Liposome Drug Loading Testing
Inquiry
At CD Formulation, our team of experienced analysts and advanced platform have collaborated with numerous enterprises and universities for several years to ensure the utmost quality in liposome assessment. Leveraging our extensive expertise in analysis of liposome drug loading, we assure that our customers' liposome products maintain exceptional quality throughout the entire research and development process, production, and clinical application.
The Importance of Liposome Drug Loading Testing
"Drug load" refers to the number of drugs contained in a certain quality of liposome, which is closely related to the concentration of drugs in the preparation, and has a wide range of applications in the quality evaluation of liposome, process optimization, preparation screening and so on. The drug loading modes of different liposomes are different, and the drug loading capacity is also different. The drug loading directly affects the clinical dosage of the drug. Therefore, higher drug loading is beneficial to meet clinical needs, and accurate determination of drug loading in liposomes is very important for the development of liposomes.
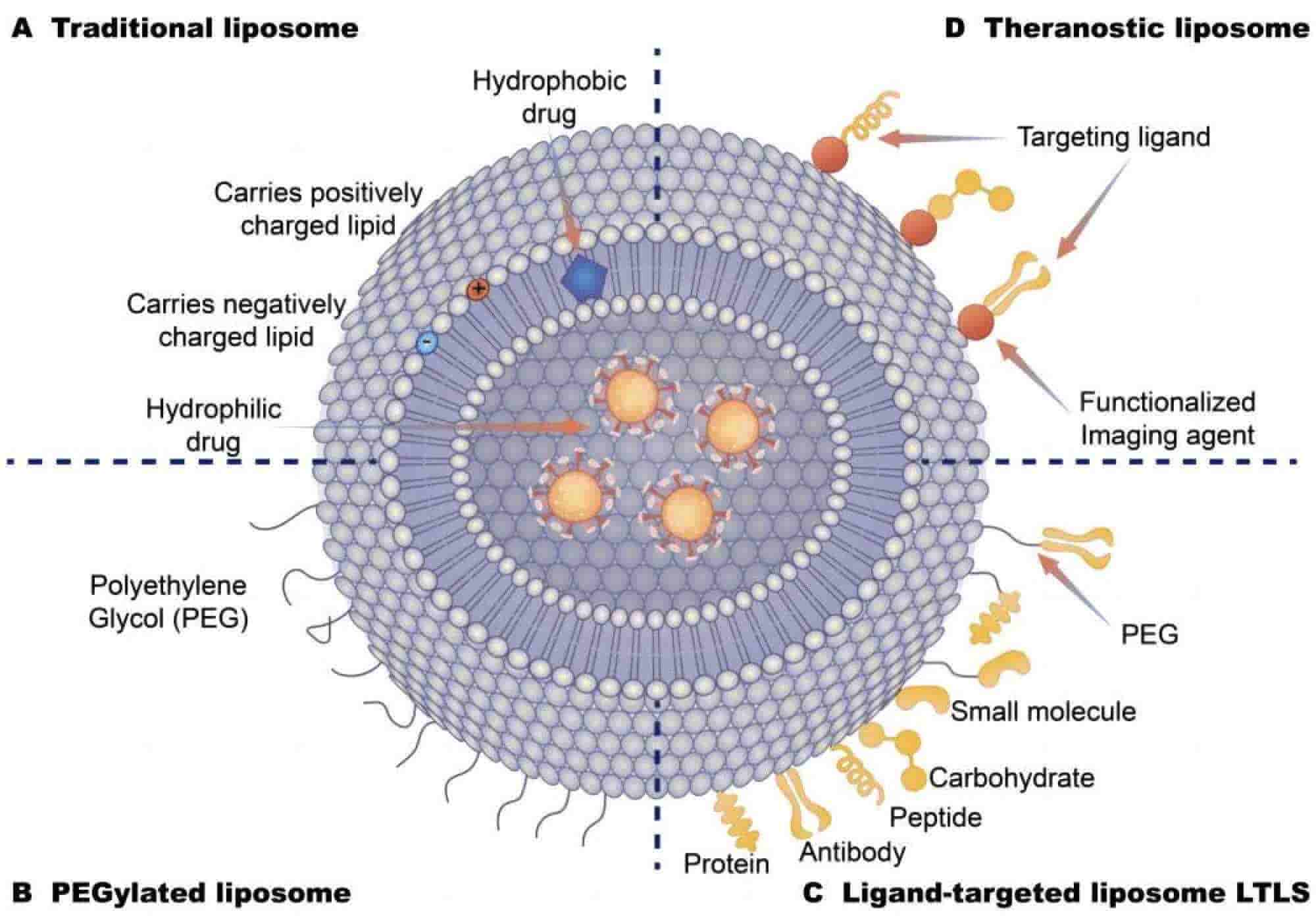 Fig.1 Different types of liposomal drug delivery systems. (He, Yeqing,et al. 2021)
Fig.1 Different types of liposomal drug delivery systems. (He, Yeqing,et al. 2021)
What Can We Do About Liposome Drug Loading Testing?
