Liposomal formulations typically consist of active pharmaceutical ingredients, structural and functional components, and various excipients. Impurities within these formulations can compromise the structure and stability of liposomes or pose potential health risks. Rigorous analysis and regulation of these impurities are essential to ensure the quality, safety, and efficacy of liposome-based products. CD Formulation is committed to providing meticulous and professional liposome impurity analysis services tailored to meet the needs of pharmaceutical companies and research institutions. Our expertise ensures precise identification and regulation of impurities to enhance formulation quality and safety.
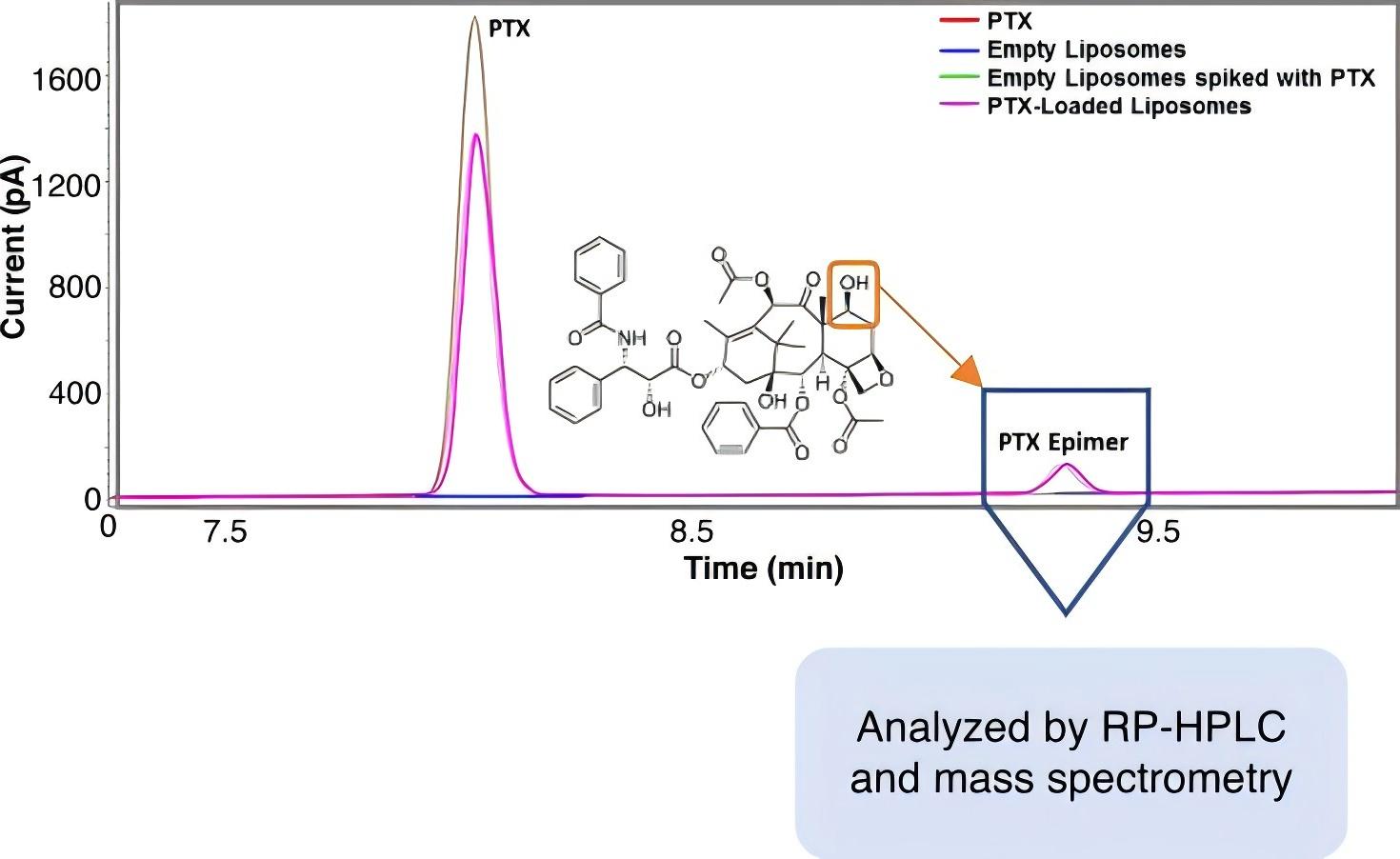 Fig.1 PTX-Loaded liposome analyzed by RP-HPLC and mass spectrometry. (Clogston JD, 2022)
Fig.1 PTX-Loaded liposome analyzed by RP-HPLC and mass spectrometry. (Clogston JD, 2022)
Why is Liposome Impurity Analysis Needed?
