Viral Vector Purity Evaluation
Inquiry
The use of viral vectors is at the heart of gene therapy, and they are capable of efficiently delivering therapeutic genes to target cells. In the case of adeno-associated viruses, for example, although adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) are the vectors of choice in gene therapy due to their low immunogenicity and high targeting properties, the production process may produce by-products and contaminants, which, if not adequately eliminated, may cause adverse reactions in patients. Therefore it is crucial to ensure the purity of viral vectors in gene therapy. CD Formulation has many years of research and service experience in gene therapy formulation development, and we offer complete quality control for gene therapy formulation development, including viral vector purity evaluation.
The Importance of Viral Vector Purity Evaluation
- Ensure product quality. As a key component of gene therapy, the purity of viral vectors directly affects the safety and effectiveness of gene therapy. Viral vectors with low purity may contain a variety of impurities that may cause unwanted immune responses.
- Improved therapeutic efficacy. High-purity viral vectors can reduce the ineffective dose and improve the transduction efficiency, thus enhancing the effect of gene therapy.
- Reduce the risk of side effects. The purification degree of viral vectors is directly related to the safety of treatment.
- Compliance with regulatory requirements. Comply with the specifications and requirements of regulatory agencies through strict quality control of the final product.

Explore Our Viral Vector Purity Evaluation
We have established a comprehensive technology platform for testing the purity of viral vectors, including SDS PAGE, capillary electrophoresis, qPCR, digital PCR, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and mass spectrometry. Below we describe in detail the use of these methods to detect the purity of viral vectors.
SDS-PAGE
This is a technique for separating proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. In viral vector purity testing, SDS-PAGE can be used to assess the purity of proteins in viral vector samples. By comparing the clarity and intensity of the viral vector protein bands with those of the impurity proteins, the purity of the sample can be estimated. This method is fast and inexpensive, and we generally use it for rapid screening in the early R&D phase.
Capillary electrophoresis
This is an efficient, high-resolution separation technique that utilizes a high-voltage electric field to drive the separation of sample components within a capillary tube. In viral vector purity testing, CE can be used to analyze the charge heterogeneity and molecular weight distribution of viral vectors to assess purity.
Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
qPCR is a molecular biology technique that quantitatively analyzes DNA copy number by monitoring the fluorescence signal during DNA amplification in real-time. In viral vector purity testing, qPCR can be used to quantify the genomic copy numbers of viral vectors to assess the concentration and purity of viral vectors.
Digital PCR
ddPCR is a variant of qPCR that achieves absolute quantification by dividing the sample into thousands of microdroplets for independent PCR reactions, each containing 0 or 1 template DNA molecule. In viral vector purity testing, we utilize ddPCR which can be used to accurately determine the copy number of viral vectors, and is particularly suited for the detection and accurate quantification of low abundance samples.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
ELISA is an antigen-antibody reaction-based assay that quantifies an antigen by producing a color change when an enzyme-labeled antibody binds to the antigen. In viral vector purity testing, ELISA can be used to detect the presence of viral vector proteins or specific antigens to assess purity.
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
HPLC is a separation technique based on the difference in partition coefficients of different components between stationary and mobile phases. In viral vector purity testing, HPLC can be used to analyze the protein composition and purity of viral vectors, and we commonly use it for the separation and analysis of complex samples.
Our processs of Viral Vector Purity Evaluation
The specific procedure of SDS-PAGE in viral vector purity detection is taken as an example.
Experiment preparation
In this part, we need to prepare reagents, such as acrylamide, electrophoresis buffer, staining solution and decolorizing solution, etc. We also need to prepare instruments, such as SDS-PAGE electrophoresis apparatus and decolorizing shaker.
Gel preparation
We will mix the separation gel buffer, acrylamide, water, SDS, APS, and TEMED in a certain ratio according to the desired gel concentration. subsequently, the mixed gel solution will be poured into the electrophoresis mold and a comb will be inserted to form the sample wells.
Sample processing
For this session, we mixed the viral vector samples with loading buffer, which usually requires boiling in boiling water for 5 minutes to denature the proteins. And the possible formation of precipitate is removed by centrifugation.
Sample up electrophoresis
We add the samples to the up-sampling wells of the gel for electrophoresis.
Staining and decolorization
After electrophoresis was completed, we took the gel out of the glass plate and put it into the staining solution for staining, after staining, the gel was put into the decolorizing solution for decolorization until the background was clear and the bands were obvious.
Analysis of results
We can estimate the purity of the viral vector proteins in the samples by comparing the migration distance of the sample bands with the standard protein bands.
