Custom Polymer-modified Liposome Service
Inquiry
Liposomes have been widely used as drug delivery systems to increase the solubility and permeability of hydrophilic or hydrophobic drugs. However, conventional liposomes are easily degraded by pH, enzymes, and the immune system in the biological environment. Therefore, its application in some pathways will immediately release the drug, unable to maintain the stability of the active substance. One solution to overcome this problem is to modify the structure of liposomes by using polymers. With our expertise and technology accumulation in the field of liposomes, the scientific research team at CD Formulation can provide professional solutions for customizing and characterizing diverse polymer-modified liposomes.
What Are Polymer-modified Liposomes?
Multifunctional polymers (both natural and synthetic) have long been used as drug-delivery vehicles due to their customizable structure, properties, and functions. According to the characteristics of the added polymer, the polymer-modified liposomes showed excellent performance in improving the stability of the colloid, prolonging the cycle time, targeting and triggering release. In short, surface modification of liposomes with polymers generally involves the following strategies:
1. The liposomes were grafted with polymer and coated with physical adsorbed polymer.
2. Multifunctional liposomes are also designed by incorporating polymers with a variety of specific functions.
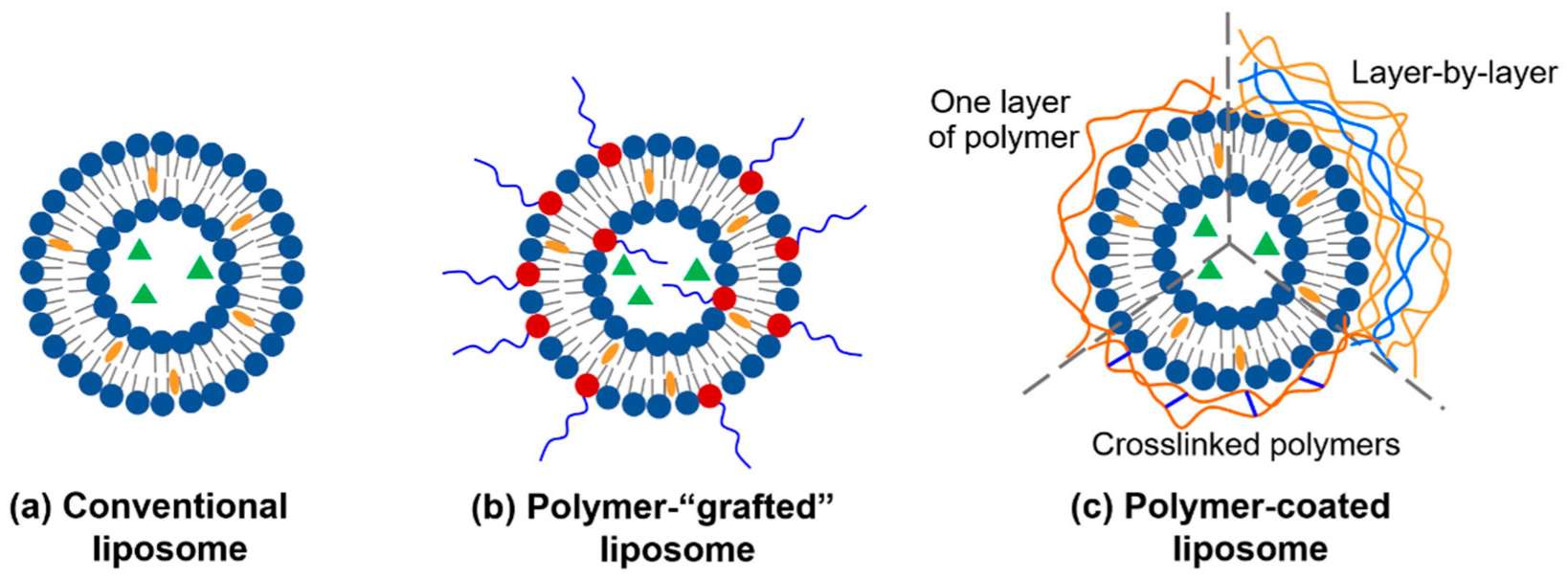 Fig.1 Liposomes for drug delivery: (a) conventional liposome, (b) polymer- "grafted" liposome, and (c) polymer-coated liposome. (Cao Y, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Liposomes for drug delivery: (a) conventional liposome, (b) polymer- "grafted" liposome, and (c) polymer-coated liposome. (Cao Y, et al., 2022)
Explore Our Custom Polymer-modified Liposome Service
Screening of Polymers and Modification Modes
Different polymers modify liposomes in ways that are different, so we provide screening services and provide the polymer or copolymer, polymer derivatives, including, chitosan, atelocollagen, modified xanthan gum department, alginate, cyclodextrin, gelatin, poly (acrylic acid), etc.
