Retroviral Vector Development Service
Inquiry
Retroviral vectors are highly efficient transfer systems for introducing exogenous genes into target cells. Retroviral vectors are derived from RNA viruses and are capable of reverse transcribing their genomes into double-stranded viral DNA, which can be stably inserted into the host genome. Retroviral vectors have been the most preferred gene transfer system for clinical gene therapy. Research and development of retroviral vectors play an important role in advancing gene therapy. CD Formulation stays at the forefront of gene therapy development and combines state-of-the-art development services with specific technologies to facilitate the rapid development and deployment of retroviral vector development. We are reputable and have been recognized by industry insiders for our significant services in the field of gene therapy development.
Advantages of Retroviral Vectors Development
- Stability and integration. Retroviral vectors possess the ability to integrate their genetic material into the host cell's DNA. This integration ensures stable and long-term expression of the therapeutic gene. Once integrated, the therapeutic gene becomes a permanent part of the host cell's genome and is passed on to its progeny during cell division.
- Large gene capacity. Retroviral vectors have a relatively large capacity to carry genetic material. They can accommodate genes of up to 8-10 kilobases, which is sufficient for many therapeutic genes. This capacity allows for the delivery of complex genes or gene combinations required for effective gene therapy.
- Efficient gene delivery. Retroviral vectors exhibit high efficiency in delivering genes into target cells. They have evolved to efficiently infect dividing cells, which makes them suitable for use in rapidly dividing cells such as stem cells or certain types of cancer cells. Retroviruses can specifically target cells expressing their surface receptors, further enhancing their delivery efficiency.
- Tissue and cell type specificity. Retroviral vectors can be modified to display specific surface proteins or receptors on their outer surface. This modification enables them to target specific tissues or cell types, enhancing their specificity and reducing off-target effects. By engineering the viral envelope proteins, retroviral vectors can be retargeted to a wide range of cell types.
What We Offer to Develop Retroviral Vectors?
Selection of suitable vector
The first step is to select an appropriate retrovirus as the basis for the vector. Commonly used retroviruses include the Moloney murine leukemia virus (MMLV), the lentivirus family (e.g., human immunodeficiency virus, HIV), and the foamy virus. Each retrovirus has specific characteristics that determine its suitability for various applications.
Construction of retroviral vectors
Once a retrovirus is selected, our scientists modify its genetic material to create a retroviral vector. This involves removing or disabling certain viral genes essential for viral replication while retaining the genes necessary for packaging the viral genome into viral particles.
Insertion of the target gene into the vector genome
Our researchers insert the desired genetic material into the vector's genome to enable the retroviral vector to carry therapeutic genes.
Optimization and packaging of viral vectors
The modified retroviral vector is then packaged into viral particles by introducing it into packaging cells that provide the necessary viral proteins in trans.
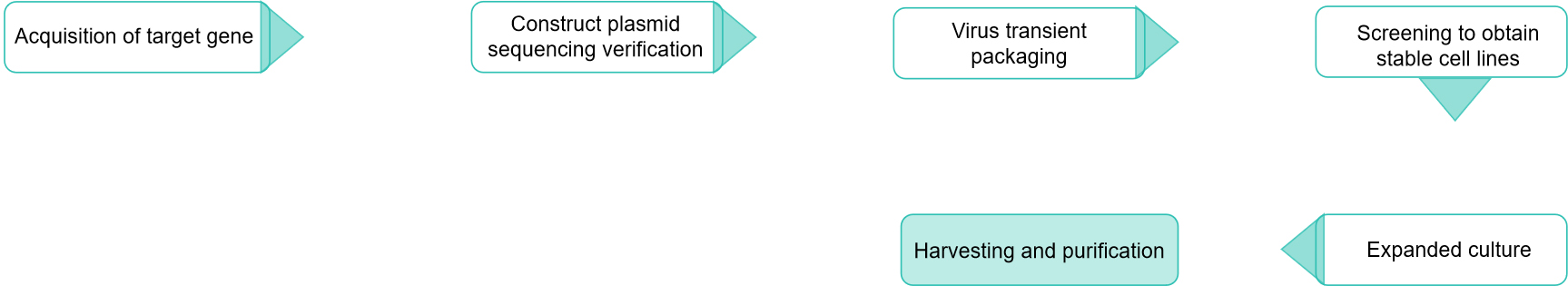 Fig.1 Our development process of retrovirus vectors. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Our development process of retrovirus vectors. (CD Formulation)
Application of Retroviral Vectors Development
- Genetic disorders. Retroviral vectors have shown promise in treating genetic disorders caused by single gene mutations. For instance, severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) due to adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency has been successfully treated using retroviral vectors. The vectors deliver the correct copy of the ADA gene into the patient's hematopoietic stem cells, restoring immune function.
- Hematological disorders. Retroviral vectors have been used to treat various hematological disorders, including inherited blood disorders like β-thalassemia and sickle cell disease. These vectors are used to introduce functional copies of genes involved in red blood cell production or hemoglobin synthesis into hematopoietic stem cells. The modified stem cells are then transplanted into the patient, leading to the production of healthy blood cells.