Analyzing impurities is important when it comes to understanding liposomes. We call substances that impact the purity of a drug compound 'impurities'. These impurities can be grouped into three categories: organic, inorganic, and residual solvents according on their physical and chemical properties. Additionally, we can categorize them by toxicity into general impurities and mutagenic ones. Lastly, we can also sort them by their origin into process-related impurities and degradation-related ones. Process-related impurities include leftover starting materials, reagents, intermediates, and by-products. On the other hand, degradation products form as the drug breaks down through processes like hydrolysis, oxidation, ring-opening reactions, or polymerization. Therefore, stringent impurity management within liposome formulations is essential for the quality requirement of raw materials and excipients.
Comprehensive Liposome Impurity Analysis Services
Identification of Raw Materials and Excipients
We employ a range of analytical techniques. They include HPLC, LC-MS, and H-NMR, to identify the components of liposome formulations. By integrating analysis results like retention time, molecular weight, and NMR data, we assist our clients in accurately identifying these components. We also employ the GPC method to assess the molecular weight and dispersity of PEG-lipid.
Raw Materials and Excipients Purity Testing
We have established a range of detection methodologies to assess the purity of liposome components, including the application of UPLC-CAD technology for evaluating the purity of cationic lipids.
Control of Raw Material Impurities
Certain critical impurities in liposomes warrant meticulous monitoring, particularly the mono-fatty acid ester structure present in the neutral lipid component of phosphatidylcholine, as it may lead to red blood cell lysis. We have conducted extensive research and developed a range of analytical methodologies to establish impurity thresholds and assist clients in managing impurities throughout the liposome development process. Furthermore, the degree of unsaturation in the fatty acid constituents of neutral phospholipids must be meticulously regulated. We have developed methods for detecting and confirming the structure and degree of unsaturation of oleic acid and linoleic acid within neutral phospholipids utilizing LC-MS.
Our Capacities for Liposome Impurity Analysis
| Techniques and Platforms |
Specifics |
| Liposome Purity Testing Platform |
- UPLC-CAD technology
- Lipid purity testing
- Cholesterol Identification
- Impurities in APIs
|
| Identification of Raw Materials and Excipients Techniques |
- HPLC
- LC-MS
- GPC
- UV Spectrum and IR
- H-NMR
|
| Control of Impurities Platform |
Relevant substance control including
- Critical impurity control
- Toxic impurities after degradation control, etc.
- Impurity synthesis, purification, and separation methods
|
Why Choose CD Formulation?
Expertise in Liposome Impurity Analysis
- Proficient in liposome impurity analysis methodology development.
- Proficient in the synthesis and purification of impurities, including process impurities and degradation impurities.
A Powerful Analysis Platform
- Advanced instruments for liposome impurity study.
- The quality research platform is specifically designed for liposome drugs to efficiently evaluate impurities.
A Highly Skilled Team
- We have adeptly provided invaluable support to a multitude of enterprises and academic institutions in the exploration of liposome impurities and the advancement of analytical methodologies.
- Our technical team is comprised of a diverse array of experts in analytical chemistry and formulation development.
Published Data
Technology: headspace gas chromatography technique
Journal: International journal of pharmaceutics
IF: 3.5
Published: 2020
Results: In this study, the author reports accurately and sensitive methods for quantifying saturated free fatty acids (FFA 18:0 and FFA 16:0), phosphocholine lysate (LPC 18:0 and LPC 16:0), phosphoglycerin lysate (LPG 18:0) liposome formula. Free fatty acids were separated by C8 column, and low lipids and low lipids were separated. The C18 stationary phase is used for direct injection without the lipid extraction process. The method was validated according to USP pharmacopoeia procedures. It has been applied to the analysis of four commercial liposomal drug preparations. Compared with CAD (Charge aerosol detector) and ELSD (evaporative light), the scattering detector detection method at ppm level, the ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) -mass spectrometry (MS) method can accurately determine lysophospholipids in emulsion liposomes with high accuracy and sensitivity.