The services we are able to offer are as follows:
Development of Separation Methods
The calculation result of the drug loading of the liposome is related to the drug content in the liposome. Therefore, before the detection of the drug content in the liposome, the actual drug content should be obtained. In this service, we screen suitable separation methods for the separation of free liposomes, empty loaded and drug-coated stable liposomes.
Study on the effect of drug loading on drug effectiveness
We provide this service to help our customers determine the exact load and optimize the analysis of the load based on the pharmacodynamic assessment of the different load.
Our Workflow of Liposome Drug Loading Testing
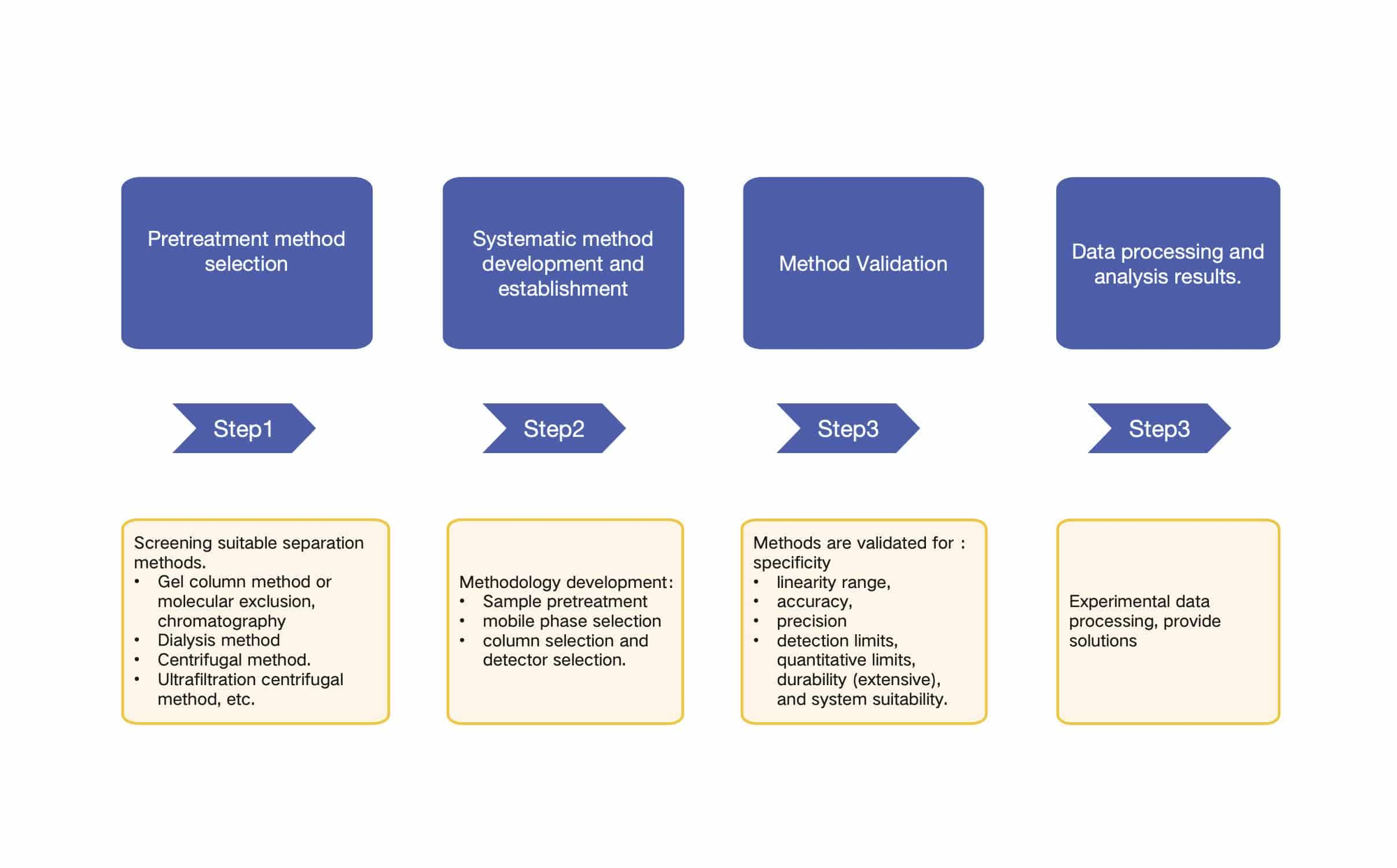 Fig.2 Workflow of liposome drug loading testing. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 Workflow of liposome drug loading testing. (CD Formulation)
Our Technologies for Liposome Drug Loading Testing
| Techniques & Platform |
Specifics |
| Pretreatment technique |
- Gel column method or molecular exclusion, chromatography),
- Dialysis method,
- Centrifugal method,
- Ultrafiltration centrifugal method, etc.
|
| Analysis platform |
- LC-MS technology: LC-MS/MS;
- Chromatographic technique: HPLC/UPLC; GC;
- Spectrum technology: UV spectrophotometer, etc.
|
Our Advantages in Liposome Drug Loading Testing
- Multi-analysis. Our platform combines a variety of analytical techniques as well as a variety of pre-treatment separation techniques, including gel column separation, dialysis, liquid chromatography, and LMS, to ensure accurate and repeatable liposomal loading analysis results.