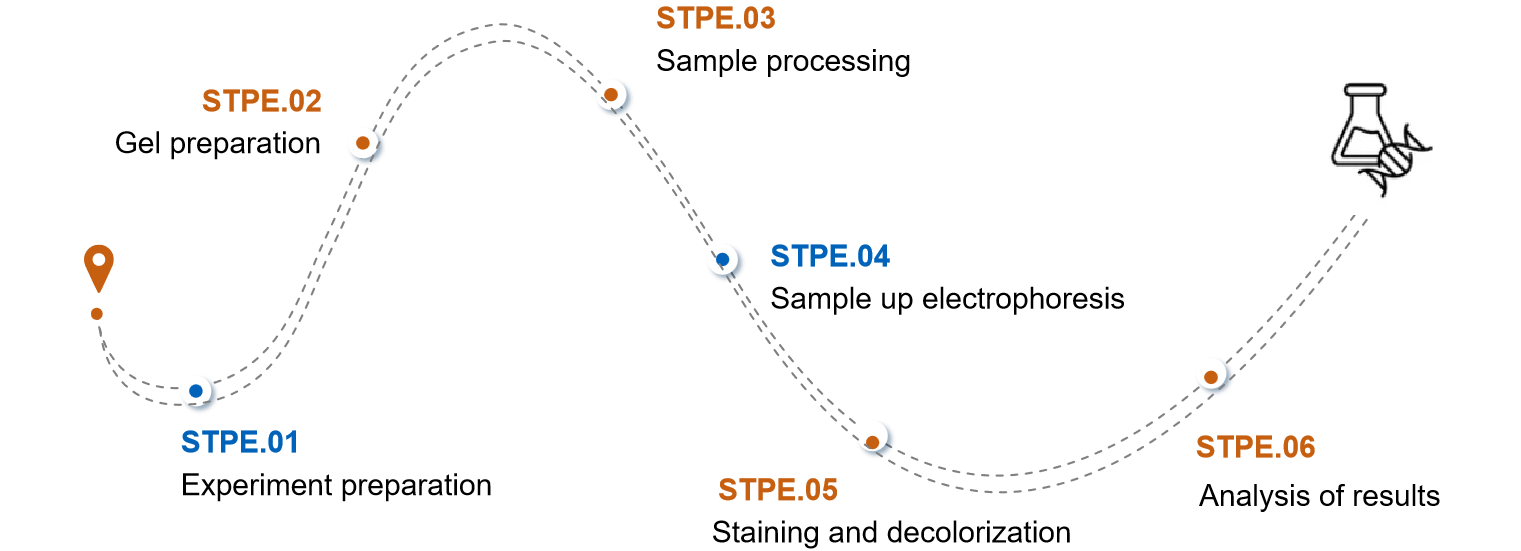 Fig.2 The process of viral vector purity evaluation. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 The process of viral vector purity evaluation. (CD Formulation)
Highlights of Our Viral Vector Purity Evaluation
- We have an advanced technology platform that enables us to rapidly test the purity of viral vectors, ensuring fast, efficient and on-time delivery of experimental results.
- Our expert technical team with rich experience and professional knowledge is able to provide customers with professional analytical methods and various analytical solutions for reliable gene therapy formulation analysis.
- We provide a wide range of viral vector characterization technical services, including viral vector purity assessment, to ensure maximum satisfaction of our customers' testing needs.
Published Data
Technology: DNA minicircle technology
Journal: Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids
IF: 8.8
Published: 2016
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors show great potential in gene therapy and are widely used in preclinical studies and basic science exploration. However, despite the increasing use of AAV vectors, the preparation of high-purity AAV vectors remains a challenge. Current techniques can remove empty capsids, but it is difficult to completely remove antibiotic resistance genes and other plasmid backbone sequences.
This study describes a new minicircle (MC) structure for replacing conventional AAV vectors and helper plasmids to produce single-stranded (ss) and self-complementary (sc) AAV vectors. This approach removes the bacterial backbone sequence during production, effectively avoiding the packaging of the plasmid backbone sequence. This is particularly important for self-complementary AAV vectors because they contain a high percentage of plasmid backbone sequences. The use of MC structures instead of traditional packaging plasmids not only significantly reduces contaminants, but also increases the transduction efficiency of scAAV vectors up to 30-fold. Therefore, MC technology provides an improved solution for the preparation of AAV vectors, which can enhance the quality and efficiency of preparation.
CD Formulation provides viral vector purity evaluation services designed to help customers ensure the safety and efficacy of their gene therapy formulations, thereby accelerating the development process of gene therapy formulations. If you are interested in us, please feel free to contact us.
References
- Schnödt M, et al. DNA Minicircle Technology Improves Purity of Adeno-associated Viral Vector Preparations. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2016;5(8):e355.
Related Services


 Fig.2 The process of viral vector purity evaluation. (CD Formulation)
Fig.2 The process of viral vector purity evaluation. (CD Formulation)