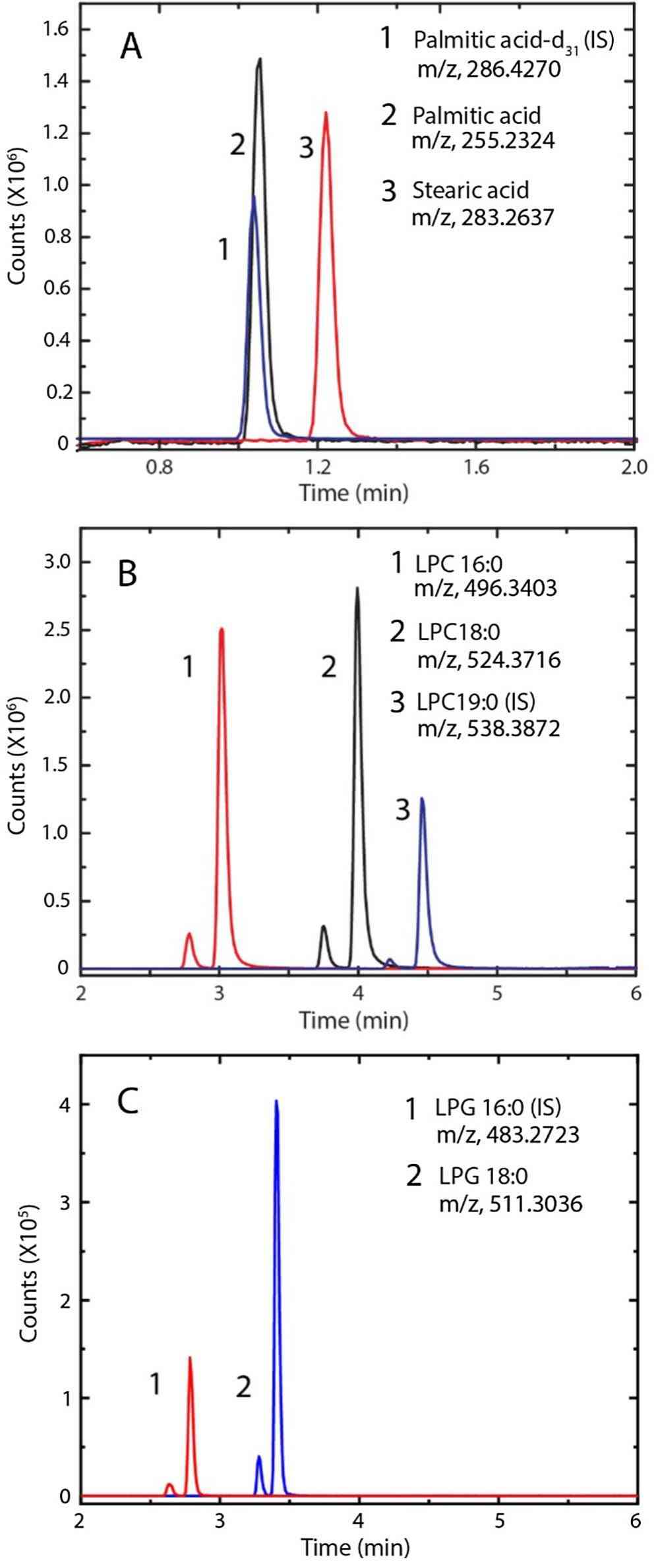 Fig.2 Representative chromatograms of FFAs (A), LPCs B), and LPGs (C) standards. (Siriwardane DA, et al. 2020)
Fig.2 Representative chromatograms of FFAs (A), LPCs B), and LPGs (C) standards. (Siriwardane DA, et al. 2020)
CD Formulation delivers advanced liposome impurity analysis services designed to meet the highest industry standards. Our solutions are tailored to the specific requirements of pharmaceutical enterprises and research institutions, ensuring comprehensive support for lipid-based formulation development. Contact us to learn how we can support your projects.
References
- Clogston JD. Parameters, Methods and Considerations for the Physicochemical Characterization of Liposomal Products. 2022 Jun. In: National Cancer Institute's Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Assay Cascade Protocols [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute (US); 2005 May 1. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK604275/ doi: 10.17917/B5N6-F154
- Siriwardane DA, Wang C, et al. Quantification of phospholipid degradation products in liposomal pharmaceutical formulations by ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS). International journal of pharmaceutics. 2020 Mar 30; 578: 119077.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services

 Fig.1 PTX-Loaded liposome analyzed by RP-HPLC and mass spectrometry. (Clogston JD, 2022)
Fig.1 PTX-Loaded liposome analyzed by RP-HPLC and mass spectrometry. (Clogston JD, 2022) Fig.2 Representative chromatograms of FFAs (A), LPCs B), and LPGs (C) standards. (Siriwardane DA, et al. 2020)
Fig.2 Representative chromatograms of FFAs (A), LPCs B), and LPGs (C) standards. (Siriwardane DA, et al. 2020)