- Fast. The entire liposomal loading analysis process, from the receipt of test samples to the delivery of results, is carried out with remarkable speed and efficiency. We can test multiple samples at the same time.
- Professional. Our team has successfully developed and implemented a wide range of analytical methodologies and quality benchmarks for liposome drug loading testing over the years.
Published Data
Technology: PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin technology
Journal: Acta Pharmacol Sin
IF: 1.5
Published: 2023
Results: In this study, the authors investigated the effect of drug loading on the in vivo performance of polyethylene glycol-conjugated liposome doxorubicin (PLD), preparing two different drug-loaded PLDs: high drug-loaded H-Dox with 12.9% w/w Dox/HSPC and low drug-loaded L-Dox with 2.4% w/w Dox/HSPC (the drug loading of L-Dox is approximately 5 times that of H-Dox at the same Dox dose). The authors compared the pharmacological properties and biological effects of H-Dox and L-Dox in mice, rats, or 4T1 subcutaneous tumor-bearing mice. The authors found that a reduction in doxorubicin loading does not lead to substantial changes in the pharmacological properties of PLD, such as in vitro and in vivo stability (stability), antitumor effect (equivalent efficacy), and tissue and cell distribution. Furthermore, due to less immunoreceptor (e.g., IgM and C3) deposition on each particle, in the presence of pre-existing anti-PEG Ab, PLD-induced adverse biological effects are more likely to be alleviated by prolonging circulation and reducing skin accumulation.