- Neurological disorders. Retroviral vectors hold promise for treating neurological disorders by delivering therapeutic genes to affected brain cells. In Parkinson's disease, for example, vectors can be used to introduce genes involved in dopamine production into specific regions of the brain, potentially restoring dopamine levels and improving motor symptoms.
- Cancer. Retroviral vectors can be used in cancer treatment. They can be used to deliver therapeutic genes that inhibit tumor growth, induce apoptosis (cell death), or enhance the immune response against cancer cells. Additionally, retroviral vectors have been utilized to modify immune cells, such as T cells, to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), enabling them to recognize and target cancer cells more effectively in adoptive cell therapy approaches.
Our Platforms for Retroviral Vector Development
| Technologies & Platforms |
Content Description |
| Retroviral vector design technology platform |
We have established an efficient vector design platform for the design of retroviral vectors capable of efficiently transducing target cells and integrating into the host genome. This process includes the selection of appropriate viral promoters, enhancers, and necessary splice sites to ensure stable gene expression in the host cells. |
| Targeted integration technology platform |
We have developed technologies that control the integration of viral vectors into specific safe regions of the host genome to minimize the impact on host gene function and reduce the risk of carcinogenesis. |
| Gene editing technology platform |
We can utilize gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR/Cas9, ZFNs, and TALENs, to precisely modify the genome of the host cell, enabling knockout or repair of specific genes and advancing the development of retroviral vectors. |
Highlights of Our Retroviral Vector Development Service
- Expertise. We have extensive expertise in retroviral vector development and in-depth knowledge of retroviral vectors and their use in gene therapy.
- Quality assurance. We adhere to strict regulatory guidelines and quality control measures throughout the retroviral vector development process.
- Customized solutions. We can provide customized solutions based on each client's unique needs, ensuring the design of retroviral vectors optimized for efficient gene delivery and desired therapeutic outcomes.
Published Data
Technology: Gene editing technology
Journal: Gene Ther
IF: 4.79
Published: 2021
Results: The development of retroviral vectors for gene therapy and the noteworthy advancements in the article. It emphasizes the creation of gene therapy vectors for lentiviral and gammaretroviral-based gene therapy techniques. The production of therapeutic genes without inducing toxicity, efficient entry into target cells, and large concentrations of infectious retroviral particles are all highlighted in this work. The tuning of retroviral vector systems to get elevated transgenic expression levels—a prerequisite for therapeutic efficacy—is also covered.
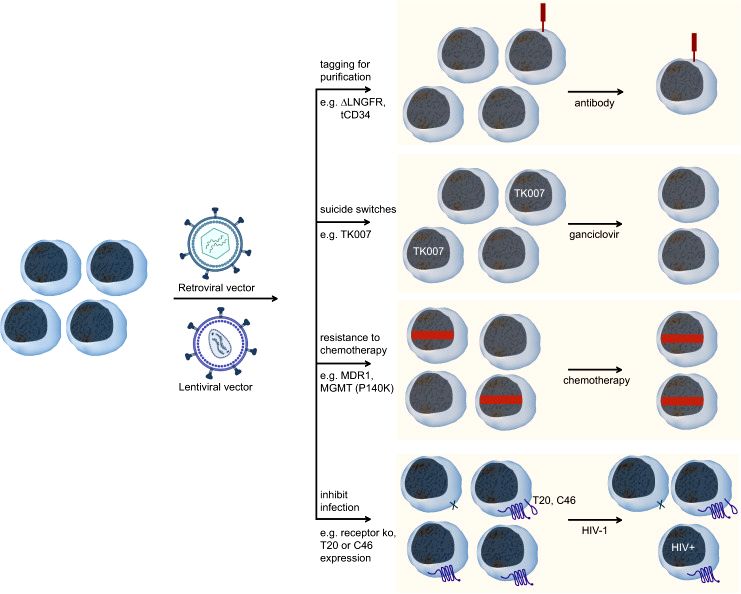 Fig.2 Several mechanisms can be employed to enrich gammaretroviral. (Morgan MA, et al, 2021)
Fig.2 Several mechanisms can be employed to enrich gammaretroviral. (Morgan MA, et al, 2021)
CD Formulation offers scientifically rigorous retroviral vector development, a technical service that involves the modification of retroviruses to create replication-defective vectors capable of delivering therapeutic genes into target cells, thus offering great promise for the application and development of gene therapy. If you are interested in us, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
- Morgan MA, Galla M, et al. Retroviral gene therapy in Germany with a view on previous experience and future perspectives. Gene Ther. 2021, 28(9):494-512.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Our development process of retrovirus vectors. (CD Formulation)
Fig.1 Our development process of retrovirus vectors. (CD Formulation) Fig.2 Several mechanisms can be employed to enrich gammaretroviral. (Morgan MA, et al, 2021)
Fig.2 Several mechanisms can be employed to enrich gammaretroviral. (Morgan MA, et al, 2021)