Polymer-Grafted Liposome Customization
Currently, the customized products we can offer under this service category include the following two:
- PEGylated liposomes
- zwitterionic polymer-lipid complexes
Polymer-Coated Liposome Customization
Currently, the customized products we can offer under this service category include the following:
- Monolayer polymer-coated liposomes
- Cross-Linked-Polymer-Caged liposomes
- Layer-by-Layer (LBY)-coated liposomes
Liposome Functionalization
Polymer-modified liposomal drug delivery systems that target specific diseases and tissues are particularly important for therapeutic applications. We offer this service to help our customers improve the targeting of polymer-modified liposomes.
- Stimuli-Responsive Polymers
Triggering the release of encapsulated therapeutic agents at the desired site is critical to achieving high bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy. The response stimulation of liposomes can effectively control the release and improve the therapeutic effect of the payload. Our services can be combined with polymer-modified liposomes in response to stimuli, thus providing greater targeting and bioavailability.
Polymer-modified Liposome Characterization
The type of surface bond between the polymer and the liposome plays a crucial role in controlling the release of the liposome and the drug. Therefore, we offer physicochemical characterization studies (particle size, potential, encapsulation rate, drug loading, stability, etc.) designed to aid in the study of subsequent drug delivery and release patterns of polymer-modified liposomes.
Our Capabilities for Customizing Polymer-modified Liposomes
| Items |
Detailed Information |
| Physicochemical characterization |
- Analysis of multiple physical and chemical properties including particle size, potential, encapsulation rate, drug loading, stability, etc.
|
| Screening of different polymers |
- Polymer or copolymer, polymer derivatives library, including, chitosan, atelocollagen, modified xanthan gum department, alginate, cyclodextrin, gelatin, poly (acrylic acid), etc.
|
| Liposome functionalization |
- To help our customers improve the targeting of polymer-modified liposomes.
- Combination with polymer-modified liposomes in response to stimuli, thus providing greater targeting and bioavailability.
|
| Study on the interaction mechanism of polymer-modified liposomes |
- The types of interactions that can occur between polymers and liposomes include physical adsorption or chemical reactions such as electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonds, disulfide bonds, covalent bonds, etc.
- The type of polymer and phospholipid may affect the rate of liposome release.
|
Our Key Advantages in Customizing Polymer-modified Liposomes
- Multi-polymerization database. We have built a multi-polymerization database to help our customers screen suitable polymers to customize polymer-modified liposome products to meet their requirements.
- Advanced polymer modification technologies and platforms. We have studied the mechanism of polymer-modified liposomes for many years, including how the order of addition of polymers during the development of liposomes affects the location of subsequent products, the reaction mechanism of different phospholipids and polymers, etc.
- Skilled teams. Our research and development team consists of many scientists with diverse disciplinary backgrounds, who have extensive experience in chemical synthesis, biological delivery system development, and immunology.
Published Data
Technology: pH-sensitive polymer-modified liposome technique
Journal: Polymer Journal
IF: 2.7
Published: 2016
Results: In this study, the authors improved the antigen delivery performance of deoxyribonucleic acid derivatives by introducing more lipophilic spacer groups near the carboxyl group. They synthesized 2-carboxycyclohexane-1-carboxylated deoxyribonucleic acid (CHex-Dex) as a pH-responsive deoxyribonucleic acid derivative. CHex-Dex forms stronger lipophilic regions at very weak acidic pH, which are more effective at disrupting lipid membranes than MGlu-Dex. CHex-Dex-modified liposomes deliver antigens to the cytoplasm of dendritic cells and induce specific cellular immunity. Therefore, CHex-Dex, as a multifunctional polysaccharide with cytoplasmic antigen delivery function and strong dendritic cell activation properties, has potential to induce cellular immunity.
