Polysaccharide-Based Nanocarrier Development
InquiryAt CD Formulation, we specialize in the rational design and engineering of polysaccharide-based nanocarriers for nucleic acid therapeutics. Leveraging our extensive expertise in carbohydrate chemistry and nanoparticles, we can develop customized carriers from natural polymers.
Applications of Polysaccharides in Nucleic Acid Delivery
Polysaccharides show great promise for delivery of nucleic acid therapeutics like DNA, RNA and oligonucleotides due to their biocompatibility, low toxicity and ability to complex with charged biomolecules. Their reactive functional groups also allow surface modifications to improve stability, targeting and controlled release.
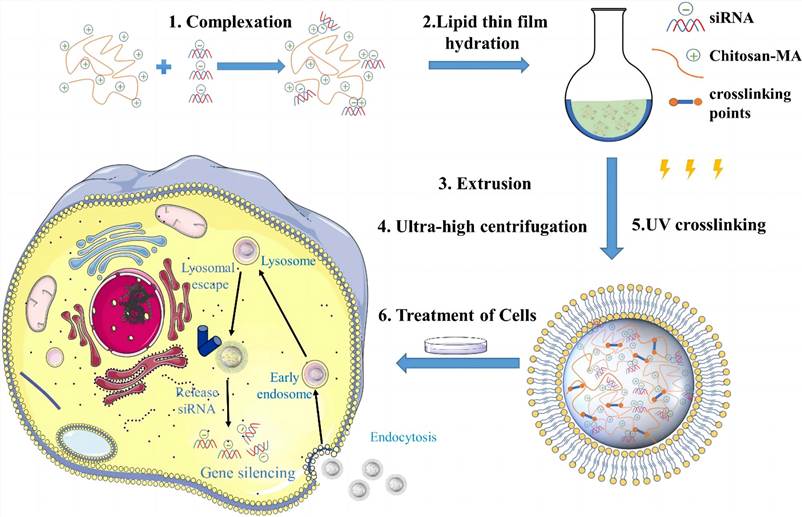 UV cross-linked chitosan-methacrylate nanogels for siRNA delivery (Cao Y.; et al. 2022)
UV cross-linked chitosan-methacrylate nanogels for siRNA delivery (Cao Y.; et al. 2022)
What Polysaccharides Can We Use in Nanocarrier Development?
| Types |
Sources |
Characteristics |
| Chitosan |
Derived from the chitin in crustacean shells. |
Chitosan can condense nucleic acids via electrostatic interactions and form nanogels/nanoparticles. |
| HA |
Derived from microbial fermentation or animal tissues. |
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is an anionic polysaccharide with targeting capabilities, facilitating cellular-specific interactions. |
| Alginate |
Obtained from brown seaweed cell walls. |
Alginate is an anionic polysaccharide that forms gel-like structures in the presence of divalent cations, providing controlled release and protection of nucleic acids. |
| Dextran |
Produced by the microbial fermentation of sugar sources like sucrose or glucose. |
Dextran is a water-soluble polysaccharide that can be modified to introduce desired functionalities, serving as a carrier for encapsulating and delivering nucleic acids. |
| Cyclodextrin |
Derived from starch through enzymatic conversion. |
They possess hydrophobic cavities that can form inclusion complexes with hydrophobic drugs or nucleic acids, improving solubility and stability. |
| Pullulan |
Produced by the microbial fermentation of starch. |
Pullulan is a biodegradable polysaccharide with film-forming properties. |
Types of Polysaccharide-Based Nanocarriers We Can Develop
- Polysaccharide Nanoparticles
We use precision design and optimization of formulation variables such as monomer type and ratio, cross-linking density, and environmental triggers during self-assembly to generate nanocarriers with controlled size, functionality, biodegradability, and nontoxicity.
Our expertise lies in the development of polysaccharide coatings that can be applied to nanoparticles or other carriers. By utilizing layer-by-layer or selective surface functionalization approaches, we tailor polysaccharide coatings for drug delivery systems, suitable for developments involving biomaterial surfaces, tissue engineering scaffolds, and implantable devices.
We optimize formulation parameters such as cross-linking mechanisms, porosity and responsive materials to tailor hydrogels with specific degradation and swelling properties according to customer needs. These hydrogels enable sustained release and localized delivery of nucleic acids, allowing flexibility in biomedical applications.
- Polysaccharide-Inorganic Hybrid Nanocarriers
Our capabilities extend to the development of polysaccharide-inorganic hybrid nanocarriers, combining materials like polysaccharides with gold nanoparticles or magnetic nanoparticles. Our formulation scientists can produce multifunctional platforms with enhanced imaging, stimuli-sensitivity or protection abilities.
Advantages of Our Polysaccharide-Based Nanocarrier Development Services
- Utilizing polysaccharides, our developed nanoparticles overcome physiological barriers in drug delivery, prolonging residence time and enhancing accumulation at diseased sites.
- We can tailor polysaccharide nanocarriers to deliver targeted drugs to the intestine, providing therapeutic benefits for diseases such as colon cancer and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Polysaccharides are rich in terminal functional groups and are easy to modify. We can modify various groups in polysaccharides to give them mucoadhesion, pH responsiveness and other specific needs.
- We offer comprehensive characterization techniques to assess the physicochemical properties and performance of polysaccharide-based nanocarriers, ensuring quality and reproducibility.
Whether you need assistance with formulation and material optimization, characterization, process development or full program management, CD Formulation can support your nucleic acid delivery system development projects. If you are interested in leveraging our capabilities to realize the potential of polysaccharide nanomedicines, please contact us!
References
- Cao Y.; et al. Designing siRNA/chitosan-methacrylate complex nanolipogel for prolonged gene silencing effects. Sci Rep. 2022, 12(1):3527.
- Karayianni M.; et al. Chitosan-based nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery: technological aspects, applications, and future perspectives. Pharmaceutics. 2023, 15(7):1849.
- Haley R.M.; et al. Cyclodextrins in drug delivery: applications in gene and combination therapy. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2020, 10(3):661-677.
Related Services



 UV cross-linked chitosan-methacrylate nanogels for siRNA delivery (Cao Y.; et al. 2022)
UV cross-linked chitosan-methacrylate nanogels for siRNA delivery (Cao Y.; et al. 2022)