Custom pH-sensitive Liposome Service
Inquiry
pH-sensitive liposomes are advanced delivery systems engineered to release encapsulated drugs in response to changes in serum pH, thereby enhancing therapeutic efficacy. These liposomes effectively transport therapeutics, gene fragments, and reagents into cells via the endocytosis pathway. At CD Formulation, we leverage our extensive expertise in nanodelivery systems and proprietary nanoparticle technology to offer bespoke pH-sensitive liposome solutions, supporting researchers and pharmaceutical companies in their innovative pursuits.
What are pH-sensitive Liposomes?
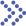
As a drug carrier, liposomes have the characteristics of targeting and slow release, which can improve drug efficacy and reduce drug toxicity to a certain extent. Nevertheless, in comparison to conventional liposomes, there are still numerous limitations in their clinical application. At sites of tumor stroma, ischemic infection, or inflammation, pH is much lower than surrounding normal tissue. Based on the changes in pH value within pathological tissues, a novel type of liposome known as pH-sensitive liposome has been developed. This innovation offers significant advantages in targeted delivery and controlled drug release within cells. The membrane structure of pH-sensitive liposomes changes with the adjustment of pH from 7.4 to 5.3 to 6.3, which can cause the liposome membrane to fuse with the endosome membrane, thereby releasing water-soluble contents.
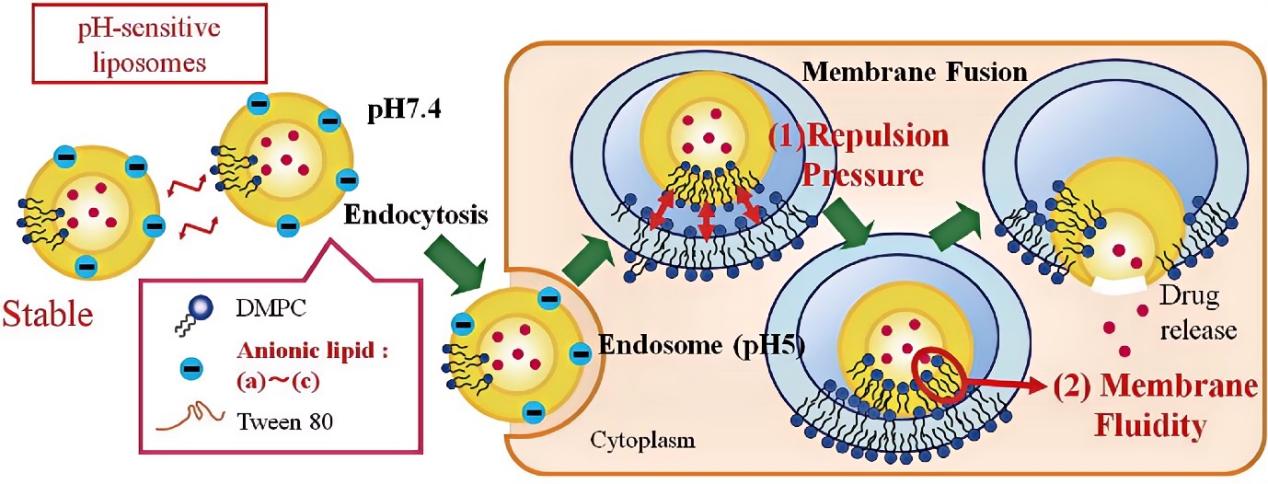 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of pH sensitivity of the anionic liposomes at acidic pH. (Aoki, Asami, et al., 2015)
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of pH sensitivity of the anionic liposomes at acidic pH. (Aoki, Asami, et al., 2015)
Our pH-sensitive Liposome Customization Service
pH-sensitive lipid screening for liposomes triggering
The primary excipient in pH-sensitive liposomes is unsaturated phosphatidylethanolamine. In acidic environments, the carboxyl groups of the phosphatidylethanolamine become protonated, leading to a reduction in the three-dimensional volume of the hydrophilic side. This reduction ultimately destabilizes the liposome membrane and results in the release of encapsulated biologically active molecules. Commonly used polymorphic lipids for pH-sensitive liposome preparation are referred to unsaturated phosphatidyl ethanolamine (PE). We can offer screening of lipids such as diacetylphosphatidyl ethanolamine (DAPE), palmitoyl oleoylphosphatidyl ethanolamine (POPE), dioleylphosphatidyl ethanolamine (DOPE), citracony-dioleoyl-phosphatidyl-ethanolamine (C-DOPE), N-citraconyl-dioleoyl-phosphatidylserine (C-DOPS), etc.
