the lipids that form the liposome bilayer. (Pereira Gomes I, et al., 2019) Fig.2 Workflow of liposome phase transition temperature analysis. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 Workflow of liposome phase transition temperature analysis. (CD Formulation) Fig.3 Schematic illustration mechanism of interaction between Mox and lipid bilayer. (Irina M. Le-Deygen, et al., 2023)
Fig.3 Schematic illustration mechanism of interaction between Mox and lipid bilayer. (Irina M. Le-Deygen, et al., 2023)