Viral Vector Characterization
Inquiry
In gene therapy, viral vectors, as an important gene delivery tool, are critical for quality control. Characterization and analysis of the key properties of viral vectors are essential to ensure their quality researchers with a comprehensive, reliable gene therapy solution. CD Formulation uses state-of-the-art instrumentation and advanced technological methods to continually optimize the viral vector characterization process to provide a comprehensive, reliable gene therapy solution for researchers.
Advantages of Viral Vector Characterization
- Ensuring therapeutic safety. Characterization of viral vectors helps ensure their safety in gene therapy. The introduction of potential biosafety risks can be avoided by analyzing in detail the genomic structure, biophysical properties, and biological activity of viral vectors. For example, adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors have been widely used in gene therapy due to their low pathogenicity and high safety profile.
- Improved efficacy. Characterization of viral vectors helps optimize their transduction efficiency and infectivity. Accurate bioanalysis ensures that viral vectors can efficiently deliver therapeutic genes to target cells. For example, the infectivity and transfection efficiency of AAV vectors are evaluated in cell culture and animal models to improve the efficacy of gene therapy.
- Quality control. Characterization of viral vectors is a critical part of product quality control for gene therapy. Detailed characterization of viral vectors ensures that each batch meets stringent quality standards. For example, analysis of the purity, titer, and particle morphology of AAV vectors is an important part of their quality control.
- Vector optimization. Characterization data of viral vectors can be used to guide vector design and optimization. For example, by altering the capsid proteins of AAV vectors, their targeting to specific cells or tissues can be improved, thereby increasing the efficiency and accuracy of gene delivery.
Our Services for Viral Vector Characterization
Characterization of viral vectors in gene therapy involves several aspects, including the critical quality attributes (CQAs) of viral vectors, genomic structure, biophysical properties, biological activities, and interactions with host cells. Let's take adeno-associated viral(AAV)vectors as an example and list some of the key characterization aspects.
Measurement of titer
Titer is essential to gene therapy's efficacy. Titer assays often measure the number of copies of the gene sequence in the AAV vector to determine the titer using techniques like quantitative PCR. One of the most important aspects of gene therapy, this step guarantees that the patient gets an appropriate dosage of the working gene.
Analysis of purity
The safety of the treatment is directly correlated with the purity of the AAV vector. Purity analysis includes removing some contaminants like DNA, proteins, and other remnants of viruses. Techniques like high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gel electrophoresis are frequently employed to guarantee the high purity of AAV vectors to lower the possibility of negative reactions.
Assessment of integrity
The integrity of AAV vectors is related to their stability and effectiveness in gene delivery. High-resolution techniques such as electron microscopy can be used to observe the morphological structure of AAV particles to ensure that no structural damage occurs during delivery. This is essential to maintain the function and longevity of AAV vectors.
Measurement of infectivity
The infectivity of the AAV carrier refers to its delivery efficiency in the target cells, which is directly related to the efficacy of the treatment. The determination of infectivity needs to be carried out in the actual treatment target cells, usually through cell culture and animal model experiments, etc., to assess the infectivity of AAV vectors on different cell types.
Viral particle size and distribution
The particle size and distribution of AAV vectors are also important quality attributes. Techniques such as flow cytometry can be used to determine the particle size and distribution of AAV vectors to ensure that they meet the design specifications, which can help improve gene delivery efficiency.
 Fig.1 Viral vector characterization services. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Viral vector characterization services. (CD Formulation)
Our Platforms for Viral Vector Characterization
With the rapid growth of the gene therapy market. The demand for characterization and quality control of viral vectors and viruses is rapidly increasing. Our research and technical teams can combine several advanced techniques for viral vector characterization.
| Platforms & Technologies |
Content Description |
| SEC-MALS |
Size exclusion chromatography with multi-angle static light scattering (SEC-MALS), without relying on any reagents (dyes) or indirect determinations (fluorescence techniques), SEC-MALS allows for the determination of molecular weights not only for total molecular weights but also for coat proteins and DNA. |
| LC-MS technology |
Liquid chromatography (LC) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) technologies have a long history of use in the development, characterization, and quality testing of viral vectors. We optimize and streamline workflows to assess the quality of viral vectors. |
| Biophysical determination technology |
For example, biophysical properties such as size, shape, surface properties, and thermal stability of AAV particles are key parameters that can be measured by electron microscopy, gel filtration, and dynamic light scattering. |
Highlights of Our Viral Vector Characterization
- Professional technical team. We have a professional team of experienced bioscientists, virologists, and bioengineers who can accurately and efficiently characterize viral vectors.
- Advanced equipment and technology. We are equipped with the latest laboratory equipment and use cutting-edge technology to ensure the accuracy and efficiency of characterization.
- Customized services. We can provide customized viral vector characterization solutions according to the needs of different customers, including but not limited to genome structure analysis, biophysical property determination, and biological activity evaluation.
- Strict quality control. We implement strict quality control processes to ensure the safety, efficacy, and consistency of viral vectors.
Published Data
Technology: Biophysical determination technology
Journal: J Virol
IF: 4.8
Published: 2003
Adeno-associated viruses (AAV) provide enormous promise for treating a wide range of severe human illnesses when used as gene delivery vectors. More than a hundred naturally occurring AAV capsid variants have been described and categorized into phylogenetic evolutionary branches based on their sequences. For example, AAV8, AAV9, AAVrh.10, and other intensively studied coatings have been advanced for preclinical and clinical use. The less studied coatings may also have desirable properties such as potency differences, tissue tropism, and reduced immunogenicity, for example. These data will help to build a broader knowledge base of structure-function in the field, provide opportunities for shell engineering, and enable the use of novel shells with unique properties.
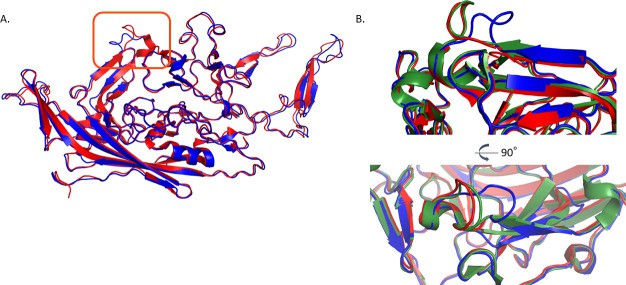 Fig.2 Atomic structure of AAV7 capsid protein VP3. (Yost SA, et al., 2023)
Fig.2 Atomic structure of AAV7 capsid protein VP3. (Yost SA, et al., 2023)
CD Formulation provides viral vector characterization and analysis services to ensure the safety and efficacy of gene therapy. Through in-depth research and continuous optimization, our technical service can help researchers to better understand the biological properties of viral vectors in gene therapy, thus advancing the development of the gene therapy field. If you are interested in us, please feel free to contact us.
References
- Yost SA, et al. Characterization and biodistribution of under-employed gene therapy vector AAV7. J Virol. 2023 Nov 30;97(11):e0116323.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Viral vector characterization services. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Viral vector characterization services. (CD Formulation) Fig.2 Atomic structure of AAV7 capsid protein VP3. (Yost SA, et al., 2023)
Fig.2 Atomic structure of AAV7 capsid protein VP3. (Yost SA, et al., 2023)