Customization for liposomes triggered by pH-sensitive peptides/proteins
This service assists clients in the development of pH-sensitive liposomes by incorporating pH-sensitive peptides/proteins into the liposomal structure. Examples of such pH-sensitive peptides/proteins include GALA, hemin (influenza INF peptide) N-terminal, or Listeriolysin O inserted into phospholipid double fusion peptide or protein. In a neutral pH environment, the peptide or protein remains inactive; however, in an acidic environment, the conformational change of the fusion peptide or protein promotes membrane fusion between the liposome and cell membrane, ultimately leading to content release.
Customization for liposomes triggered by pH-sensitive polymers
Currently, polymers used for pH-sensitive liposome design include poly alkyl acrylics, succinylated PEG, and N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) copolymers. We are also researching the use of alternative polymers to construct pH-responsive liposomes.
Our pH-sensitive Liposome Customization Workflow
 Fig.2 Schematic diagram of our workflow for pH-sensitive liposome customization. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of our workflow for pH-sensitive liposome customization. (CD Formulation)
Our Platforms for pH-sensitive Liposome Customization
We have established a proprietary platform for the development of pH-sensitive liposomes and can offer the following technologies:
| Techniques and Platforms |
Specifics |
| pH-sensitive Triggering Molecule Screening Platform |
- This platform supports screening different types of pH-sensitive triggering molecules such as pH-sensitive peptides/proteins, pH-sensitive lipids, pH-sensitive polymers, etc.
|
| In Vitro Characterization Platform |
- In vitro release evaluation platform
- pH stimulation response assessment.
|
| Mechanisms Study Platform of Intracellular Delivery Mediated by pH-sensitive Liposomes |
- The platform provides technical support for the construction of pH-sensitive liposomes stable at physiological pH and temperature by studying the substrate of pH-response delivery systems.
|
| Application Development Platform of pH-sensitive Liposomes |
- To explore the application possibilities of pH-sensitive liposomes in various fields.
- Conventional application areas include anti-cancer therapy, anti-infection therapy, gene therapy, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents.
- Special fields, such as indicator delivery systems, enzyme delivery systems, biosensors, etc.
|
Applications of pH-sensitive Liposomes
| Drug Delivery |
Anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory |
| Gene Therapy |
Active targeting technology
Non-viral vector |
| Biomedical Science |
pH biosensors, cell diagnostic reagents |
| Imaging |
MRI contrast agents |
| Vaccine |
Vaccine adjuvants
|
Why Choose CD Formulation?
- Advanced pH-sensitive liposome development techniques and platforms. Through the diversification of technology and the integration of various platforms, we aim to provide our customers with comprehensive, customized services, from development, validation, and characterization to the final delivery of high-quality pH-sensitive liposome products to our customers.
- Skilled teams. Our research team consists of a group of scientists who are proficient in immunology, medicine, biology, and other disciplines, and have extensive experience in developing biological delivery systems, especially pH-sensitive liposome delivery systems.
- Diverse and flexible customization. Our pH-sensitive liposomes can be customized to meet the needs of various industries. For example, cancer research, anti-inflammatory research, contrast agent development, biosensor research, and so on.
Published Data
Technology: Programmed liposome and PH-sensitive liposome techniques
Journal: J Nanobiotechnol
IF: 10.2
Published: 2019
Results: This paper describes a programmed release drug delivery system that avoids drug efflux and nuclear transport through a simple nanostructured drug strategy. Liposome-based nanostructured drugs (LNSD) based on programmed liposomes consist of two modules: doxorubicin (DOX) is loaded into tetrahedral DNA (TD, ~ 10 nm) to form small nanostructured DOX, and the nanostructured DOX is encapsulated into PH-sensitive liposomes. In vitro and in vivo studies have shown multiple benefits for the treatment of drug-resistant tumors:
(1) It not only enhances the uptake of DOX by cells but also maintains the optimal concentration of DOX in drug-resistant tumor cells through the anti-efflux effect induced by nanostructures.
(2) Small nanostructured DOX enters the nucleus effectively through size-dependent nuclear transport and is treated intensively.