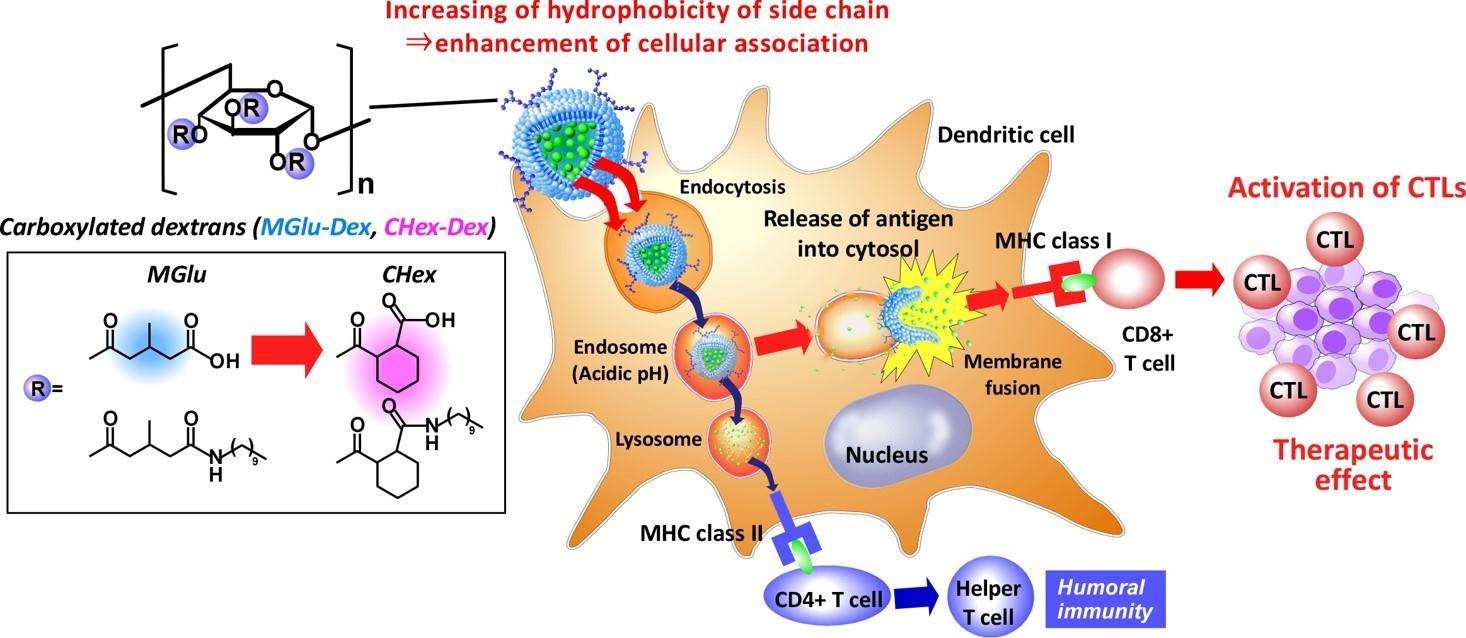 Fig.2 Scheme illustration of pH-sensitive polymer-modified liposomes. (Yuba, E, 2016)
Fig.2 Scheme illustration of pH-sensitive polymer-modified liposomes. (Yuba, E, 2016)
As a global nanoparticle development company, CD Formulation has extensive experience in the development and customization of polymer-modified liposomes. If you need any help, please do not hesitate to contact us.
References
- Cao Y, Dong X, et al. Polymer-Modified Liposomes for Drug Delivery: From Fundamentals to Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(4): 778.
- Yuba, E. Design of pH-sensitive polymer-modified liposomes for antigen delivery and their application in cancer immunotherapy. Polym J, 2016, 48, 761–771.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Liposomes for drug delivery: (a) conventional liposome, (b) polymer- "grafted" liposome, and (c) polymer-coated liposome. (Cao Y, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Liposomes for drug delivery: (a) conventional liposome, (b) polymer- "grafted" liposome, and (c) polymer-coated liposome. (Cao Y, et al., 2022) Fig.2 Scheme illustration of pH-sensitive polymer-modified liposomes. (Yuba, E, 2016)
Fig.2 Scheme illustration of pH-sensitive polymer-modified liposomes. (Yuba, E, 2016)