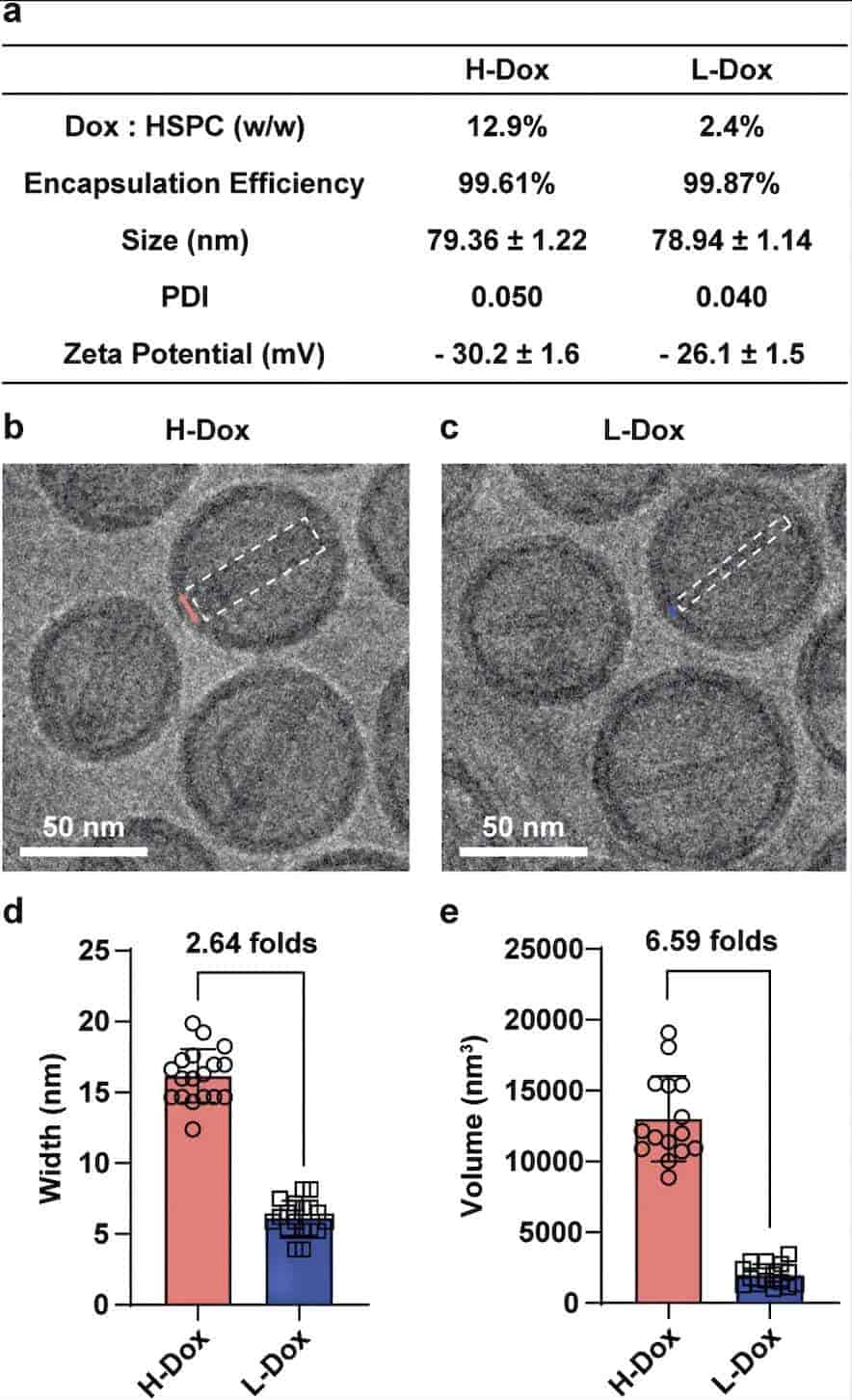 Fig.3 Characterization of H-Dox and L-Dox. (Yu YF, et al., 2024)
Fig.3 Characterization of H-Dox and L-Dox. (Yu YF, et al., 2024)
The CD Formulation team possesses extensive project experience in the analysis of thermodynamic properties related to liposome membranes and has consistently delivered exceptional and satisfactory service to numerous clients throughout the years. For further information, please feel free to contact us.
References
- He, Yeqing; He, Guandi; et al. Specifically Targeted Transport of Plasma Membrane Transporters: From Potential Mechanisms for Regulating Cell Health or Disease to Applications. Membranes. 2021.
- Yu YF, Wu EC, et al. Reexamining the effects of drug loading on the in vivo performance of PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024;45(3):646-659.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Different types of liposomal drug delivery systems. (He, Yeqing,et al. 2021)
Fig.1 Different types of liposomal drug delivery systems. (He, Yeqing,et al. 2021) Fig.2 Workflow of liposome drug loading testing. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 Workflow of liposome drug loading testing. (CD Formulation)  Fig.3 Characterization of H-Dox and L-Dox. (Yu YF, et al., 2024)
Fig.3 Characterization of H-Dox and L-Dox. (Yu YF, et al., 2024)