(3) Improving pharmacokinetics and biodistribution by reducing the leakage of DOX during circulation. The system developed in this study has the potential to provide new treatments for drug-resistant tumors.
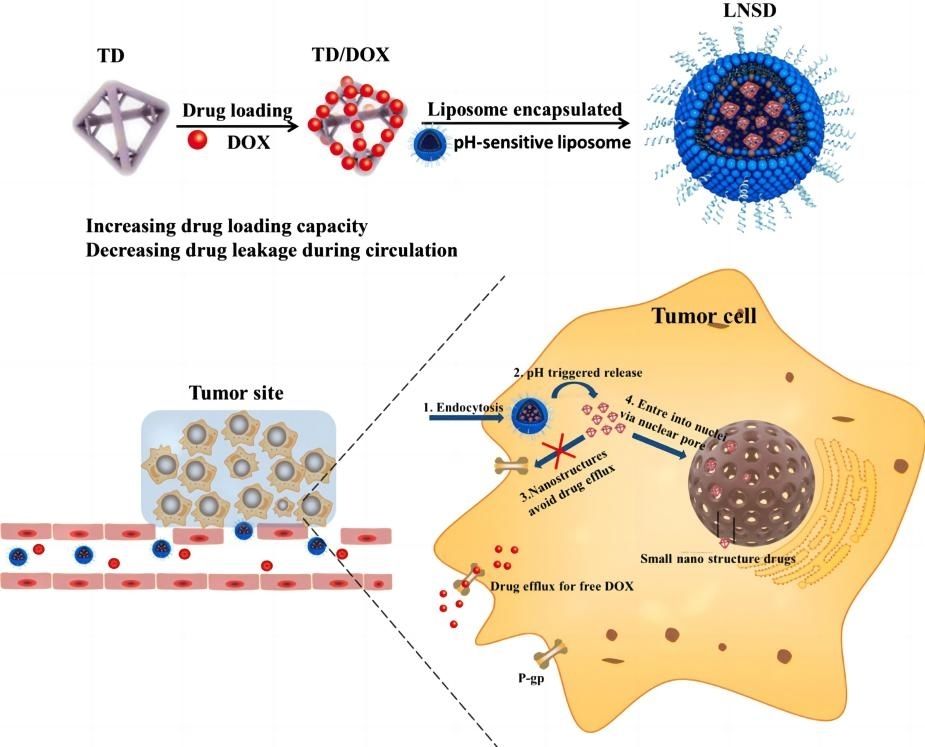 Fig.3 Mechanism of ultrasmall nanostructured drug-based pH-sensitive liposome for effective treatment of tumor. (Zhanwei Zhou, et al., 2019)
Fig.3 Mechanism of ultrasmall nanostructured drug-based pH-sensitive liposome for effective treatment of tumor. (Zhanwei Zhou, et al., 2019)
CD Formulation has established a specialized platform for the development of pH-sensitive liposomes in order to offer customers a wide range of highly effective pH-sensitive liposome products. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you require any assistance.
References
- Aoki, Asami, Hikaru Akaboshi, et al. "Preparation of pH-sensitive anionic liposomes designed for drug delivery system (DDS) application." Journal of oleo science. 2015, 64 2: 233-42.
- Li, Y., Zhai, Y., et al. Ultrasmall nanostructured drug based pH-sensitive liposome for effective treatment of drug-resistant tumor. J Nanobiotechnol. 2019. 17, 117.
How It Works
STEP 2
We'll email you to provide your quote and confirm order details if applicable.
STEP 3
Execute the project with real-time communication, and deliver the final report promptly.
Related Services


 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of pH sensitivity of the anionic liposomes at acidic pH. (Aoki, Asami, et al., 2015)
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of pH sensitivity of the anionic liposomes at acidic pH. (Aoki, Asami, et al., 2015) Fig.2 Schematic diagram of our workflow for pH-sensitive liposome customization. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of our workflow for pH-sensitive liposome customization. (CD Formulation) Fig.3 Mechanism of ultrasmall nanostructured drug-based pH-sensitive liposome for effective treatment of tumor. (Zhanwei Zhou, et al., 2019)
Fig.3 Mechanism of ultrasmall nanostructured drug-based pH-sensitive liposome for effective treatment of tumor. (Zhanwei Zhou, et al., 2019)